Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2023; 15(7): 768-780
Published online Jul 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i7.768
Published online Jul 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i7.768
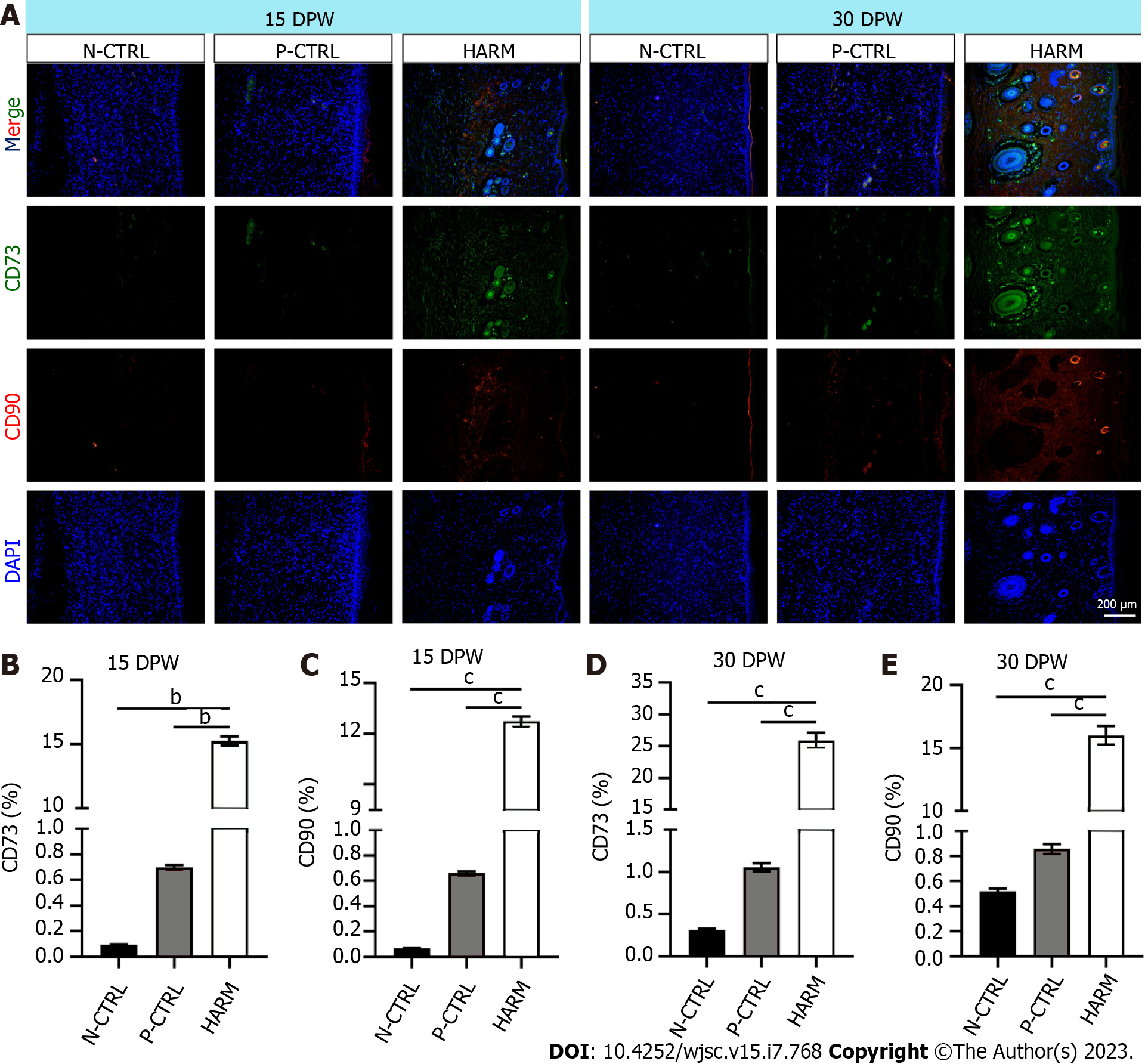
Figure 5 Effects of hydrogels from the antler reserve mesenchyme on the expression of stem cell markers in healed skin of rat wounds.
A: CD73 and CD90 immunofluorescence staining; B and C: Expression percentages of CD73 and CD90 on 15 DPW; D and E: Expression percentages of CD73 and CD90 on 30 DPW. Note that the HARM group had the highest percent of CD73 and CD90 compared to the other two groups. DPW: Days post-wounding; HARM: Hydrogels derived from antler reserve mesenchyme; N-CTRL: Negative control; P-CTRL: Positive control. n = 3; mean ± SEM; statistically significant at bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001.
- Citation: Zhang GK, Ren J, Li JP, Wang DX, Wang SN, Shi LY, Li CY. Injectable hydrogel made from antler mesenchyme matrix for regenerative wound healing via creating a fetal-like niche. World J Stem Cells 2023; 15(7): 768-780
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v15/i7/768.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v15.i7.768