Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Stem Cells. May 26, 2023; 15(5): 476-489
Published online May 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i5.476
Published online May 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i5.476
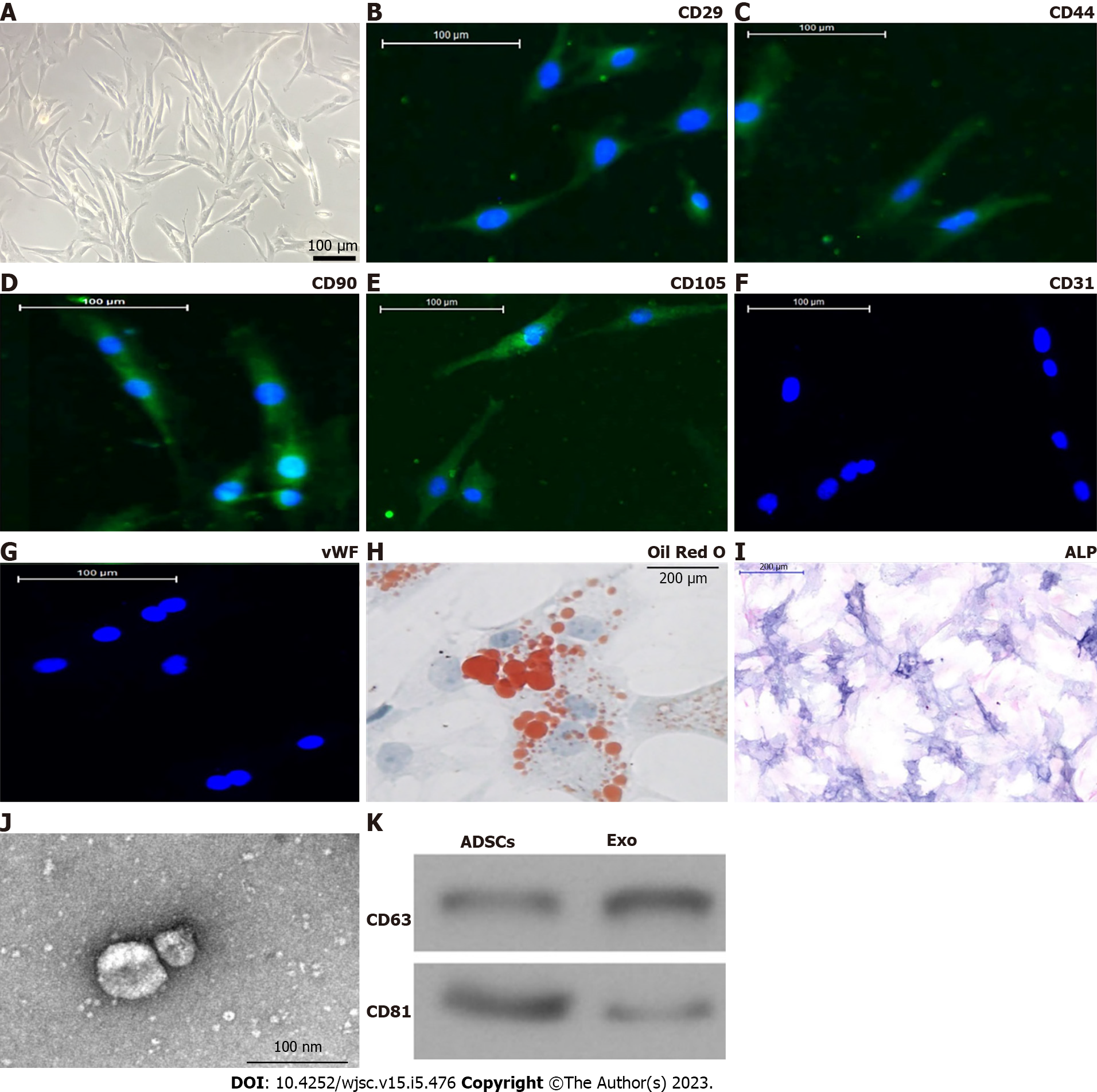
Figure 1 Characterization of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and exosomes.
A: Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADSCs) showed a typical cobblestone-like morphology. Scale bar: 100 μm; B–G: Immunofluorescence staining of cell surface markers. ADSCs exhibited positive expression of cluster of differentiation 90 (CD90), CD29, CD44, and CD105, but not von Willebrand factor or CD34. Scale bar: 100 μm; H and I: The differentiation potential of ADSCs assessed by Oil Red O (H) and alkaline phosphatase (I) staining. Scale bar: 200 μm; J: Transmission electron micrographs demonstrated ADSC exosome morphology. Scale bar: 100 nm; K: Western blotting detection of CD81 and CD63 expression in exosomes and ADSCs.
- Citation: Wang Z, Feng C, Liu H, Meng T, Huang WQ, Song KX, Wang YB. Exosomes from circ-Astn1-modified adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells enhance wound healing through miR-138-5p/SIRT1/FOXO1 axis regulation. World J Stem Cells 2023; 15(5): 476-489
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v15/i5/476.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v15.i5.476