Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2023; 15(7): 713-733
Published online Jul 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i7.713
Published online Jul 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i7.713
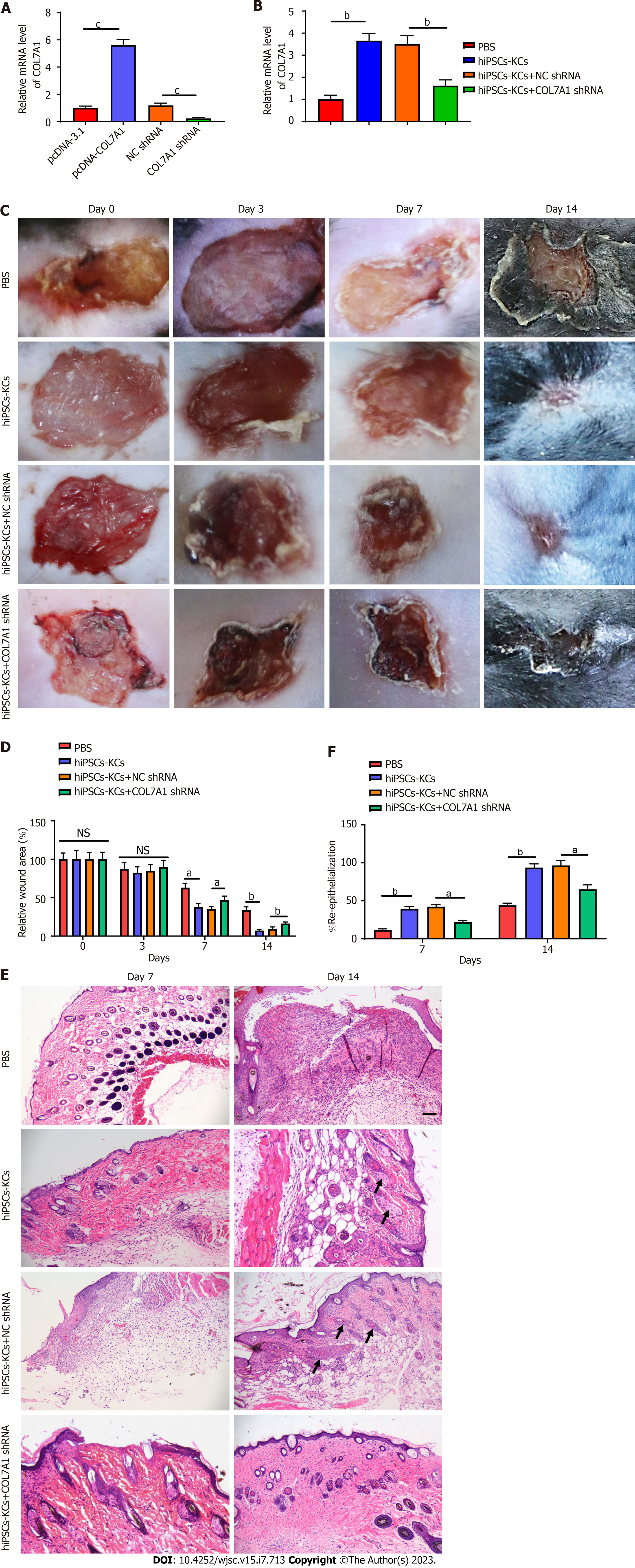
Figure 4 COL7A1 inhibition abolished the promoting effects of human induced pluripotent stem cells derived keratinocytes on burn healing and re epithelialization in mice.
A: RT-qPCR detection of the COL7A1 mRNA levels in human induced pluripotent stem cells derived keratinocytes (hiPSCs-KCs) after transfection of pcDNA- COL7A1 or COL7A1 shRNA; B: RT-qPCR detection of the COL7A1 mRNA levels in burned skin of mice after transplantation of hiPSCs-KCs or COL7A1 knock-downed hiPSCs-KCs; C: At 3, 7, 14 d after hiPSCs-KCs transplantation, the healing of burn wounds in mice was recorded by taking photographs with a digital camera; D: Statistical analysis of relative size of burn wounds in each group of mice; E: Hematoxylin-eosin staining was performed after burn tissues were paraffin sectioned at 7 and 14 d after hiPSCs-KCs transplantation, and then wound healing as well as re-epithelialization were observed by histological sections in each group, scale bar: 200 µm; F: Re-epithelialization ratio of the burned window in mice of each group. Data: Mean ± SEM. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. n = 10. NS: Not significant; PBS: Phosphate buffered saline; hiPSCs: Human induced pluripotent stem cells; KCs: Keratinocytes.
- Citation: Wu LJ, Lin W, Liu JJ, Chen WX, He WJ, Shi Y, Liu X, Li K. Transplantation of human induced pluripotent stem cell derived keratinocytes accelerates deep second-degree burn wound healing. World J Stem Cells 2023; 15(7): 713-733
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v15/i7/713.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v15.i7.713