Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2022; 14(7): 527-538
Published online Jul 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i7.527
Published online Jul 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i7.527
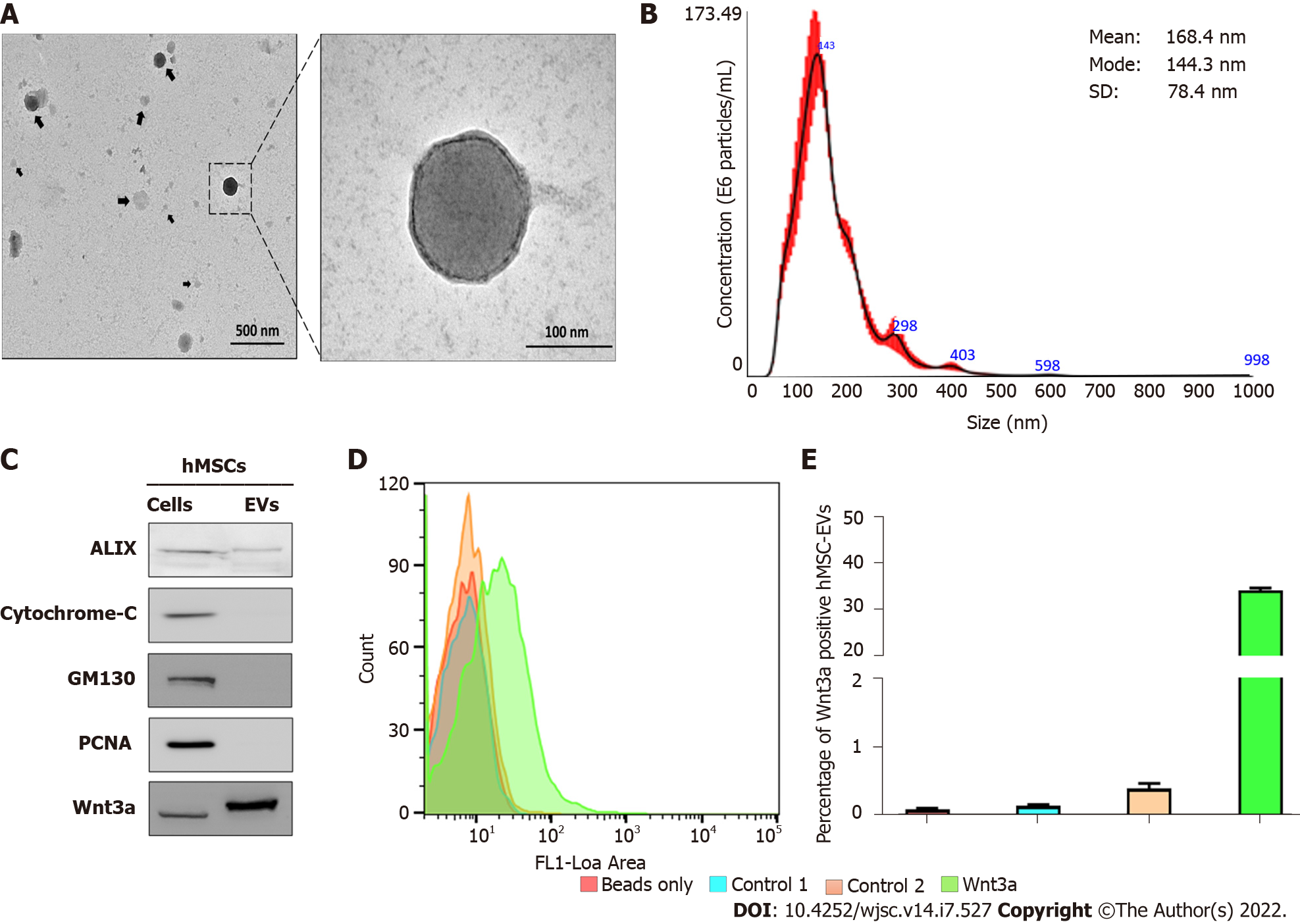
Figure 1 Isolation and characterization of human mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles.
A: The morphology of human mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles (hMSC-EVs) was confirmed using transmission electron microscopy (scale bars: 500 and 100 nm); B: hMSC-EV size was determined using nanoparticle tracking analysis (n = 5); C: Western blot analysis using Alix, cytochrome C, GM130, PCNA, and Wnt3a antibodies on hMSCs and hMSC-EVs; D and E: Flow cytometry count graphs of only beads, control 1 (beads + hMSC-EVs), control 2 [beads + hMSC-EVs + Secondary fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) antibody], and Wnt3a (beads + hMSC-EVs + Wnt3a antibody + Secondary FITC antibody) (n = 3). The values obtained from experiments are shown mean ± SD. FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate; hMSC-EVs: Human mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles, NTA: Nanoparticle tracking analysis.
- Citation: Rajendran RL, Gangadaran P, Kwack MH, Oh JM, Hong CM, Sung YK, Lee J, Ahn BC. Application of extracellular vesicles from mesenchymal stem cells promotes hair growth by regulating human dermal cells and follicles. World J Stem Cells 2022; 14(7): 527-538
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v14/i7/527.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v14.i7.527