Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Stem Cells. Sep 26, 2023; 15(9): 908-930
Published online Sep 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i9.908
Published online Sep 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i9.908
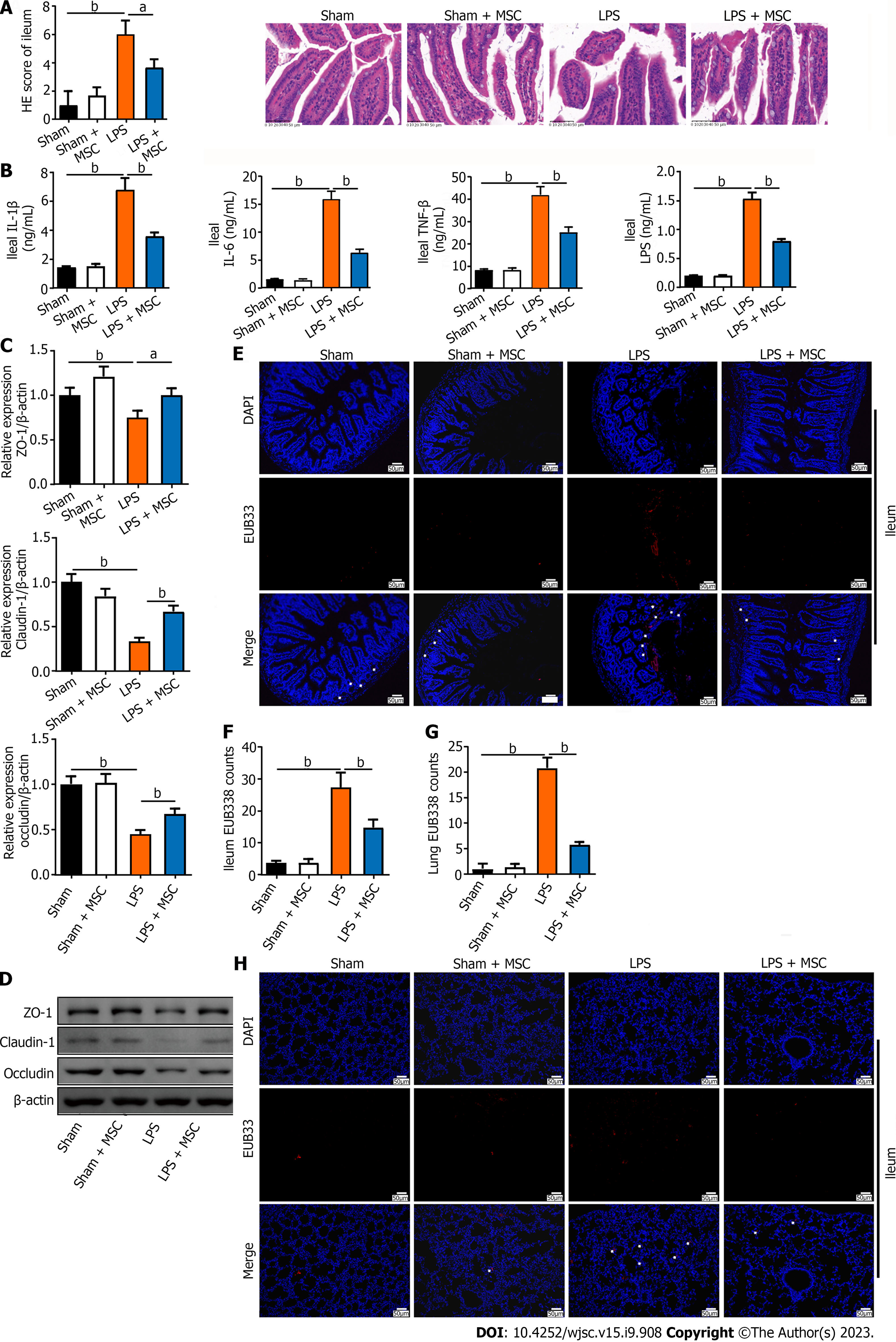
Figure 3 Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells improve histopathology, inflammation, and endothelial barrier integrity of the ileum in acute lung injury mice.
A: Ileum tissue injury in acute lung injury (ALI) mice was observed after hematoxylin-eosin staining. ALI mice had severe ileum tissue injury while human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell (HUC-MSC) treatment improved such injury (n = 3); B: Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) levels in the ileum were measured by ELISA (n = 12), and ALI mice had higher levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and LPS compared to sham mice, while HUC-MSC treatment decreased the levels of these factors; C: Zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1), claudin-1, and occludin levels were measured to observe the integrity of the ileum barrier (n = 3); D: Representative western blot bands of ZO-1, claudin-1, and occludin; E-H: Bacterial translocation was determined by fluorescence in situ hybridization, and the EUB338 counts in the ileum epithelium and lung per field were quantified (n = 3). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; ZO-1: Zonula occludens-1; HE: Hematoxylin-eosin; IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor.
- Citation: Lv L, Cui EH, Wang B, Li LQ, Hua F, Lu HD, Chen N, Chen WY. Multiomics reveal human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells improving acute lung injury via the lung-gut axis. World J Stem Cells 2023; 15(9): 908-930
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v15/i9/908.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v15.i9.908