Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Stem Cells. Aug 26, 2023; 15(8): 842-865
Published online Aug 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i8.842
Published online Aug 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i8.842
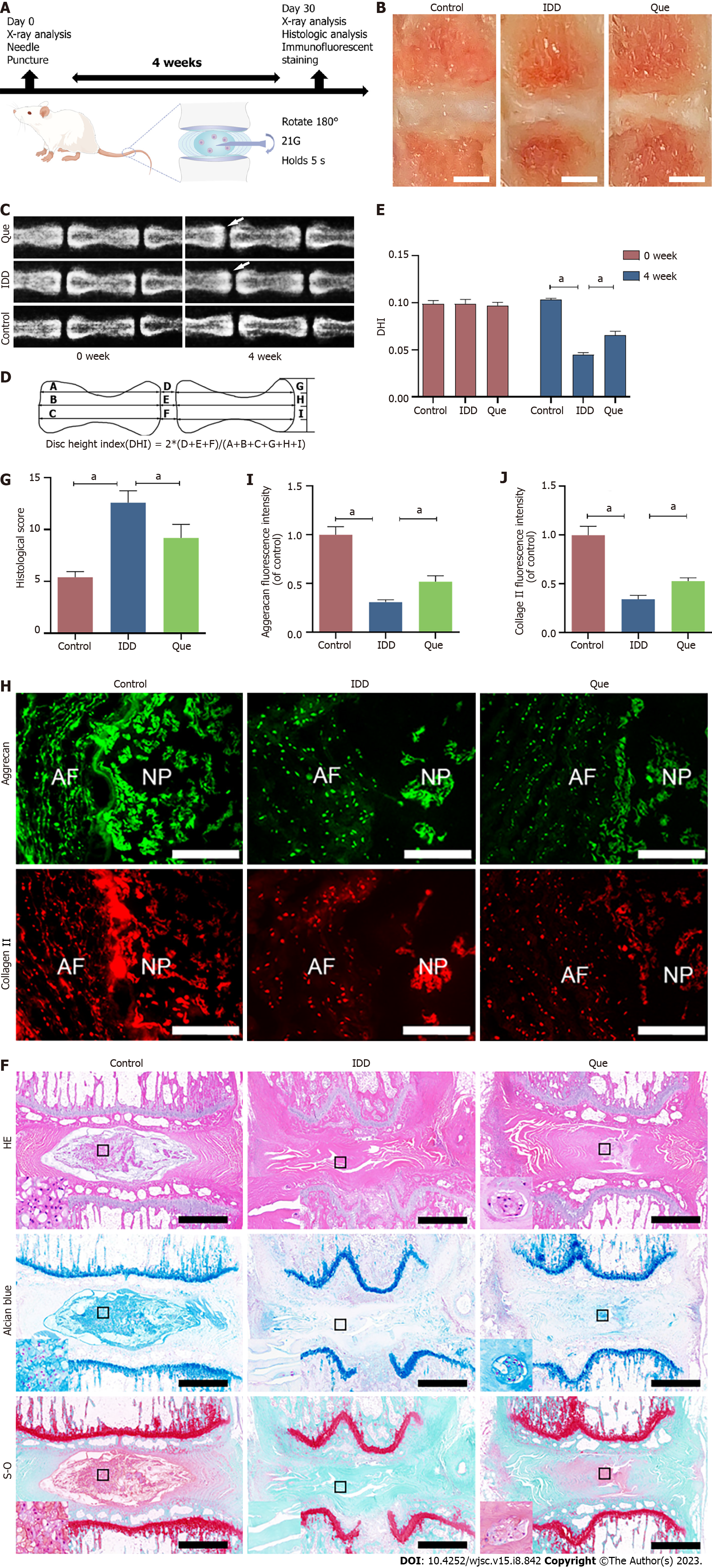
Figure 12 Quercetin ameliorates IVDD invivo.
A: Schematic of the basic process of in vivo experiment (By Figdraw); B: Macroscopic appearances of rat tail intact disc mid-sagittal sections in control group, intervertebral disc degeneration group and quercetin group (Scar bar = 2 mm); C: The X-ray in different groups at 0 wk and 4 wk after puncturing; D: Measurements of intervertebral disc height index (DHI); E: Quantitative analysis of DHI; F-G: Hematoxylin-eosin staining and quantitative analysis of histological score at 4 wk after puncture in different groups (scale bar = 1mm); H: The expression of aggrecan and collagen type II in different groups (scale bar = 400 μm); I-J: Quantitative analysis of aggrecan and collagen type II in different groups. Data are represented as mean ± SD. Significant differences between groups are indicated as aP < 0.05, n = 3. HE: Hematoxylin-eosin; NP: Nucleus pulposus; AF: Annulus fibrosus; IDD: Intervertebral disc degeneration; TBHP: Tert-butyl hydroperoxide; Que: Quercetin.
- Citation: Zhao WJ, Liu X, Hu M, Zhang Y, Shi PZ, Wang JW, Lu XH, Cheng XF, Tao YP, Feng XM, Wang YX, Zhang L. Quercetin ameliorates oxidative stress-induced senescence in rat nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells via the miR-34a-5p/SIRT1 axis. World J Stem Cells 2023; 15(8): 842-865
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v15/i8/842.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v15.i8.842