Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. Nov 26, 2024; 16(11): 906-925
Published online Nov 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i11.906
Published online Nov 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i11.906
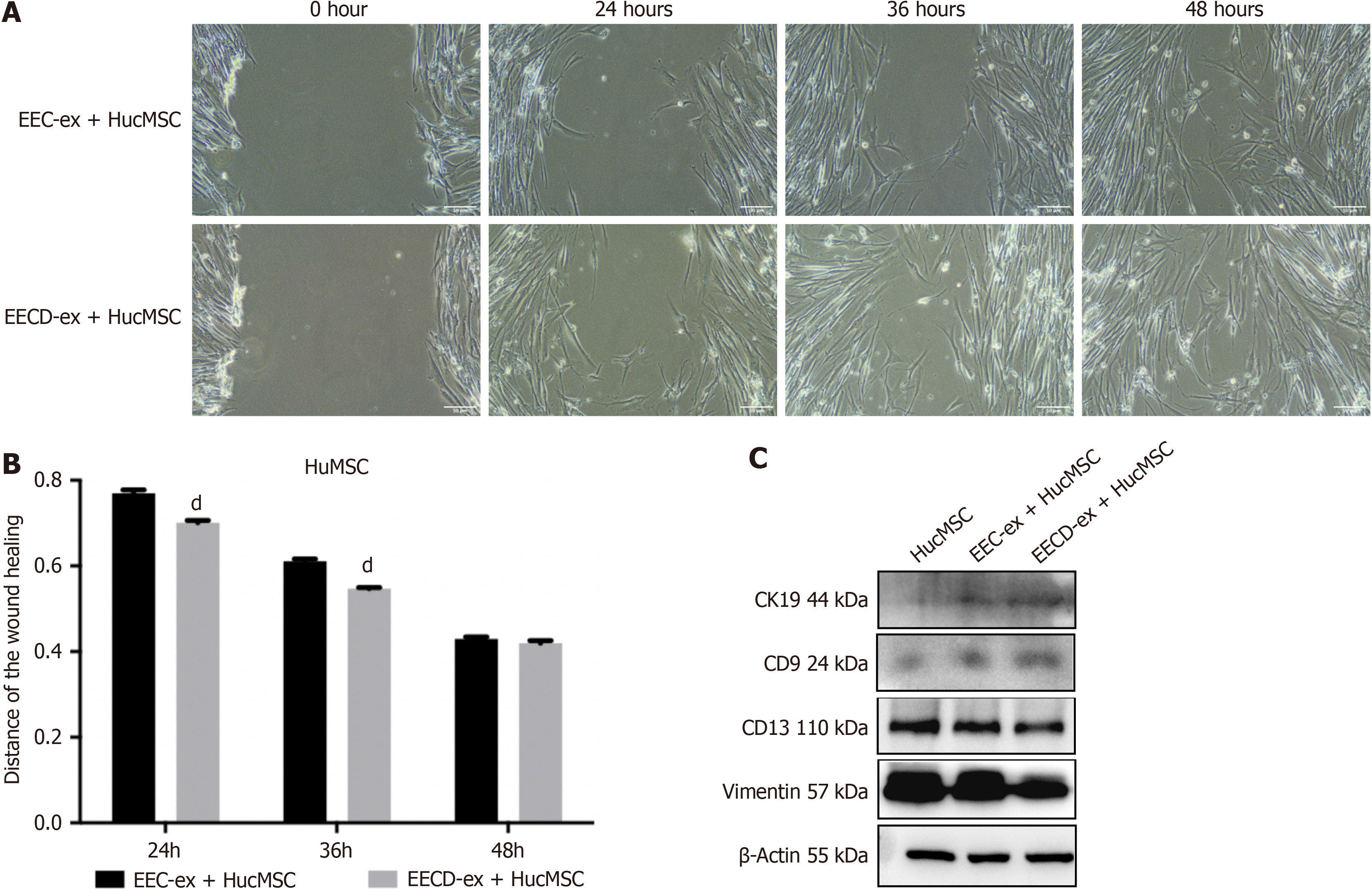
Figure 2 Exosomes derived from hypoxia-damaged endometrial epithelial cells promote human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell migration and differentiation into endometrial epithelial cells.
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells were cocultured with exosomes isolated from normal endometrial epithelial cells or exosomes derived from hypoxia-damaged endometrial epithelial cells. A and B: Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell migration detected using wound healing assay; C: CD9, CK19, CD13, and vimentin protein levels determined by Western blotting. n = 3. dP < 0.0001. Data are described as the mean ± SD. HucMSC: Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells; EEC-ex: Exosomes isolated from normal endometrial epithelial cells; EECD-ex: Exosomes derived from hypoxia-damaged endometrial epithelial cells.
- Citation: Zhang WY, Wang HB, Deng CY. Effects of miR-214-5p and miR-21-5p in hypoxic endometrial epithelial-cell-derived exosomes on human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(11): 906-925
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i11/906.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i11.906