Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Stem Cells. Sep 26, 2023; 15(9): 908-930
Published online Sep 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i9.908
Published online Sep 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i9.908
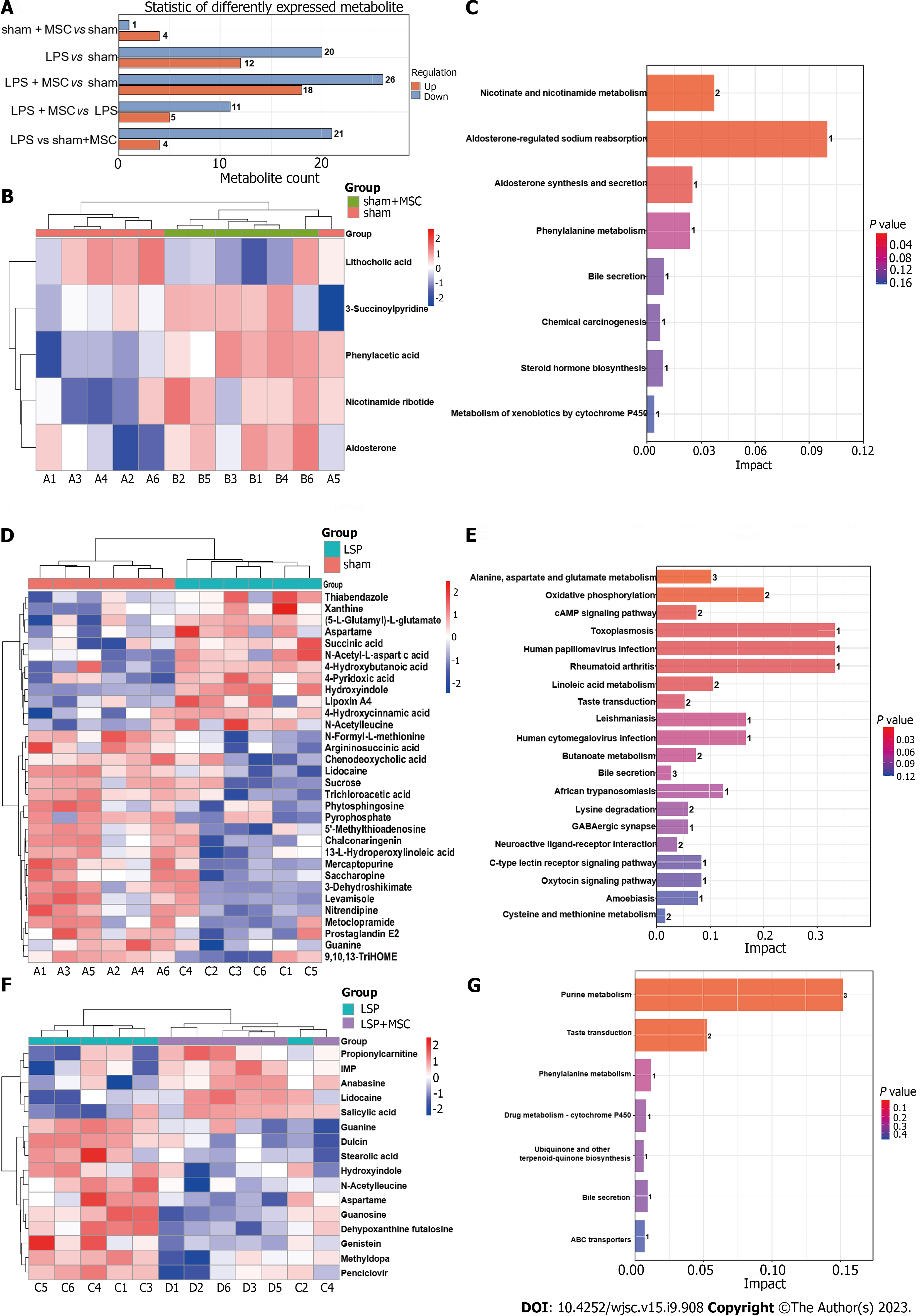
Figure 8 Screening of differently expressed metabolites in acute lung injury mice treated with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (n = 6).
A: Statistic of differently expressed metabolites under liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry mode; B: Heatmaps of sham + mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) group vs sham group; C: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways enriched by differently expressed metabolites of sham + MSC group vs sham group; D: The lipopolysaccharide (LPS) group vs sham group were used to analyze and display differently expressed metabolites; E: KEGG pathway enriched by differently expressed metabolites of LPS group vs sham group; F: Heatmaps of LPS group vs LPS + MSC group; G: KEGG pathways enriched by differently expressed metabolites of sham + MSC group vs sham group. LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell.
- Citation: Lv L, Cui EH, Wang B, Li LQ, Hua F, Lu HD, Chen N, Chen WY. Multiomics reveal human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells improving acute lung injury via the lung-gut axis. World J Stem Cells 2023; 15(9): 908-930
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v15/i9/908.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v15.i9.908