Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Stem Cells. Sep 26, 2022; 14(9): 714-728
Published online Sep 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i9.714
Published online Sep 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i9.714
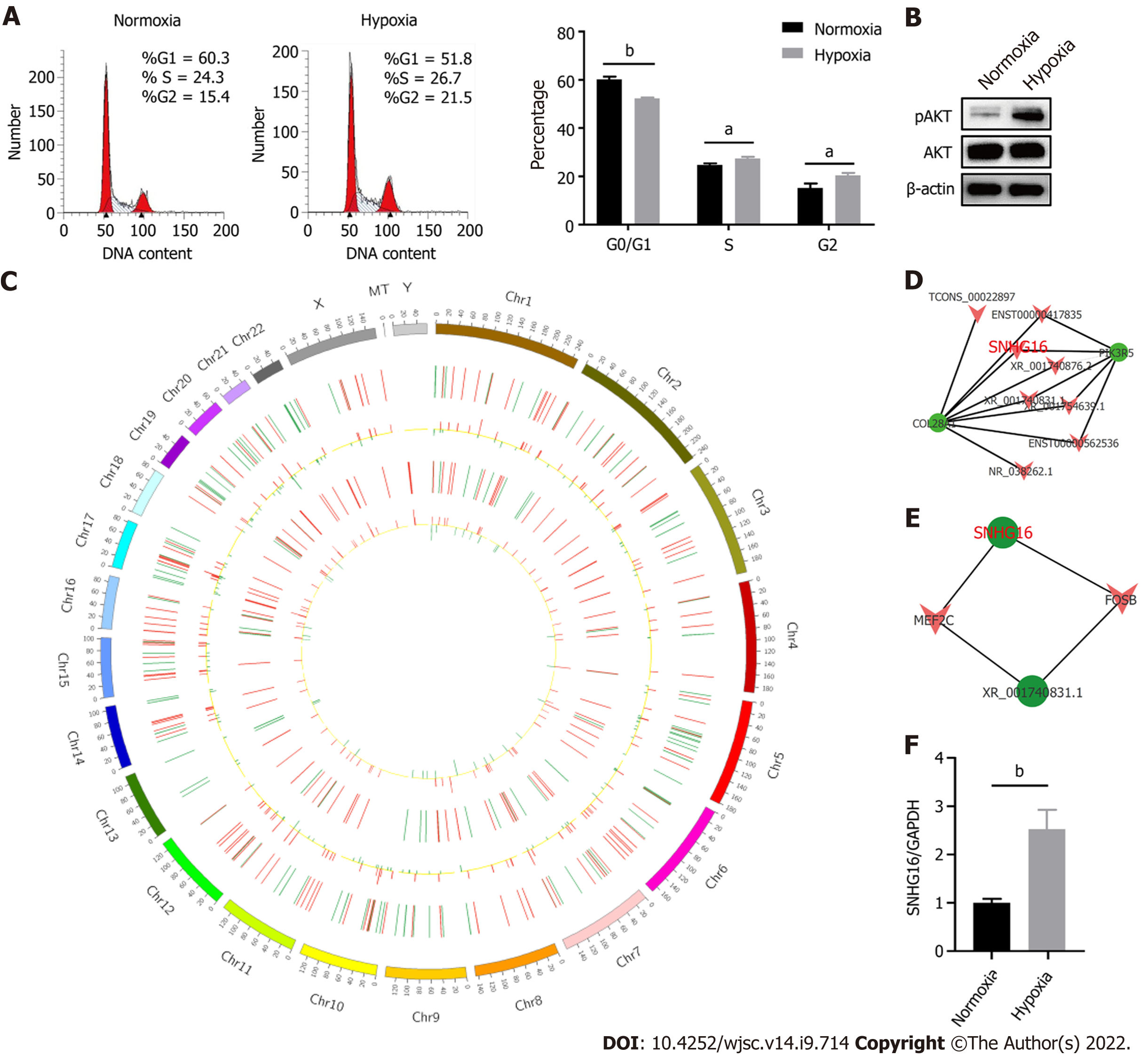
Figure 4 SNHG16 was a potential promotor of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell proliferation ability.
A: Cell cycle analysis of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hP-MSCs) under hypoxic culture via flow cytometry; B: Western blot analysis of AKT phosphorylation in hP-MSCs exposed to hypoxia; C: Circos plot of the long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs)-messenger (m)RNA co-expression network. The outermost circle is the autosomal distribution. The second and third circles are the distribution of differentially expressed lncRNAs on chromosomes. The red line represents upregulation, and the green line represents downregulation. Higher bars indicate a greater number of differential genes in the interval. The fourth and fifth circles are the distribution of differentially expressed genes on chromosomes, with the same interpretation as lncRNA; D: Part of lncRNA-mRNA interaction network analysis visualized using the Cytoscape software; E: Part of the association analysis of differentially expressed lncRNAs and transcription factors; F: Effects of hypoxia on the expression of SNHG16 in hP-MSCs by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. Data are presented as means ± standard deviation. bP < 0.01.
- Citation: Feng XD, Zhou JH, Chen JY, Feng B, Hu RT, Wu J, Pan QL, Yang JF, Yu J, Cao HC. Long non-coding RNA SNHG16 promotes human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell proliferation capacity through the PI3K/AKT pathway under hypoxia. World J Stem Cells 2022; 14(9): 714-728
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v14/i9/714.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v14.i9.714