Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Stem Cells. Nov 26, 2023; 15(11): 999-1016
Published online Nov 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i11.999
Published online Nov 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i11.999
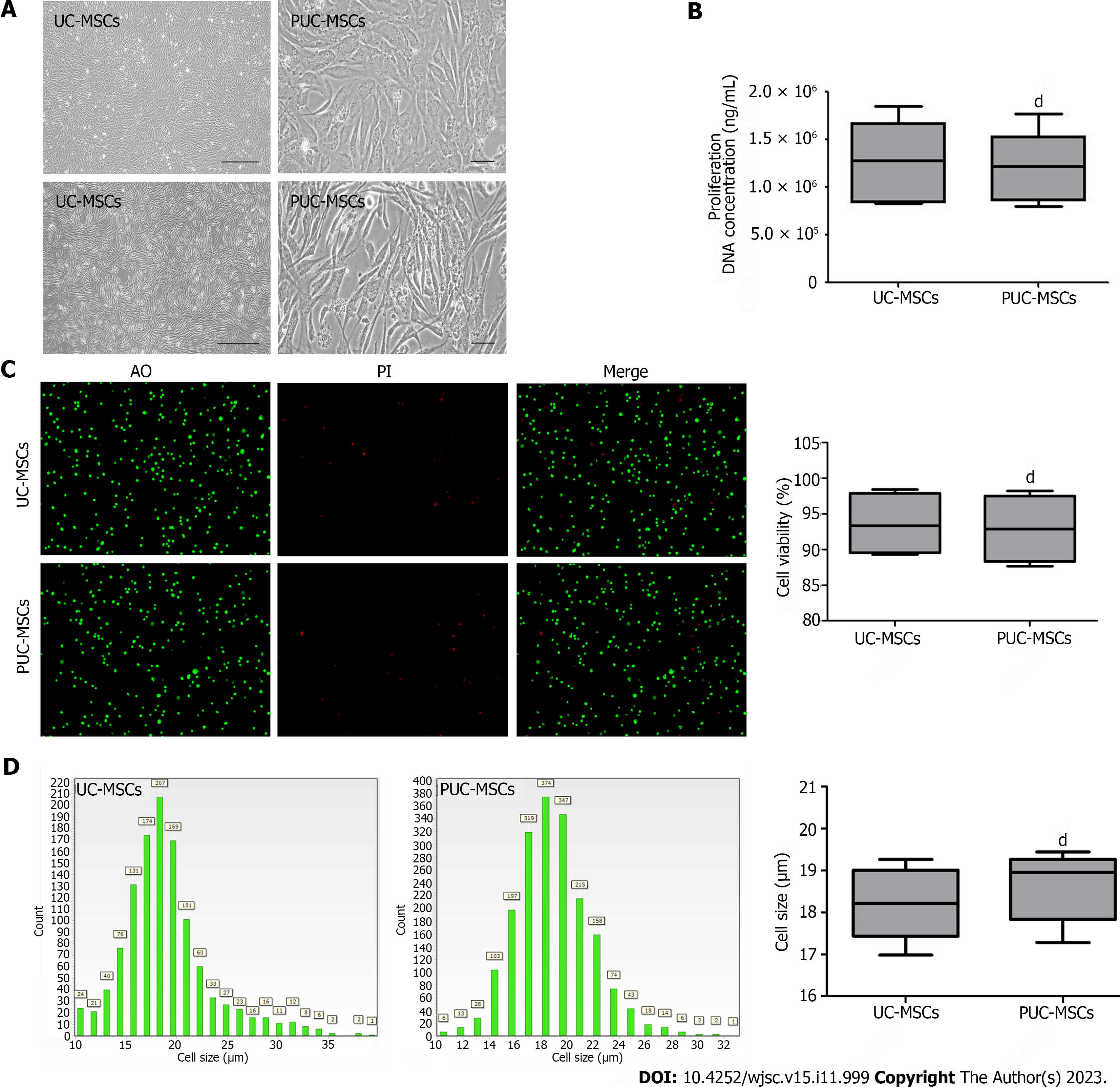
Figure 1 Morphology, viability, proliferation, and size of mesenchymal stem cells.
A: Representative micrographs showing umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (UC-MSCs) and primed umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (PUC-MSCs). Microscopy observation of cell morphology revealed that UC-MSCs were elongated after hypoxia and inflammatory factor pretreatment (Bar = 200 μm); B: The DNA concentration was measured by an ultramicro nucleic acid protein detector. The DNA concentration of PUC-MSCs was not significantly different from that of UC-MSCs, and pretreatment had no effect on their proliferation; C: Cell viability was determined by an acridine orange (AO) propidium iodide (PI) staining cell image analyzer, and no significant difference between UC-MSCs and PUC-MSCs was observed; D: Cell size was determined with a cell imaging analyzer, and the sizes of the UC-MSCs and PUC-MSCs were comparable. dP > 0.05.
- Citation: Li H, Ji XQ, Zhang SM, Bi RH. Hypoxia and inflammatory factor preconditioning enhances the immunosuppressive properties of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2023; 15(11): 999-1016
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v15/i11/999.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v15.i11.999