Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Stem Cells. May 26, 2022; 14(5): 330-346
Published online May 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i5.330
Published online May 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i5.330
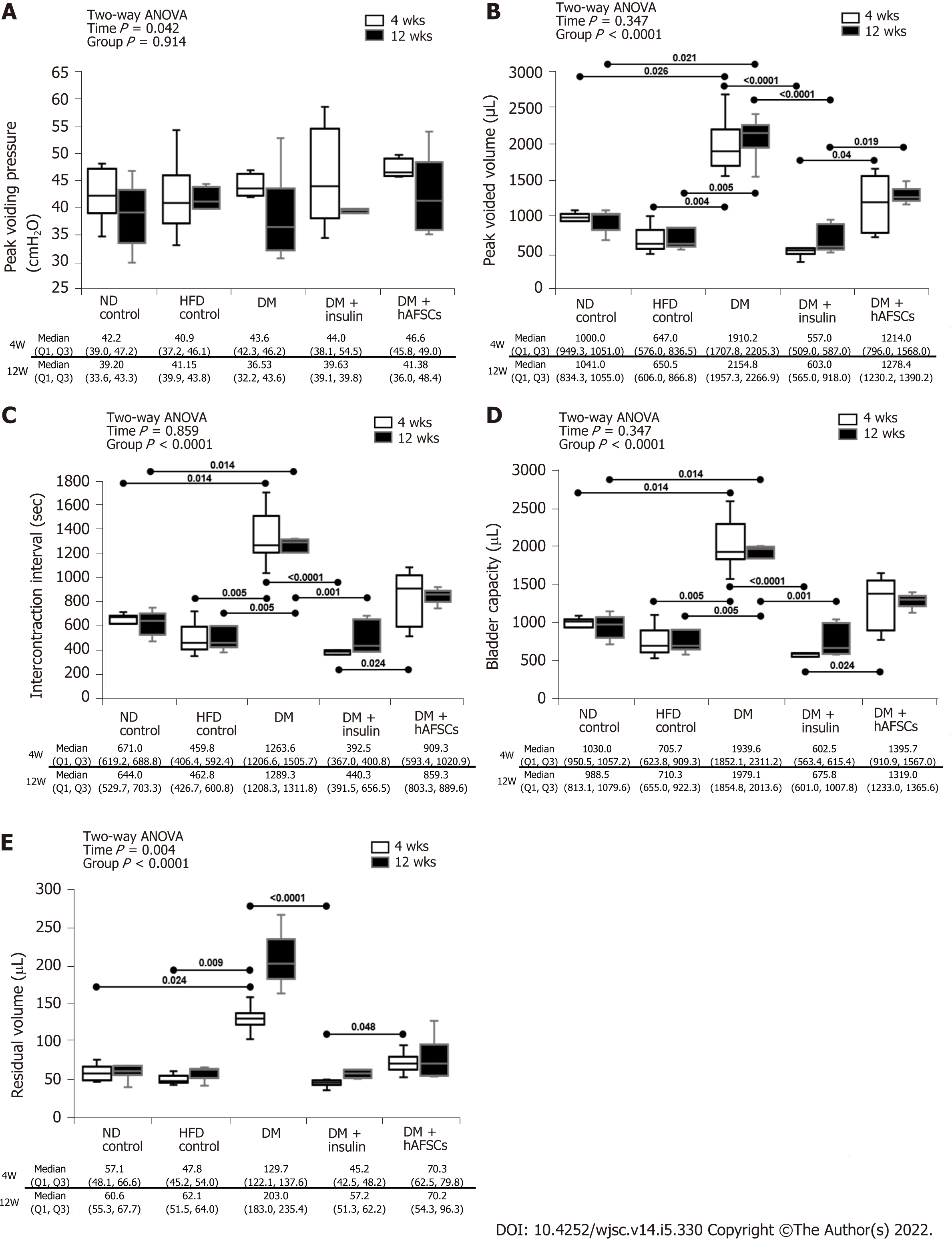
Figure 2 Cystometric results in different groups.
Compared with the controls, type 2 diabetes (DM) rats had significantly worse voided volume, intercontraction interval, bladder capacity, and residual volume after DM induction. These bladder dysfunctions can be improved after insulin treatment but not after human amniotic fluid stem cells (hAFSCs) therapy. The DM + hAFSCs rats had significantly higher peak voided volume, longer intercontraction interval, larger bladder capacity, and more residual volume than DM + insulin rats mainly at 4 wk (only peak voided volume also at 12 wk). n = 6. Statistics: Median with first and third quartile (Q1, Q3) for continuous variables. Two-way analysis of variance was used for initial analysis. Kruskal-Wallis test with post hoc Bonferroni test for intergroup analysis. Mann-Whitney U test for the comparison between 4 wk and 12 wk. P values are shown in each comparison. A: Peak voiding pressure; B: Peak voided volume; C: Intercontraction interval; D: Bladder capacity; E: Residual volume. ND: Normal diet; DM: Diabetes mellitus; hAFSCs: Human amniotic fluid stem cells; HFD: High-fat diet.
- Citation: Liang CC, Shaw SW, Huang YH, Lee TH. Human amniotic fluid stem cell therapy can help regain bladder function in type 2 diabetic rats. World J Stem Cells 2022; 14(5): 330-346
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v14/i5/330.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v14.i5.330