Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Stem Cells. Apr 26, 2023; 15(4): 196-208
Published online Apr 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i4.196
Published online Apr 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i4.196
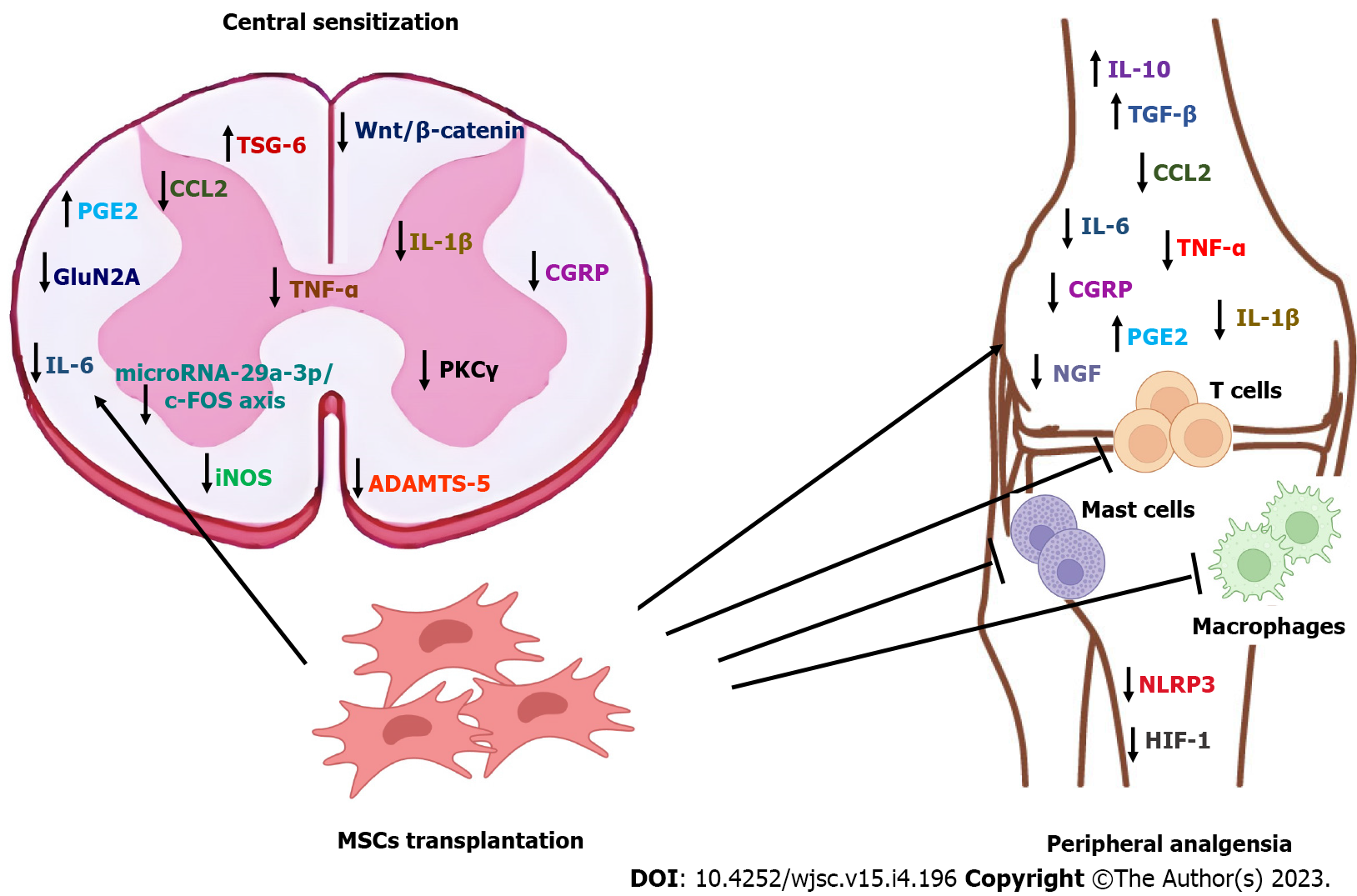
Figure 1 Graphical summary of proved and anticipated analgesic mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cells in osteoarthritis.
Mesenchymal stem cell (MSCs) transplantation reverts central sensitization and induces peripheral analgesia due to their anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties and by attenuation of specific pain pathways via exosomes-derived microRNAs and MSCs paracrine factors. TSG-6: TNF-stimulated gene 6 protein; CCL2: Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2; PGE2: Prostaglandin E2; GluN2A: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit 2A; IL-6: Interleukin 6; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase; TNF α: Tumor necrosis factor α; IL-1β: Interleukin-1β; CGRP: Calcitonin gene-related peptide; PKCγ: Protein kinase C γ; ADAMTS-5: A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 5; IL-10: Interleukin 10; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor β; NGF: Nerve growth factor; NLRP3: NLR family pyrin domain containing 3; HIF-1: Hypoxia inducible factor 1.
- Citation: Almahasneh F, Abu-El-Rub E, Khasawneh RR. Mechanisms of analgesic effect of mesenchymal stem cells in osteoarthritis pain. World J Stem Cells 2023; 15(4): 196-208
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v15/i4/196.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v15.i4.196