Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2022; 14(7): 556-576
Published online Jul 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i7.556
Published online Jul 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i7.556
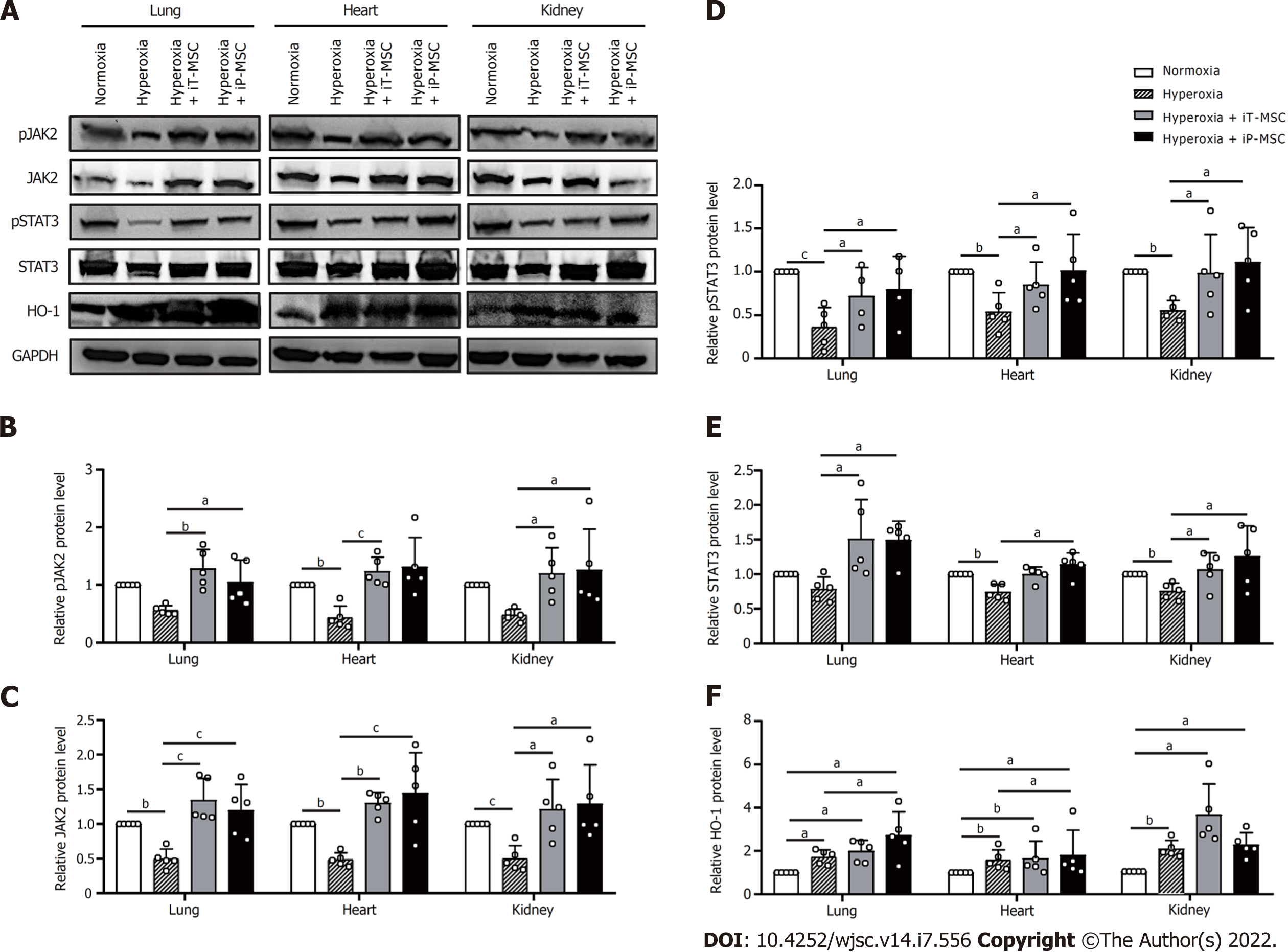
Figure 7 Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells activated the heme oxygenase-1 and JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway to protect against hyperoxia-induced multiple-organ injury.
A: The protein extracted from tissue homogenates of the lungs, heart, and kidneys were collected for western blotting to detect heme oxygenase-1, JAK2, STAT3 protein expression levels, as well as their phosphorylation; B–F: Statistical analyses of protein expression levels of the above-mentioned genes. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001. iT: Intratracheal; iP: Intraperitoneal; HO-1: Heme oxygenase-1; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell.
- Citation: Dong N, Zhou PP, Li D, Zhu HS, Liu LH, Ma HX, Shi Q, Ju XL. Intratracheal administration of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuates hyperoxia-induced multi-organ injury via heme oxygenase-1 and JAK/STAT pathways. World J Stem Cells 2022; 14(7): 556-576
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v14/i7/556.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v14.i7.556