Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Stem Cells. Aug 26, 2022; 14(8): 616-632
Published online Aug 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i8.616
Published online Aug 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i8.616
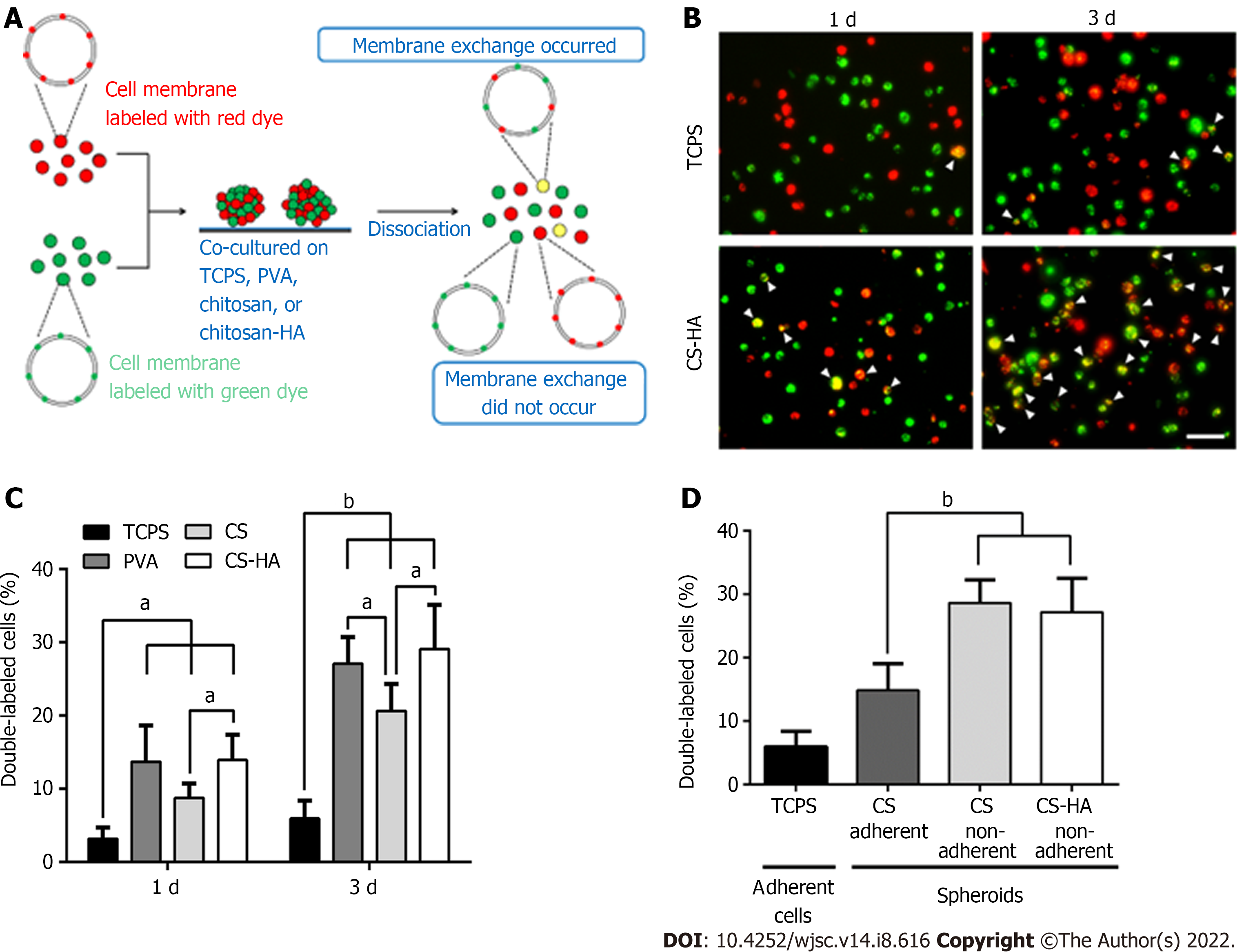
Figure 4 Membrane fluidity for mesenchymal stem cells cultured on tissue culture polystyrene and for mesenchymal stem cells spheroids formed on various substrates.
A: Illustration of experimental procedures for determination of the membrane fluidity; B: Double-labeled cells (with yellow color) are indicated by white arrowheads. Scale bar: 100 μm; C: Population percentages of the double-labeled cells collected from the tissue culture polystyrene (TCPS), polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), chitosan (CS), or CS-hyaluronan (CS-HA) substrates as indicated. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, among the indicated groups; D: Population percentages of double-labeled cells were measured from adherent and non-adherent mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) spheroids on CS and CS-HA substrates after 3 d of incubation. The adherent MSCs cultured on TCPS plates served as the control group in this experiment. bP < 0.01, among the indicated groups. PVA: Polyvinyl alcohol; MSC: Mesenchymal stem cells; CS-HA: CS-hyaluronan; CS: Chitosan.
- Citation: Wong CW, Han HW, Hsu SH. Changes of cell membrane fluidity for mesenchymal stem cell spheroids on biomaterial surfaces. World J Stem Cells 2022; 14(8): 616-632
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v14/i8/616.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v14.i8.616