Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. Oct 26, 2024; 16(10): 873-895
Published online Oct 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i10.873
Published online Oct 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i10.873
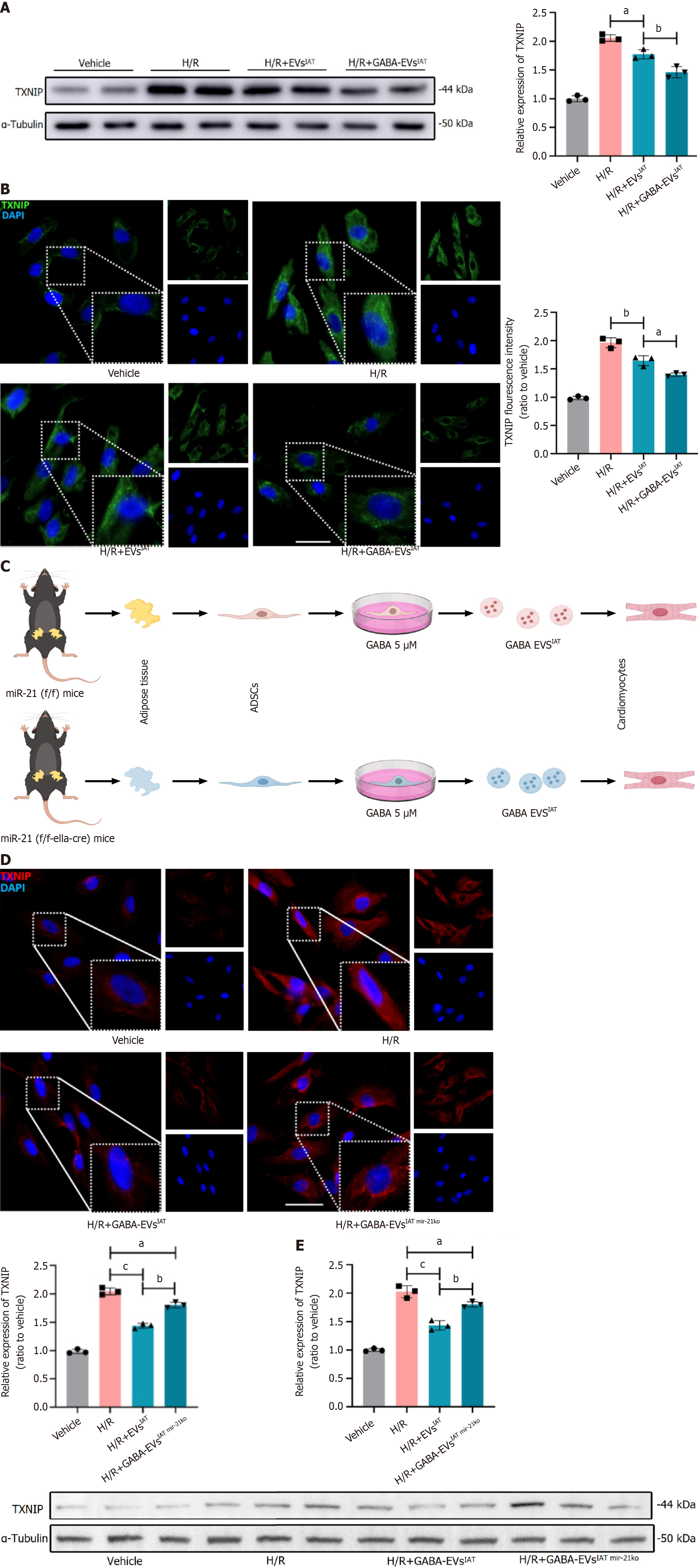
Figure 5 MicroR-21-5p derived from gamma-aminobutyric acid-induced adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells from inguinal adipose tissue regulate thioredoxin-interacting protein expression in protein degree.
A: Representative immunoblots and quantitative analysis of thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) at the protein level in neonatal mouse cardiomyocytes (NMCMs) (n = 3); B: Representative micrographs of NMCMs stained with TXNIP antibody (n = 3; scale bars = 200 μm); C: Experiment design. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADSCs) were isolated from both miR-21 KO and miR-21f/f mice inguinal adipose tissue (IAT), and extracellular vesicles (EVs) were extracted respectively; D: Representative micrographs of NMCMs stained with TXNIP antibody (n = 3; scale bars = 200 μm); E: Representative immunoblots and quantitative analysis of TXNIP at the protein level in NMCMs (n = 3). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. GABA: Gamma-aminobutyric acid; H/R: Hypoxia and reoxygenation.
- Citation: Wang FD, Ding Y, Zhou JH, Zhou E, Zhang TT, Fan YQ, He Q, Zhang ZQ, Mao CY, Zhang JF, Zhou J. Gamma-aminobutyric acid enhances miR-21-5p loading into adipose-derived stem cell extracellular vesicles to alleviate myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via TXNIP regulation. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(10): 873-895
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i10/873.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i10.873