Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Stem Cells. Aug 26, 2023; 15(8): 807-820
Published online Aug 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i8.807
Published online Aug 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i8.807
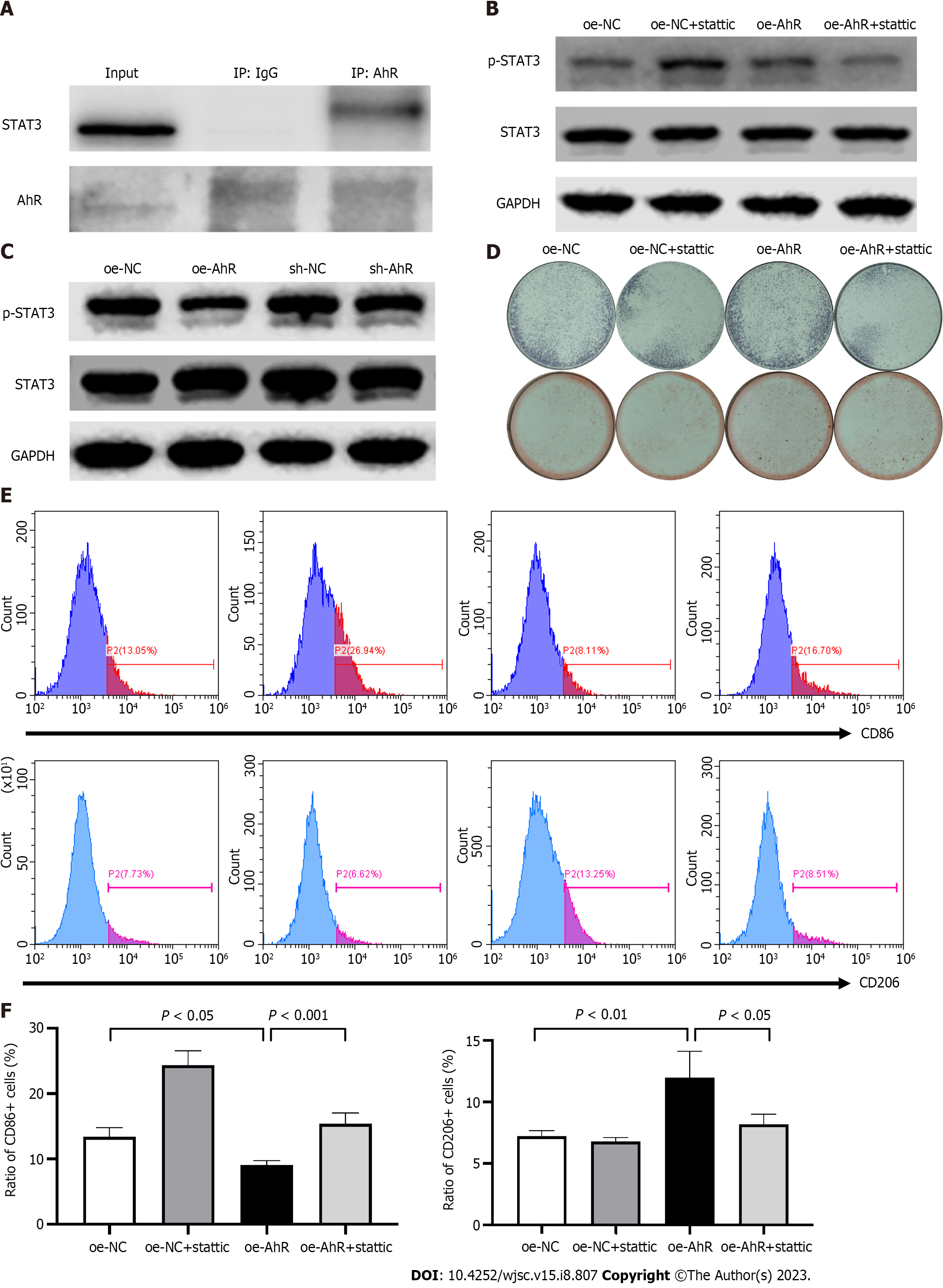
Figure 6 The molecular mechanism of the role of aryl hydrocarbon receptor in osteogenic differentiation and macrophage-modulating in mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells.
A: Co-immunoprecipitation assay showed that aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) directly interacted in mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells (mBMSCs); B: Western blot lanes demonstrated that AhR overexpression promoted phosphorylation of STAT3 compared to negative control, while AhR knockdown suppressed it; C: The specific STAT3 inhibitor stattic (2 mmol/L) partially alleviated the promoted STAT3 phosphorylation by AhR overexpression; D: Alkaline phosphatase (upper) and alizarin red staining (lower) staining indicated that 2 mmol/L stattic partially inhibited the elevated osteogenic potential by AhR overexpression; E and F: The histograms of flow cytometry and quantitative analysis manifested that 2 mmol/L stattic partially reversed the CD86 inhibition and CD206 promotion in RAW 264.7 by conditioned medium from overexpression-AhR mBMSCs. AhR: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor; oe-NC: Overexpression-negative control; oe-AhR: Overexpression-AhR; sh-NC: Knockdown-negative control; sh-AhR: Knockdown-AhR; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; p-STAT3: Phosphorylated STAT3; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
- Citation: Huang J, Wang YN, Zhou Y. Constitutive aryl hydrocarbon receptor facilitates the regenerative potential of mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells. World J Stem Cells 2023; 15(8): 807-820
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v15/i8/807.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v15.i8.807