Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. Nov 26, 2024; 16(11): 906-925
Published online Nov 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i11.906
Published online Nov 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i11.906
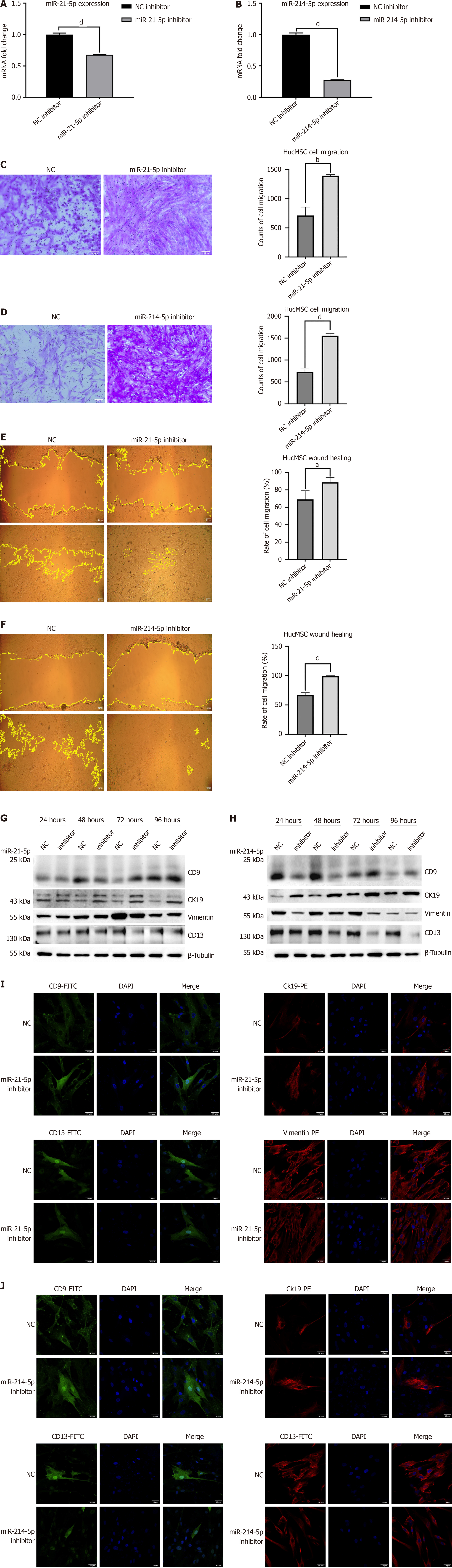
Figure 4 Silencing of miR-21-5p or miR-214-5p promotes human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell migration and differentiation into endometrial epithelial cells.
MiR-21-5p/miR-214-5p inhibitor was transfected into human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. A and B: MiR-21-5p and miR-214-5p levels measured by reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction; C and D: Cell migration determined using Transwell assay; E and F: Wound healing assay for measurement of cell migration; G and H: Protein expression of CD9, CK19, vimentin, and CD13 measured using Western blotting; I and J: Immunofluorescence staining for detecting expression of CD9, CK19, CD13, and vimentin. n = 3. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001. Data are described as the mean ± SD. HucMSC: Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells; NC: Normal control.
- Citation: Zhang WY, Wang HB, Deng CY. Effects of miR-214-5p and miR-21-5p in hypoxic endometrial epithelial-cell-derived exosomes on human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(11): 906-925
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i11/906.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i11.906