Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Stem Cells. May 26, 2023; 15(5): 281-301
Published online May 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i5.281
Published online May 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i5.281
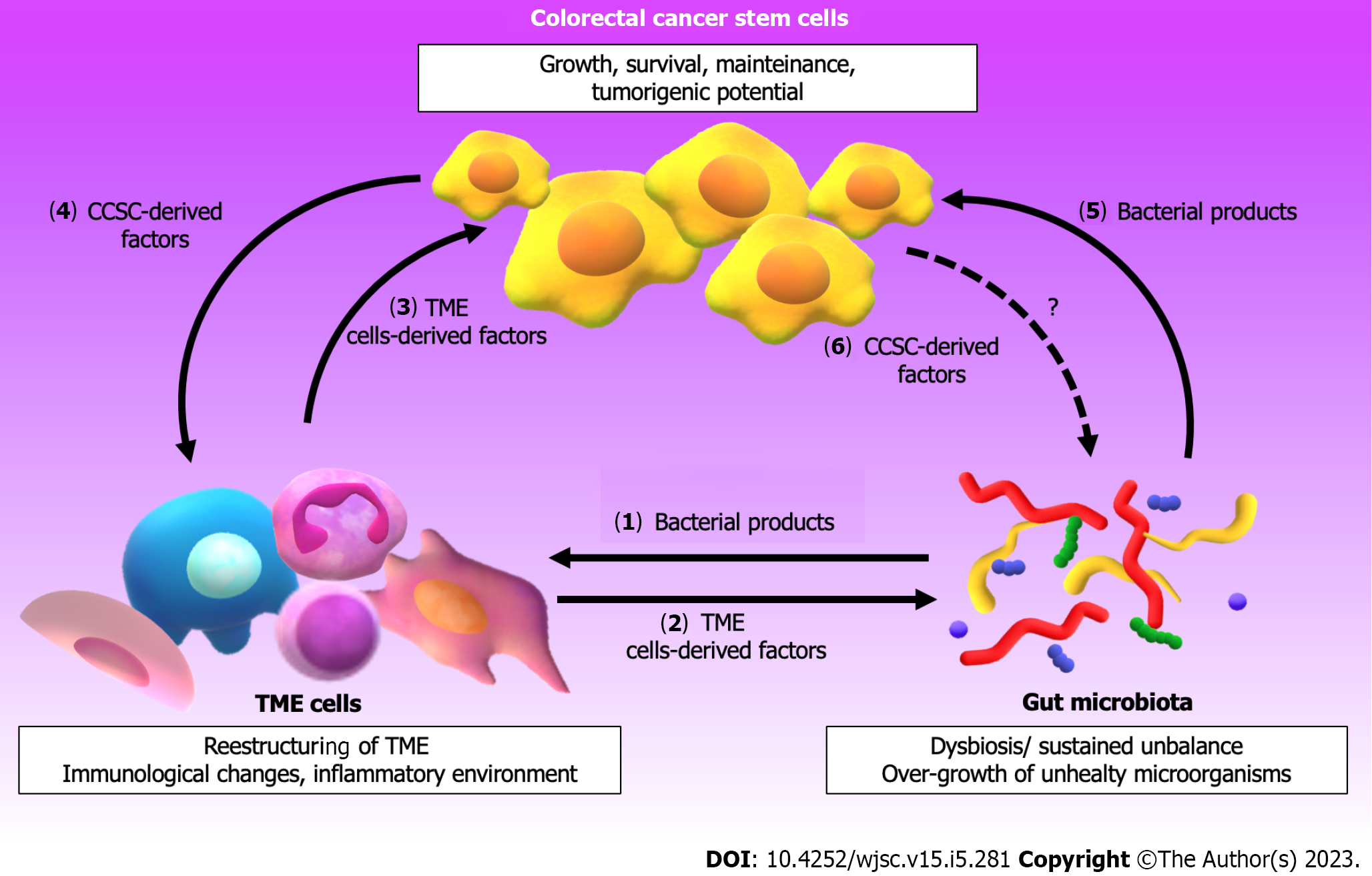
Figure 2 The interplay among the tumor microenvironment and the gut microbiota influences the stemness of colorectal cancer cells.
(1) Gut microorganisms and/or their derived products in a dysbiosis context influence the restructuration of tumor microenvironment (TME), favoring the release of several factors (growth factors, cytokines, non-coding ribonucleic acids and enzymes), immunological changes and an inflammatory environment; (2) The factors released by TME cells impact on intestinal microbiota promoting the growth of unhealthy microorganisms and their sustained unbalance; (3) Moreover, these TME factors can modulate the properties and behavior of colorectal cancer stem cells (CCSC) promoting effects such as their growth, survival, maintenance and tumorigenic potential; (4) In this context, CCSC response expressing factors that enable them to communicate with stromal cells and also influence a TME restructuration; (5) Microorganisms and/or their derived products can directly modulate the features and properties of CCSC, which in response; and (6) Probably affect the intestinal microbiota. All these associated events contribute to colorectal cancer progression. CCSC: Colorectal cancer stem cells; TME: Tumor microenvironment.
- Citation: Novoa Díaz MB, Carriere P, Gentili C. How the interplay among the tumor microenvironment and the gut microbiota influences the stemness of colorectal cancer cells. World J Stem Cells 2023; 15(5): 281-301
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v15/i5/281.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v15.i5.281