Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Stem Cells. Aug 26, 2022; 14(8): 616-632
Published online Aug 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i8.616
Published online Aug 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i8.616
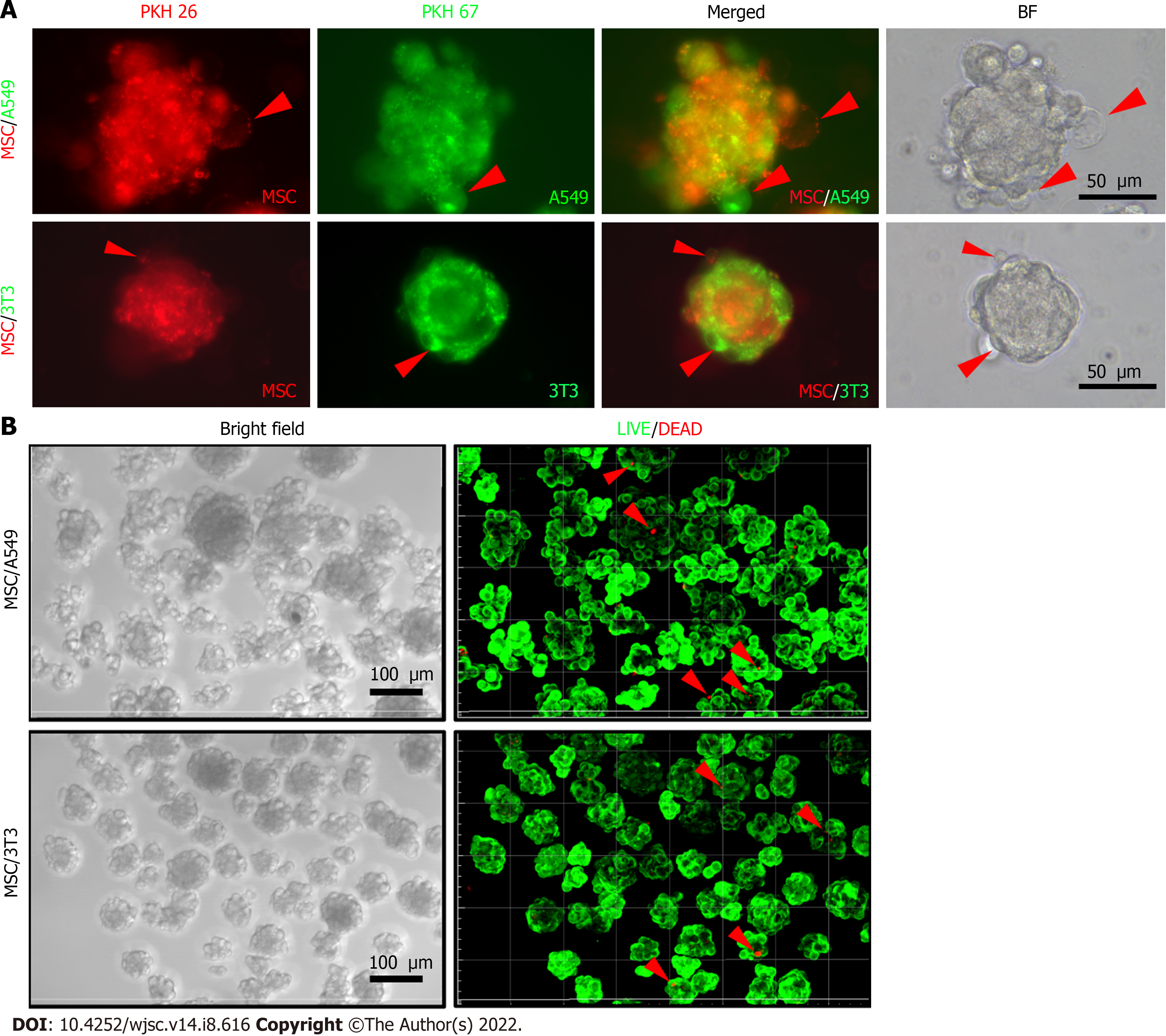
Figure 6 Morphologies and cell viability of cellular co-spheroids.
A: Fluorescent dye-labeled mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) (PKH26, red), A549 (PKH67, green), or 3T3 (PKH67, green) cells were co-cultured on chitosan-hyaluronan (CS-HA) substrates for 3 d. The image of typical cell morphologies and vesicle-like bubbles on the cell membrane of the MSC/3T3 or MSC/A549 co-spheroids were taken by the inverted microscope; B: confocal images of co-spheroids co-cultured on CS-HA substrates for 2 d. The cell viability was detected by LIVE/DEAD staining with calcein AM (green) and ethidium homodimer-1 (red). Viable cells appear as green, while the red arrows indicate dead cells (red). Z-stack images were collected at 3 μm sections (total stacks approximately 25 images). BF: Bright field; MSC: Mesenchymal stem cells.
- Citation: Wong CW, Han HW, Hsu SH. Changes of cell membrane fluidity for mesenchymal stem cell spheroids on biomaterial surfaces. World J Stem Cells 2022; 14(8): 616-632
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v14/i8/616.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v14.i8.616