Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Stem Cells. May 26, 2022; 14(5): 330-346
Published online May 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i5.330
Published online May 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i5.330
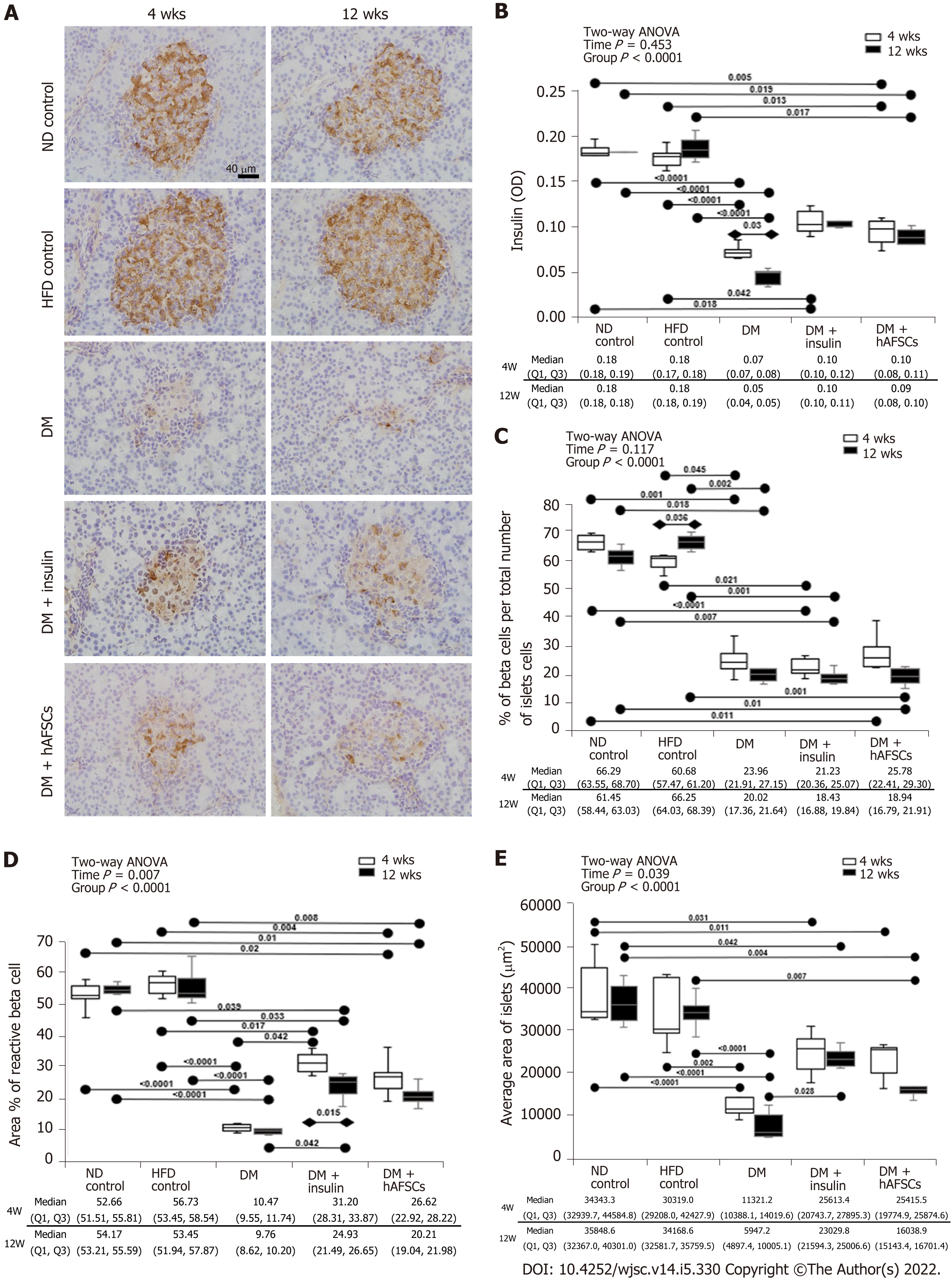
Figure 5 Insulin immunoreactivity in different groups.
Insulin immunoreactivity was decreased in the pancreatic islets of diabetes (DM) rat at 4 and 12 wk. There were also decreased beta cells per total number of islets cells, decreased area of reactive beta cell, and decreased average area of islets at 4 and 12 wk in DM rats. Insulin treatment can recover the area of reactive beta cells at 4 and 12 wk and the average area of islets at 12 wk. However, human amniotic fluid stem cells therapy did not show any effect after DM induction. n = 6. Statistics: Median with first and third quartile (Q1, Q3) for continuous variables. Two-way analysis of variance was used for initial analysis. Kruskal-Wallis test with post hoc Bonferroni test for intergroup analysis. Mann-Whitney U test for the comparison between 4 wk and 12 wk. P values are shown in each comparison. A: Insulin immunoreactivity in the pancreas; B: Immunoreactivity ratio of insulin using optical density; C: Percentage of beta cells per total number of islets cells; D: Area percentage of reactive beta cells; E: Average area of islets. ND: Normal diet; DM: Diabetes mellitus; hAFSCs: Human amniotic fluid stem cells; HFD: High-fat diet.
- Citation: Liang CC, Shaw SW, Huang YH, Lee TH. Human amniotic fluid stem cell therapy can help regain bladder function in type 2 diabetic rats. World J Stem Cells 2022; 14(5): 330-346
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v14/i5/330.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v14.i5.330