Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Stem Cells. Jun 26, 2023; 15(6): 561-575
Published online Jun 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i6.561
Published online Jun 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i6.561
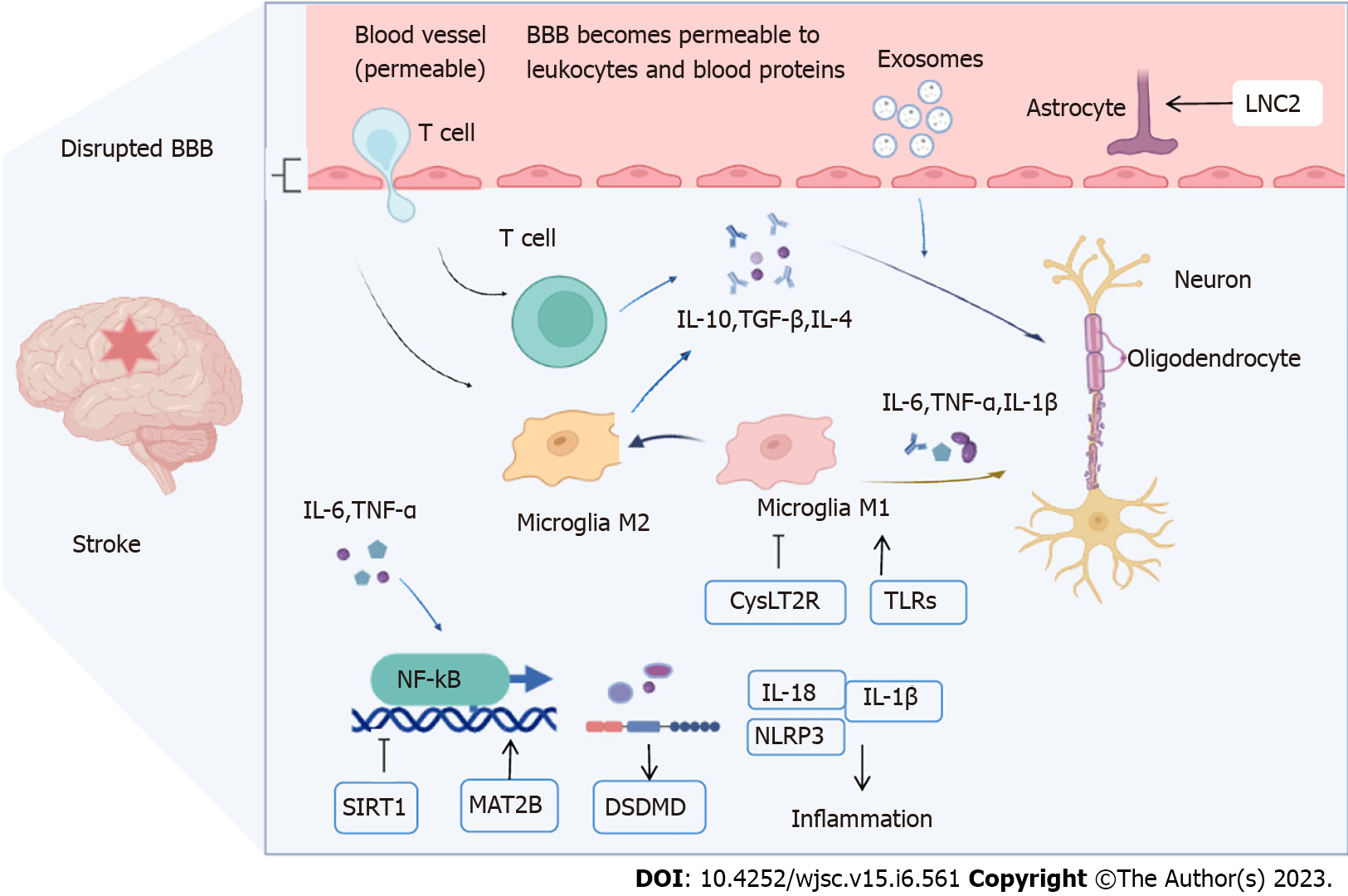
Figure 1 Pathological changes after stroke.
Blood-brain barrier (BBB) disruption after stroke is permeable to leukocytes and blood proteins. Microglia are stimulated, and these activated microglia (M1), in turn, release tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-1β, which activate the nuclear factor kappa-B inflammatory response of reactive astrocytes (A1) and further amplify this effect. Exosomes can penetrate BBB, promote microglial M1 polarization to M2 and T cell activation, mediate lipocalin-2, sirtuin 1, methionine adenosyl transferase 2B, pyrin domain-containing protein, cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 2, and other signaling pathways to promote the release of anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-10, transforming growth factor-β, and IL-4. By BioRender.com. BBB: Blood-brain barrier; CysLT2: Cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 2; IL: Interleukin; LNC2: Lipocalin-2; MAT2B: Methionine adenosyl transferase 2B; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa-B; SIRT1: Sirtuin 1; TLRs: Pyrin domain-containing protein; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α.
- Citation: Chen N, Wang YL, Sun HF, Wang ZY, Zhang Q, Fan FY, Ma YC, Liu FX, Zhang YK. Potential regulatory effects of stem cell exosomes on inflammatory response in ischemic stroke treatment. World J Stem Cells 2023; 15(6): 561-575
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v15/i6/561.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v15.i6.561