Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2022; 14(7): 556-576
Published online Jul 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i7.556
Published online Jul 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i7.556
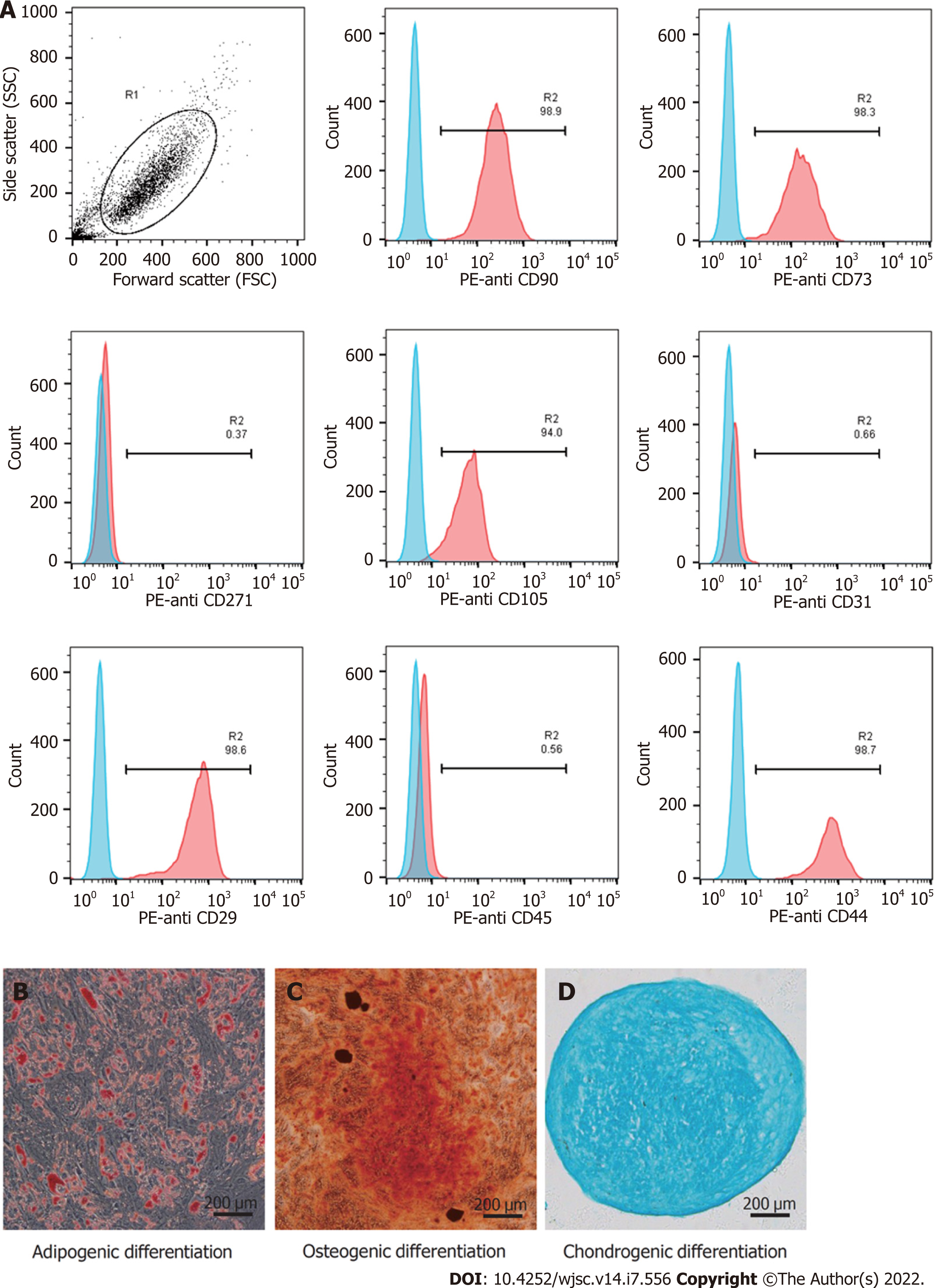
Figure 1 Identification of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
A: The human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hUC-MSCs) showed high expression of CD29, CD44, CD73, CD90, and CD105, and did not express CD31, CD45, and CD271; B–D: hUC-MSCs were positive for Oil Red O, Alizarin red, and Alcian blue staining under the corresponding induction conditions (scale bars = 200 μm).
- Citation: Dong N, Zhou PP, Li D, Zhu HS, Liu LH, Ma HX, Shi Q, Ju XL. Intratracheal administration of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuates hyperoxia-induced multi-organ injury via heme oxygenase-1 and JAK/STAT pathways. World J Stem Cells 2022; 14(7): 556-576
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v14/i7/556.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v14.i7.556