Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Stem Cells. Sep 26, 2022; 14(9): 684-699
Published online Sep 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i9.684
Published online Sep 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i9.684
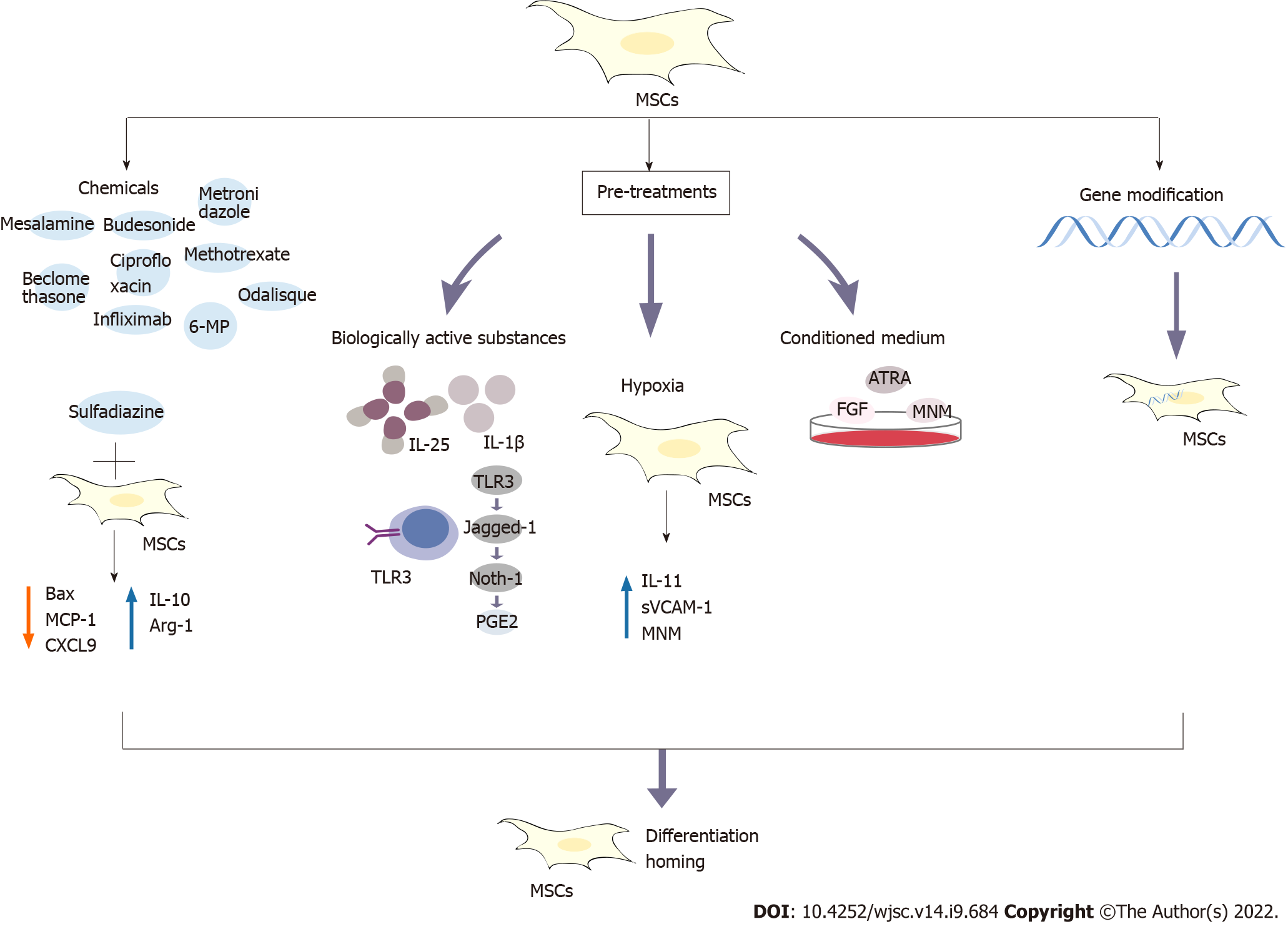
Figure 2 The developed strategies to improve the efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease include combined treatment with conventional drugs, pretreatment and gene modification.
The tested pretreatments include bioactive factors, hypoxia and medium modification. The conventional drugs include biological preparations of mesalazine, budesonide, beclomethasone, ciprofloxacin, metronidazole, 6-mercaptopurine, methotrexate, infliximab and adalimumab. For example, the combination of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and the drug sulfadiazine inhibits the nuclear factor-kappaB pathway, reduces Bax expression, prevents loss of the B cell lymphoma-2 protein, reduces the levels of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and CXCL9, increases the levels of interleukin (IL)-10 and Arg-1, and transforms inflammatory M1 macrophages into anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages. Pretreatment with IL-25 and IL-1β enhances the immunosuppressive abilities of MSCs. MSCs pretreated with Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) for a short time in vitro produce prostaglandin E2 through the TLR3-Jagged-1-Notch-1 pathway. In response to hypoxia, the levels of IL-11, soluble vascular cell adhesion protein-1 and stromal cell-derived factor-1α are significantly upregulated. MSCs have also been pretreated by modifying the culture medium, such as the addition of fibroblast growth factor, all-trans retinoic acid and modified neuronal medium. In addition, genetically modified MSCs have been developed. These methods and strategies potentially improve the immunosuppressive abilities of MSCs by promoting their homing and differentiation abilities. PGE2: Prostaglandin E2; MSCs: Mesenchymal stem cells; IL: Interleukin; 6-MP: 6-mercaptopurine; MCP-1: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; TLR: Toll-like receptor; MNM: Modified neuronal medium; sVCAM-1: Soluble vascular cell adhesion protein-1; ATRA: All-trans retinoic acid; FGF: Fibroblast growth factor.
- Citation: Shi MY, Liu L, Yang FY. Strategies to improve the effect of mesenchymal stem cell therapy on inflammatory bowel disease. World J Stem Cells 2022; 14(9): 684-699
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v14/i9/684.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v14.i9.684