Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2023; 15(7): 734-750
Published online Jul 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i7.734
Published online Jul 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i7.734
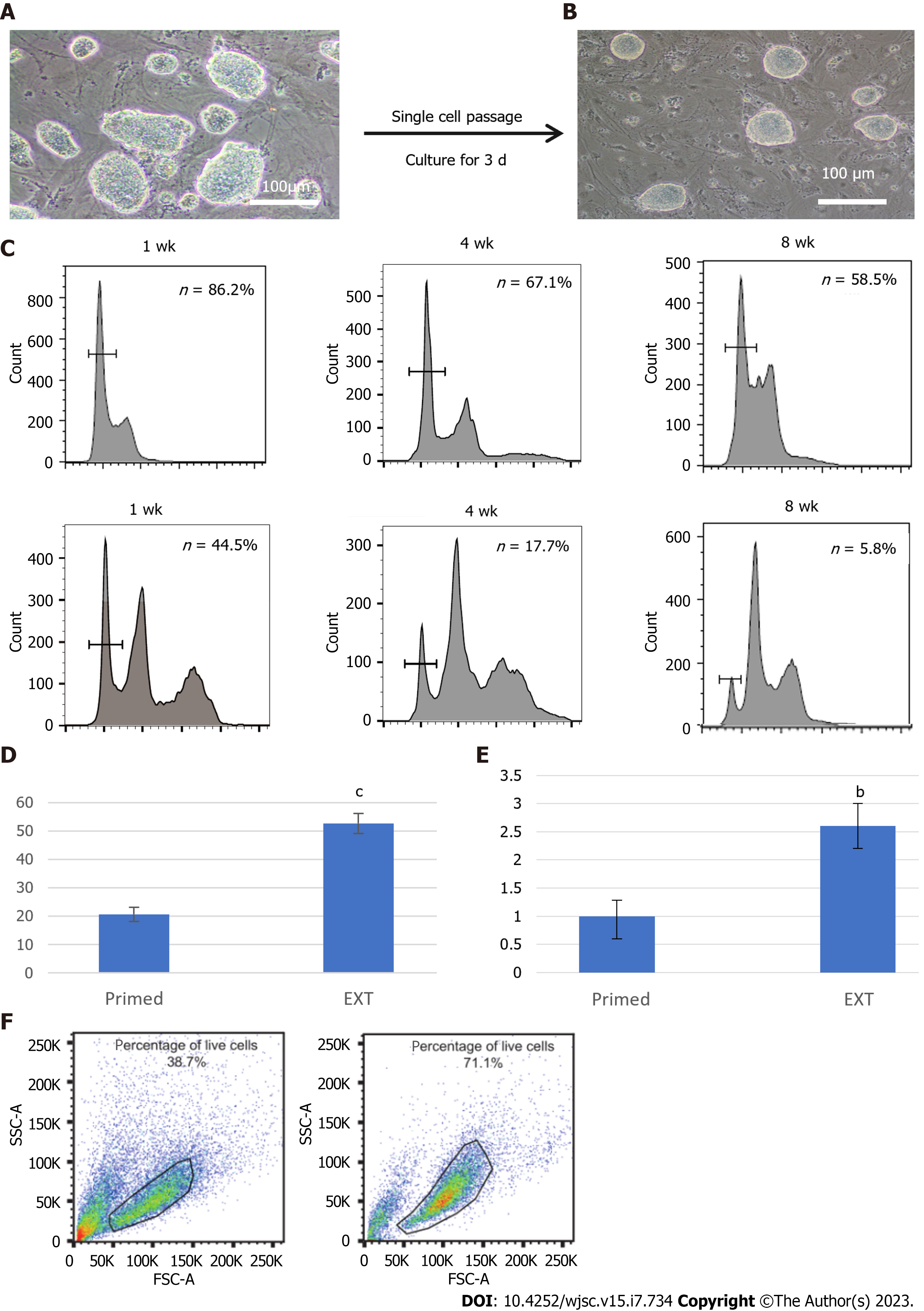
Figure 4 Comparison of pluripotency and survival of haploid embryonic stem cells in different culture media.
A: EhPGES1 formed dome-shaped colonies after culture in optimized extended medium for approximately three passages. Scale bar, 100 μm; B: Morphology of day 3 optimized hPGES1 after single cells were passaged by 0.05% trypsin-EDTA in the absence of Y27632. Scale bar, 100 μm; C: Fluorescence activated cell sorting analysis of haploid embryonic stem cells after culture for 1 wk, 4 wk, and 8 wk in different media. Haploidy maintenance capacity between the traditional (bottom) and optimized (top) culture media; D: Statistical analysis of embryoid bodies (differentiation in 5 d) under traditional culture conditions and optimized culture conditions. t-test, cP < 0.001; E: Statistical analysis of rosette areas in traditional culture conditions and optimized culture conditions. t-test, bP < 0.01; F: Fluorescence activated cell sorting analysis of the proportion of live cells among haploid neural stem cells in different culture media as evaluated by forward scatter plot and side scatter plot. Traditional culture system (left) and optimized culture system (right).
- Citation: Wang HS, Ma XR, Niu WB, Shi H, Liu YD, Ma NZ, Zhang N, Jiang ZW, Sun YP. Generation of a human haploid neural stem cell line for genome-wide genetic screening. World J Stem Cells 2023; 15(7): 734-750
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v15/i7/734.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v15.i7.734