Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2022; 14(7): 556-576
Published online Jul 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i7.556
Published online Jul 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i7.556
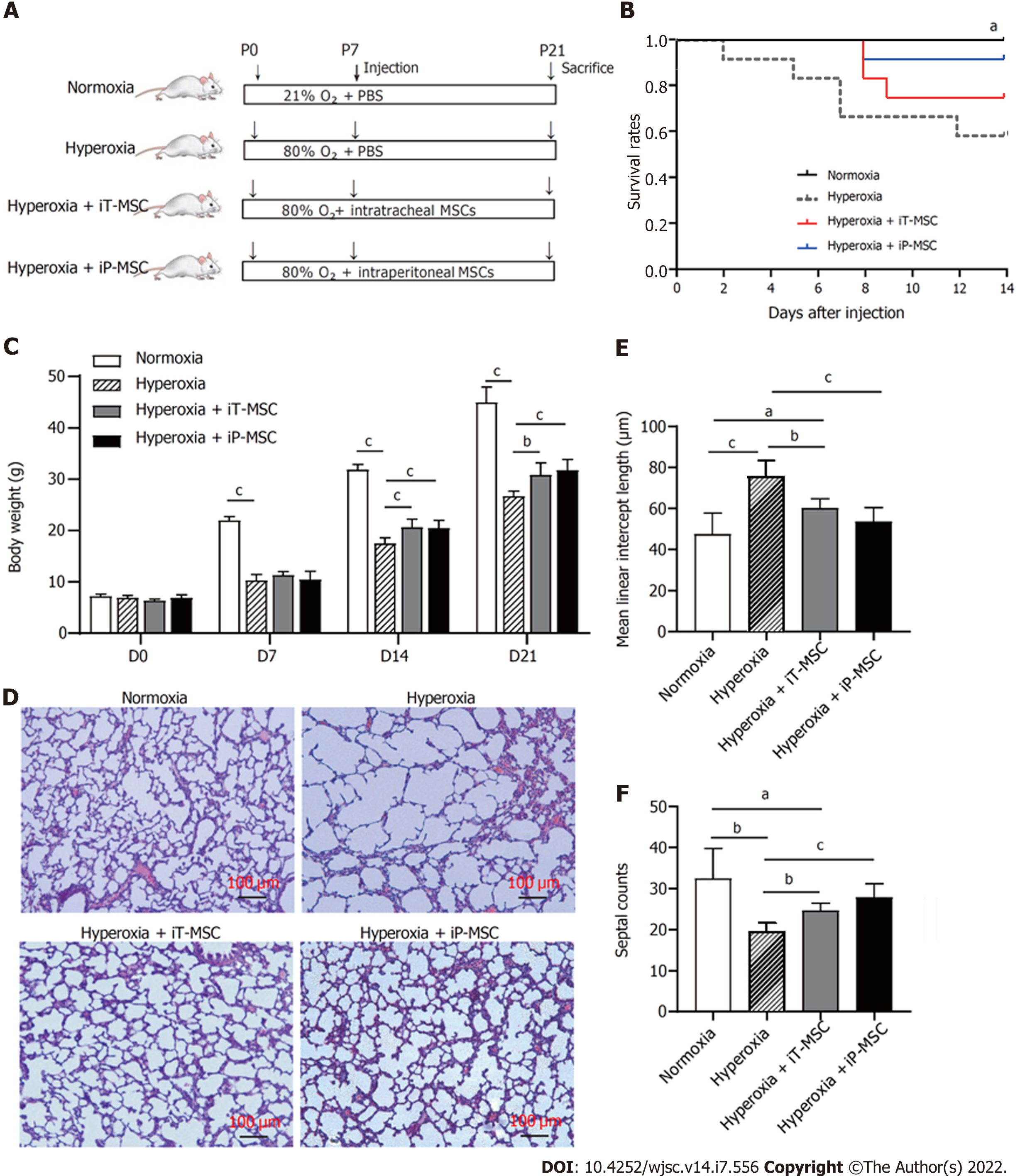
Figure 2 Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells administration increases survival rate and improves lung development.
A: Schematic diagram of the overall experimental design process and grouping; B: Kaplan-Meier survival curves of rat pups treated as indicated; C: Body weight alterations of rat pups treated as indicated; D: Representative images of harvested lung sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin for morphometric analyses (scale bars = 100 μm); E and F: Mean linear intercept and septal counts in lungs treated as indicated (n = 5 for each group, 10 fields/animal). aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001. iT: Intratracheal; iP: Intraperitoneal; P: Postnatal day; PBS: Phosphate-buffered saline; MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell.
- Citation: Dong N, Zhou PP, Li D, Zhu HS, Liu LH, Ma HX, Shi Q, Ju XL. Intratracheal administration of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuates hyperoxia-induced multi-organ injury via heme oxygenase-1 and JAK/STAT pathways. World J Stem Cells 2022; 14(7): 556-576
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v14/i7/556.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v14.i7.556