Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Stem Cells. Sep 26, 2023; 15(9): 876-896
Published online Sep 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i9.876
Published online Sep 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i9.876
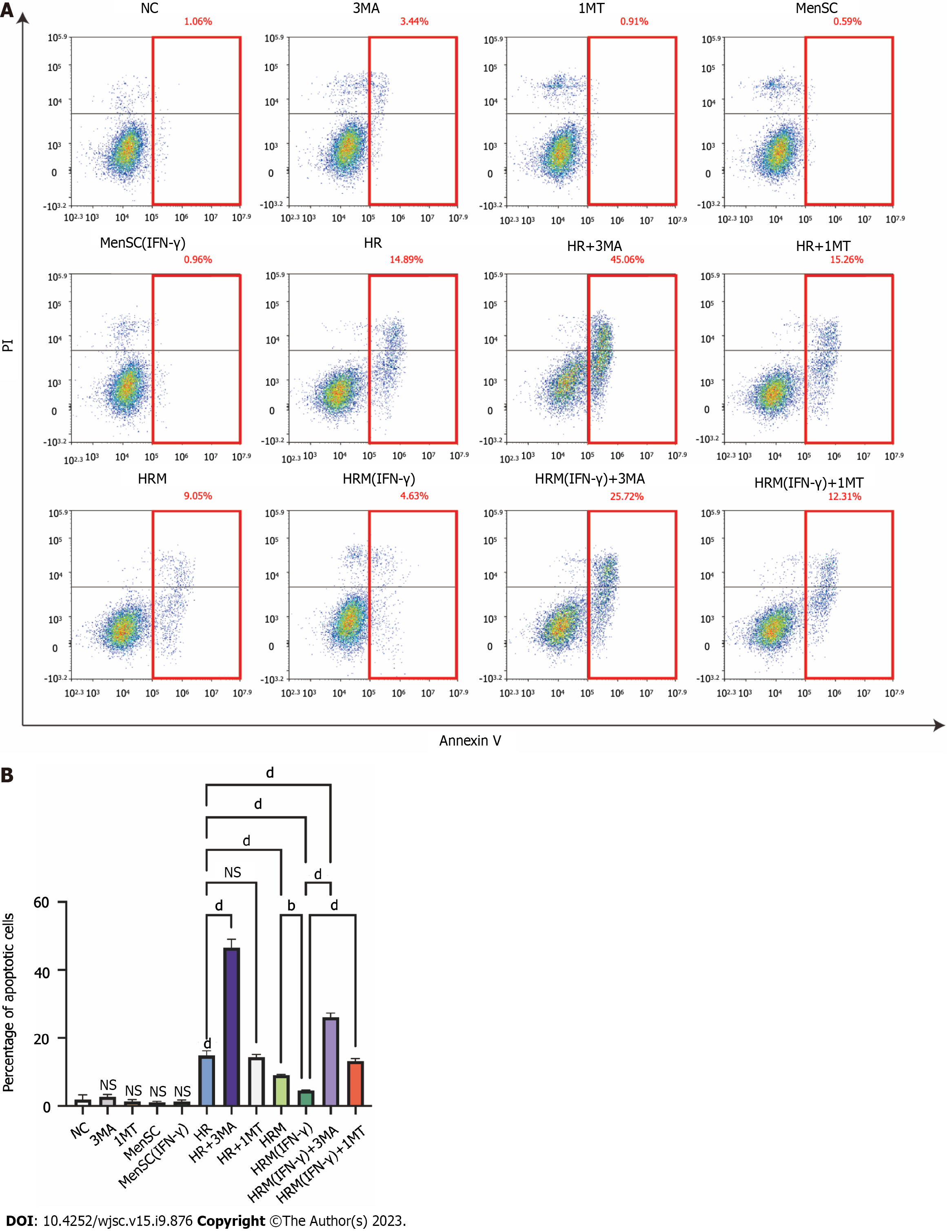
Figure 7 interferon-γ-primed menstrual blood-derived stromal cells decreased hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cell apoptosis via autophagy and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase.
A: Apoptosis of L02 cells after different treatments was analyzed; B: The sum of the percentage of early apoptotic cells and late apoptotic cells was analyzed. The total percentage of apoptotic cells (sum of the percentage of early apoptotic cells and late apoptotic cells) was analyzed. The data are shown as the mean ± SEM, n = 3; bP < 0.01, dP < 0.0001. NS represents not statistically significant. All P values were obtained by one-way ANOVA. PI: Propidium iodide; NC: Negative control; 3MA: 3-methyladenine; 1MT: 1-methyl-D-tryptophan; MenSCs: Menstrual blood-derived stromal cells; IFN-γ: Interferon-γ; HR: Hypoxia/reoxygenation; HRM: Combination treated with hypoxia/reoxygenation and menstrual blood-derived stromal cells; HRM (IFN-γ): Combination treated with hypoxia/reoxygenation and I interferon-γ-primed menstrual blood-derived stromal cells.
- Citation: Zhang Q, Zhou SN, Fu JM, Chen LJ, Fang YX, Xu ZY, Xu HK, Yuan Y, Huang YQ, Zhang N, Li YF, Xiang C. Interferon-γ priming enhances the therapeutic effects of menstrual blood-derived stromal cells in a mouse liver ischemia-reperfusion model. World J Stem Cells 2023; 15(9): 876-896
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v15/i9/876.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v15.i9.876