Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Stem Cells. Dec 26, 2023; 15(12): 1093-1103
Published online Dec 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i12.1093
Published online Dec 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i12.1093
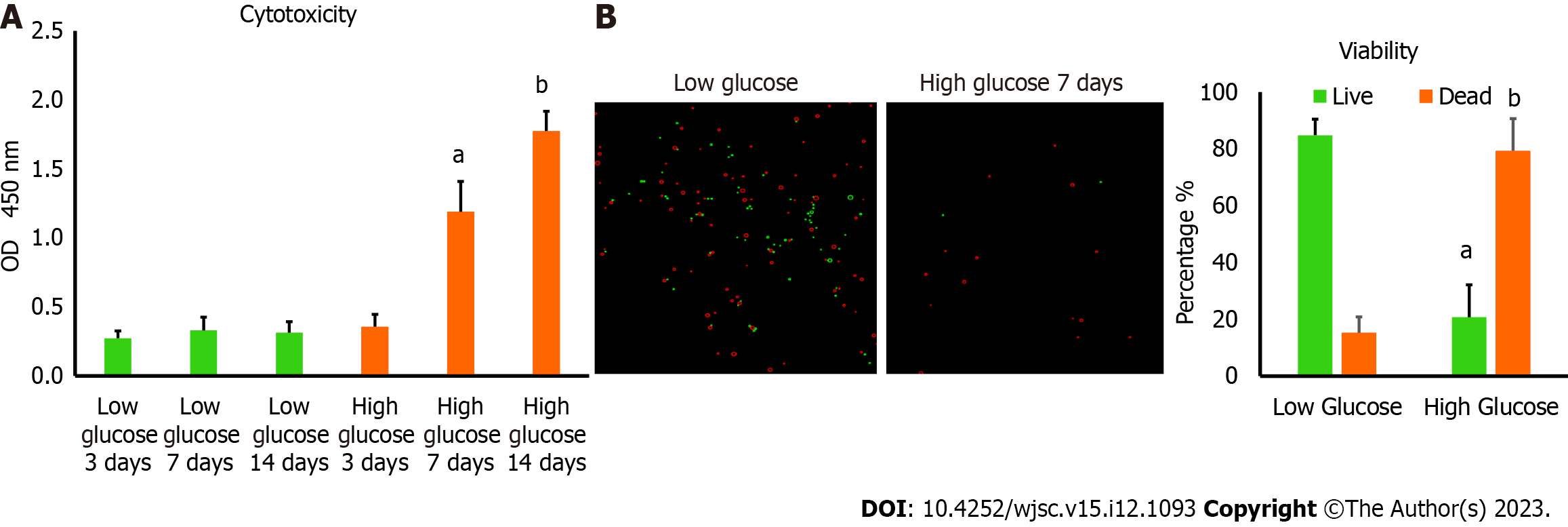
Figure 1 Culturing human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells in high glucose reduced their viability.
A: Lactate dehydrogenase cytotoxicity assay revealed higher level of cytotoxicity in human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hAD-MSCs) cultured in high glucose for 7 and 14 d compared to cells cultured in low glucose. n = 5, aP < 0.01 compared to low glucose 7 d, bP < 0.01 compared to low glucose 14 d; B: The percentage of cells viability detected by 0.4% Trypan blue showed significant reduction in the number of viable hAD-MSCs after being cultured in high glucose for 7 d. Fluorescent images of live and dead cells were obtained using Corning® CytoSmart Cell Counter. n = 5. n = 5, aP < 0.01 compared to live cells in low glucose 7 d, bP < 0.01 compared to dead cells in low glucose 7 d.
- Citation: Abu-El-Rub E, Almahasneh F, Khasawneh RR, Alzu'bi A, Ghorab D, Almazari R, Magableh H, Sanajleh A, Shlool H, Mazari M, Bader NS, Al-Momani J. Human mesenchymal stem cells exhibit altered mitochondrial dynamics and poor survival in high glucose microenvironment. World J Stem Cells 2023; 15(12): 1093-1103
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v15/i12/1093.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v15.i12.1093