Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Stem Cells. Sep 26, 2022; 14(9): 714-728
Published online Sep 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i9.714
Published online Sep 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i9.714
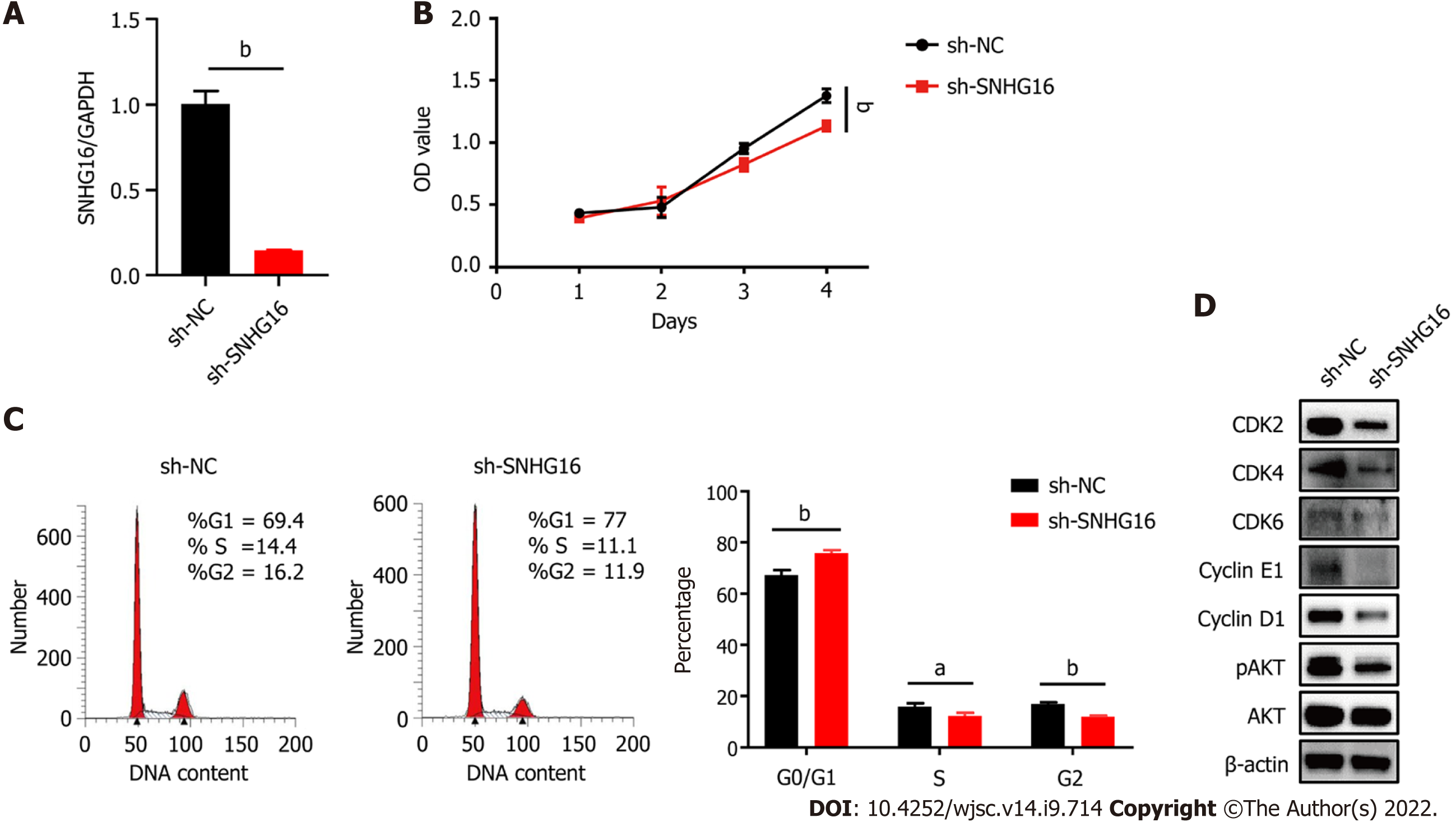
Figure 5 Knockdown of SNHG16 attenuated the proliferation ability of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
A: Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction analysis of relative SNHG16 expression after transfection of SNHG16 short hairpin RNA (sh-SNHG16) and the corresponding controls (sh-NC) in human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells; B: Cell proliferation capacity evaluated by cell counting kit-8 assay; C: Cell cycle measured by flow cytometry; D: The G1 to S phase transition-related proteins and p-AKT detected by western blot analysis. Data are presented as means ± standard deviation. bP < 0.01.
- Citation: Feng XD, Zhou JH, Chen JY, Feng B, Hu RT, Wu J, Pan QL, Yang JF, Yu J, Cao HC. Long non-coding RNA SNHG16 promotes human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell proliferation capacity through the PI3K/AKT pathway under hypoxia. World J Stem Cells 2022; 14(9): 714-728
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v14/i9/714.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v14.i9.714