Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2023; 15(7): 751-767
Published online Jul 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i7.751
Published online Jul 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i7.751
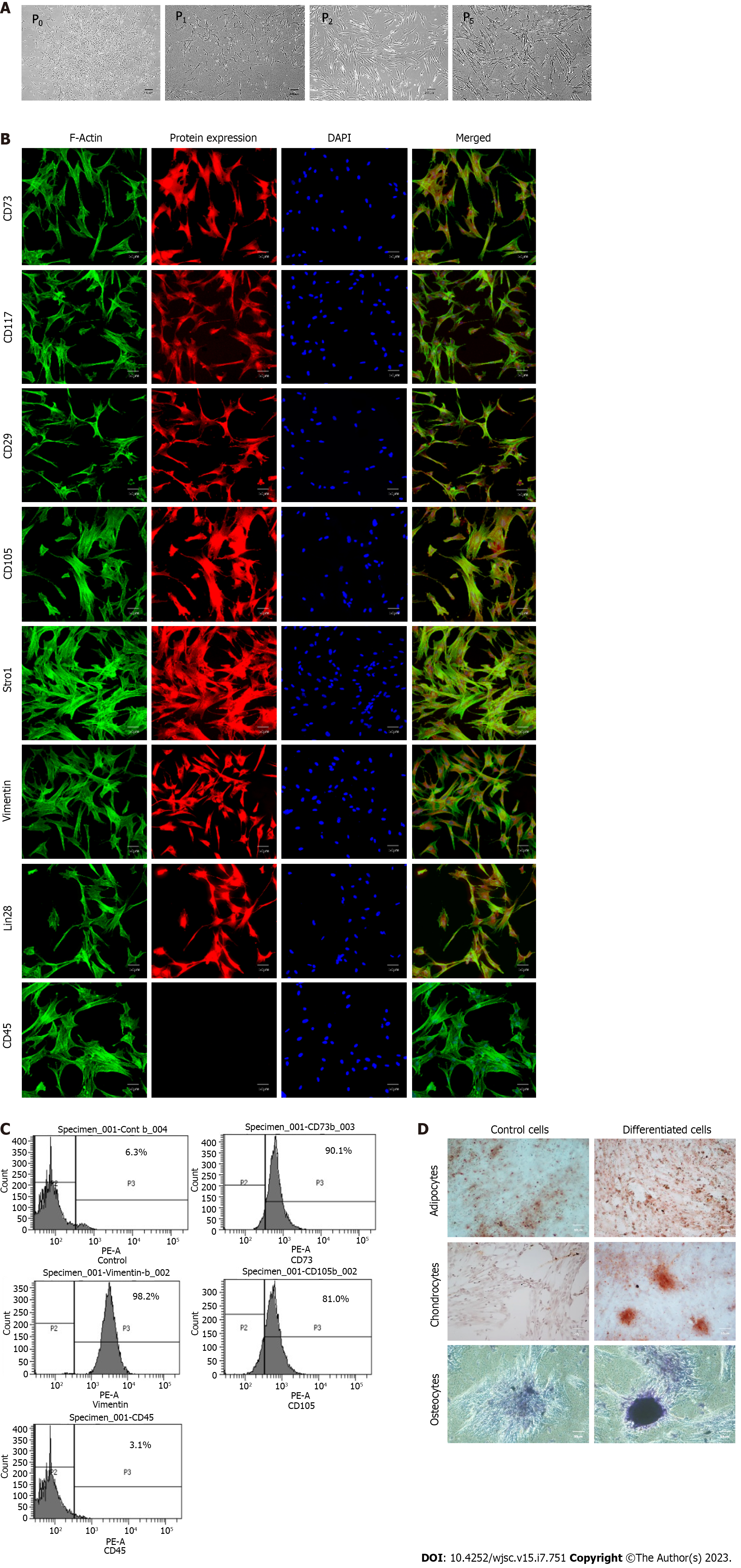
Figure 2 Characterization of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
A: Isolated human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells appeared as elongated, fibroblast-like cells which were slightly trigonal at P0 and then gradually became elongated in latter passages (P1, P2, P5); B: These cells positively expressed CD73, CD117, CD29, CD105, Stro1, Vimentin, and Lin28 while exhibiting negative expression of CD45; C: Cell surface analysis by flowcytometry showed that more than 80% of the cell population was positive for CD73, vimentin, and CD105 while less than 4% were positive for hematopoietic marker i.e. CD45; D: The cells were successfully differentiated into adipocytes, osteocytes, and chondrocytes. Oil red O stain, alizarin red S stain, and Alcian blue stain confirmed the presence of lipids vacuoles, calcium deposits, and glycosaminoglycan in adipocytes, osteocytes, and chondrocytes, respectively.
- Citation: Sahibdad I, Khalid S, Chaudhry GR, Salim A, Begum S, Khan I. Zinc enhances the cell adhesion, migration, and self-renewal potential of human umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2023; 15(7): 751-767
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v15/i7/751.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v15.i7.751