Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2023; 15(7): 734-750
Published online Jul 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i7.734
Published online Jul 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i7.734
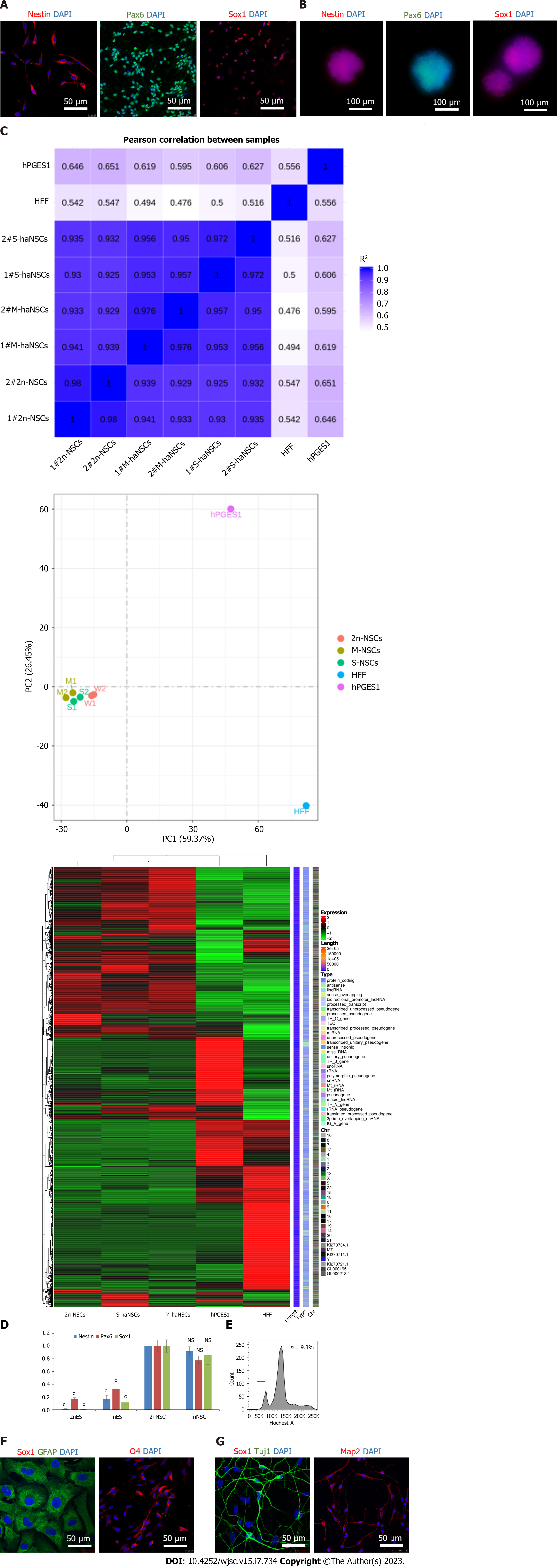
Figure 3 Identification and differentiation of haploid neural stem cells.
A: Immunofluorescence analysis of the neural stem cell (NSC)-specific markers Nestin (red), PAX6 (green), and SOX1 (red) in derived haploid NSCs (haNSCs). DAPI (blue) was used to stain the nuclei. Scale bar, 50 μm; B: Immunofluorescence analysis showed that haploid neural spheres expressed NSC-specific proteins Nestin (red), PAX6 (green) and SOX1 (red). Scale bar, 100 μm; C: Transcript levels of diploid NSCs, monolayer cultured haNSCs, haploid neural spheres, human haploid embryonic stem cells (hPGES1) and human fibroblasts; D: Real time PCR analysis of NSC marker genes (SOX1, PAX6, and Nestin); E: Fluorescence activated cell sorting of derived astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and neurons by DNA content; F: Immunofluorescence analysis of astrocytes (GFAP, green) and oligodendroglia (O4, red). DAPI (blue) was used to stain the nuclei. Scale bar, 50 μm; G: Immunofluorescence analysis of Tuj1 (green) and Map2 (red) in neurons derived from haNSCs. DAPI (blue) was used to stain the nuclei. Scale bar, 50 μm. bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001.
- Citation: Wang HS, Ma XR, Niu WB, Shi H, Liu YD, Ma NZ, Zhang N, Jiang ZW, Sun YP. Generation of a human haploid neural stem cell line for genome-wide genetic screening. World J Stem Cells 2023; 15(7): 734-750
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v15/i7/734.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v15.i7.734