Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2022; 14(7): 435-452
Published online Jul 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i7.435
Published online Jul 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i7.435
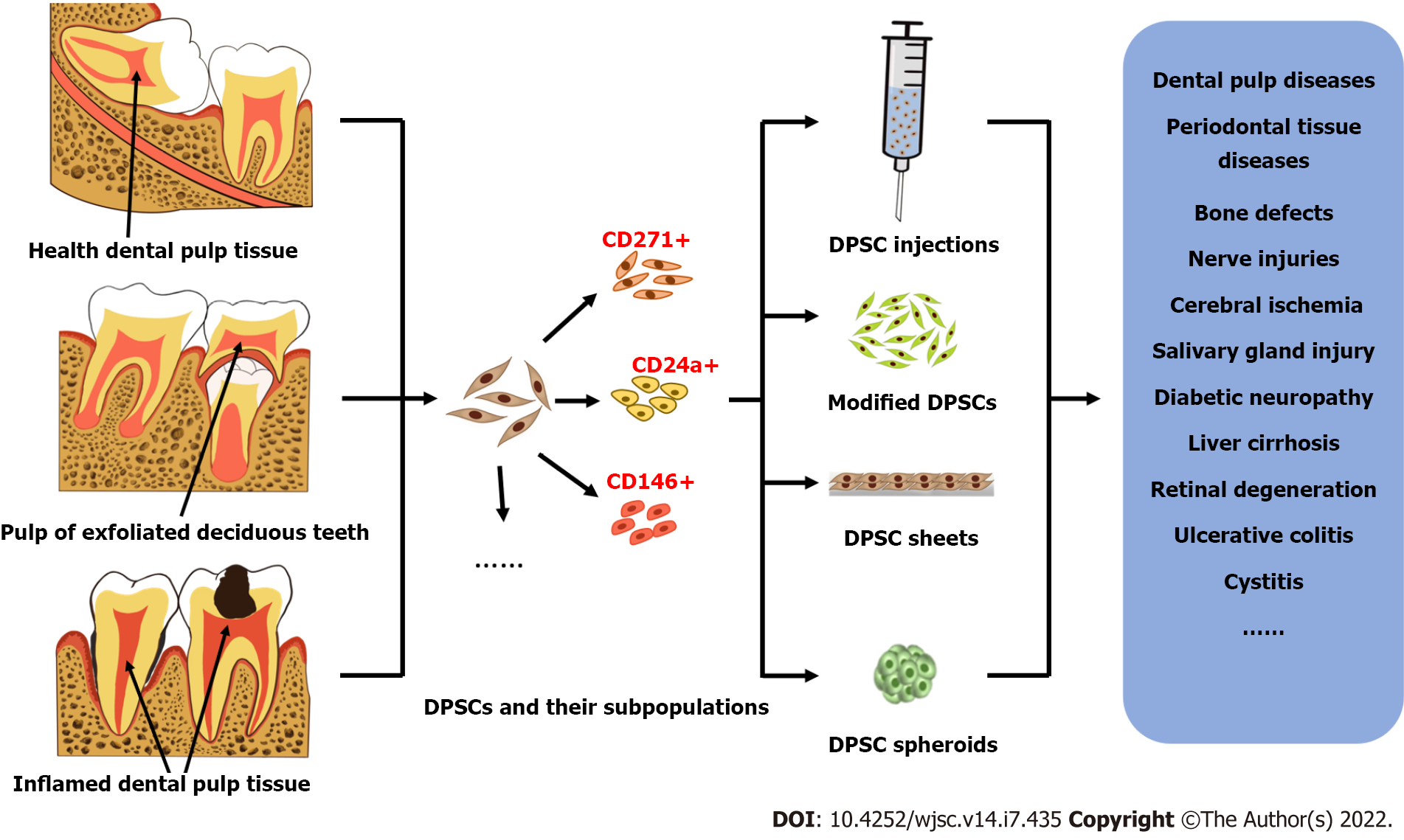
Figure 1 Overview of the main sources of dental pulp stem cells and their derivatives and examples of their applications in regenerative medicine.
Dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) can be isolated from dental pulp tissue of different ages and health statuses, such as the healthy dental pulp tissue of adult impacted teeth, the pulp of children's exfoliated deciduous teeth, and the inflamed dental pulp tissue of patients with caries or periodontitis. Using cell sorting technologies, dental pulp stem cells can be isolated into multiple cell subsets with specific phenotypes, such as CD271+ DPSCs, CD24a+ DPSCs, and CD146+ DPSCs. Several main derivatives of DPSCs derived from long-term applications, including cell injections, genetically modified cells, cell sheets and cell spheroids, which can be used in the treatment of various diseases such as dental pulp diseases, periodontal diseases, and bone defects. DPSC: Dental pulp stem cell.
- Citation: Yuan SM, Yang XT, Zhang SY, Tian WD, Yang B. Therapeutic potential of dental pulp stem cells and their derivatives: Insights from basic research toward clinical applications. World J Stem Cells 2022; 14(7): 435-452
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v14/i7/435.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v14.i7.435