Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2023; 15(7): 751-767
Published online Jul 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i7.751
Published online Jul 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i7.751
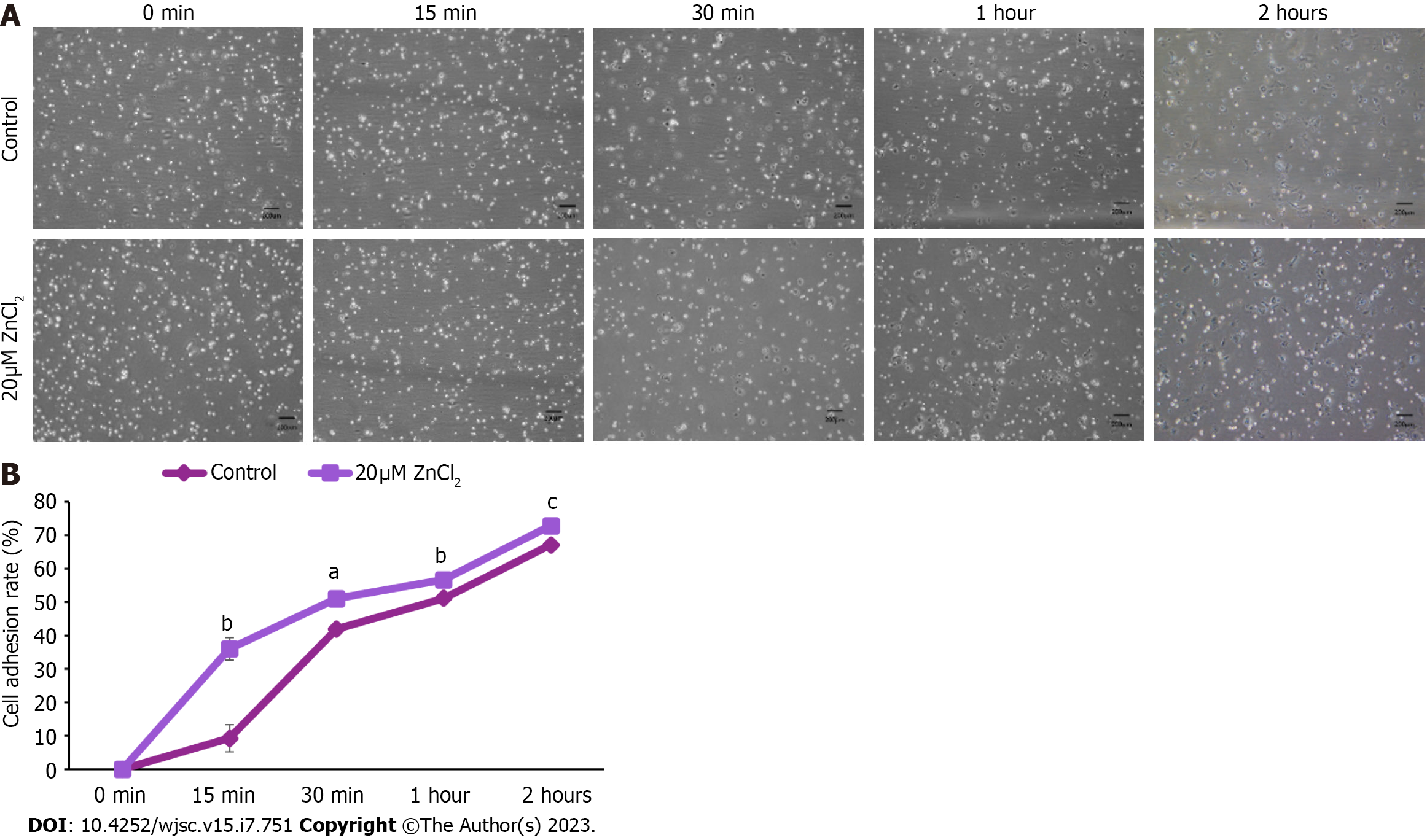
Figure 6 Effect ZnCl2 on adhesion ability of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
A: Images of human umbilical cord (hUC)-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) of the control group and 20 µM ZnCl2 treated groups at 0 min, 15 min, 30 min, 1 h, and 2 h of cell seeding. Bright, rounded, and freely floating cells represent unadhered cells while dark cells represent adhered cells; B: Significant increase was observed in the adhesion ability of hUC-MSCs of the treated group after 15 min (bP ≤ 0.01), 30 min (aP ≤ 0.05),1 h (bP ≤ 0.01), and 2 h (cP ≤ 0.001). An independent sample t-test was performed to analyze results, and data were represented as mean ± SD (n = 3).
- Citation: Sahibdad I, Khalid S, Chaudhry GR, Salim A, Begum S, Khan I. Zinc enhances the cell adhesion, migration, and self-renewal potential of human umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2023; 15(7): 751-767
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v15/i7/751.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v15.i7.751