Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Stem Cells. Sep 26, 2023; 15(9): 876-896
Published online Sep 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i9.876
Published online Sep 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i9.876
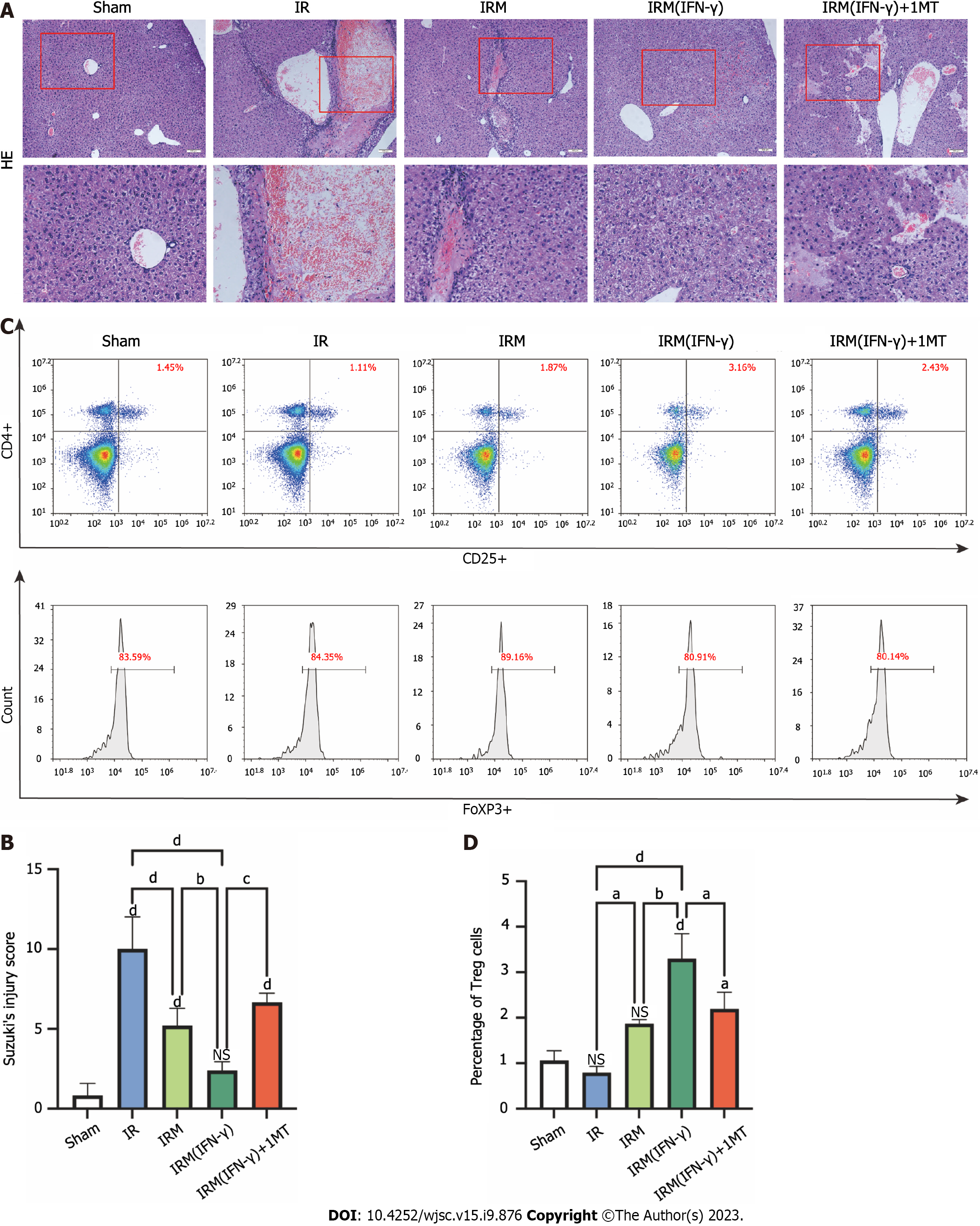
Figure 4 Interferon-γ-primed menstrual blood-derived stromal cells reduced hepatocellular damage and increased the Treg numbers in the mouse long-term ischemia-reperfusion model.
A: Representative images of histological liver sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin were obtained (hematoxylin and eosin staining, magnification 200×, images in the second row are partial magnifications of regions indicated by the red box); B: The degree of liver injury in each group was determined according to Suzuki’s injury score. The data are expressed as the means ± SEMs (n = 3-5/group); C: The numbers of CD4, CD25, and FoxP3 positive cells (regulatory T cells) in the spleen were determined by flow cytometry to estimate the ability of primed menstrual blood-derived stromal cells to induce immune tolerance; D: The percentages of Tregs are expressed as the means ± SEMs (n = 3/group). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001. NS represents not statistically significant. All P values were obtained by one-way ANOVA. MenSCs: Menstrual blood-derived stromal cells; IFN-γ: Interferon-γ; 1MT: 1-methyl-D-tryptophan; IR: Ischemia-reperfusion; IRM: Combination treated with ischemia-reperfusion and menstrual blood-derived stromal cells; IRM (IFN-γ): Combination treated with ischemia-reperfusion and interferon-γ-primed menstrual blood-derived stromal cells; HE: Hematoxylin and eosin; Treg: Regulatory T cell.
- Citation: Zhang Q, Zhou SN, Fu JM, Chen LJ, Fang YX, Xu ZY, Xu HK, Yuan Y, Huang YQ, Zhang N, Li YF, Xiang C. Interferon-γ priming enhances the therapeutic effects of menstrual blood-derived stromal cells in a mouse liver ischemia-reperfusion model. World J Stem Cells 2023; 15(9): 876-896
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v15/i9/876.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v15.i9.876