Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2023; 15(7): 734-750
Published online Jul 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i7.734
Published online Jul 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i7.734
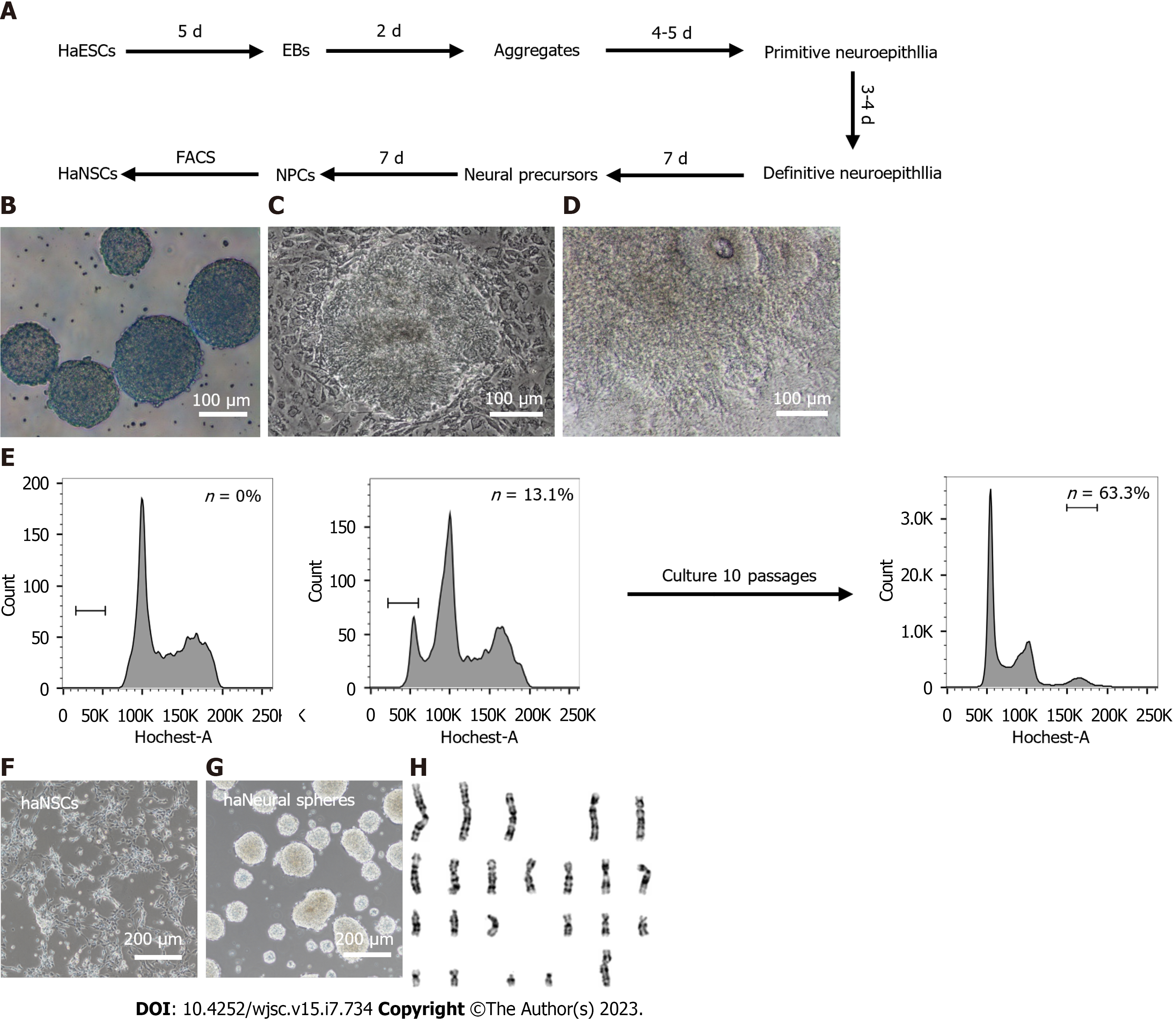
Figure 2 Derivation of human haploid neural stem cells via differentiation invitro.
A: Schematic overview of the strategy to efficiently derive haploid neural stem cell (haNSC) lines through embryoid body-mediated differentiation and fluorescence activated cell sorting; B: Morphology of 7-d aggregates. Scale bar, 100 μm; C: Morphology of primitive neuroepithelia. Dashed lines indicate the morphology of primitive neuroepithelia. Scale bar, 100 μm; D: Morphology of definitive neuroepithelia. Dashed lines indicate the morphology of definitive neuroepithelia. Scale bar, 100 μm; E: Fluorescence activated cell sorting of passage 4 human haNSCs and derived haNSCs maintained a haploid DNA content over 10 passages. Left, a diploid cell line as a control; middle, passage 4 haNSCs; right, derived haNSCs after 10; F: Morphology of sorted haNSCs. Scale bar, 200 μm; G: Morphology of haploid neural spheres from sorted haNSCs. Scale bar, 200 μm; H: G-band analysis of haNSCs with a haploid set of 23 chromosomes. haNSCs: Haploid neural stem cell; haESCs: Haploid embryonic stem cells; FACS: Fluorescence activated cell sorting; EB: Embryoid body; NPC: Neural progenitor cells.
- Citation: Wang HS, Ma XR, Niu WB, Shi H, Liu YD, Ma NZ, Zhang N, Jiang ZW, Sun YP. Generation of a human haploid neural stem cell line for genome-wide genetic screening. World J Stem Cells 2023; 15(7): 734-750
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v15/i7/734.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v15.i7.734