Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Stem Cells. Feb 26, 2022; 14(2): 183-199
Published online Feb 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i2.183
Published online Feb 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i2.183
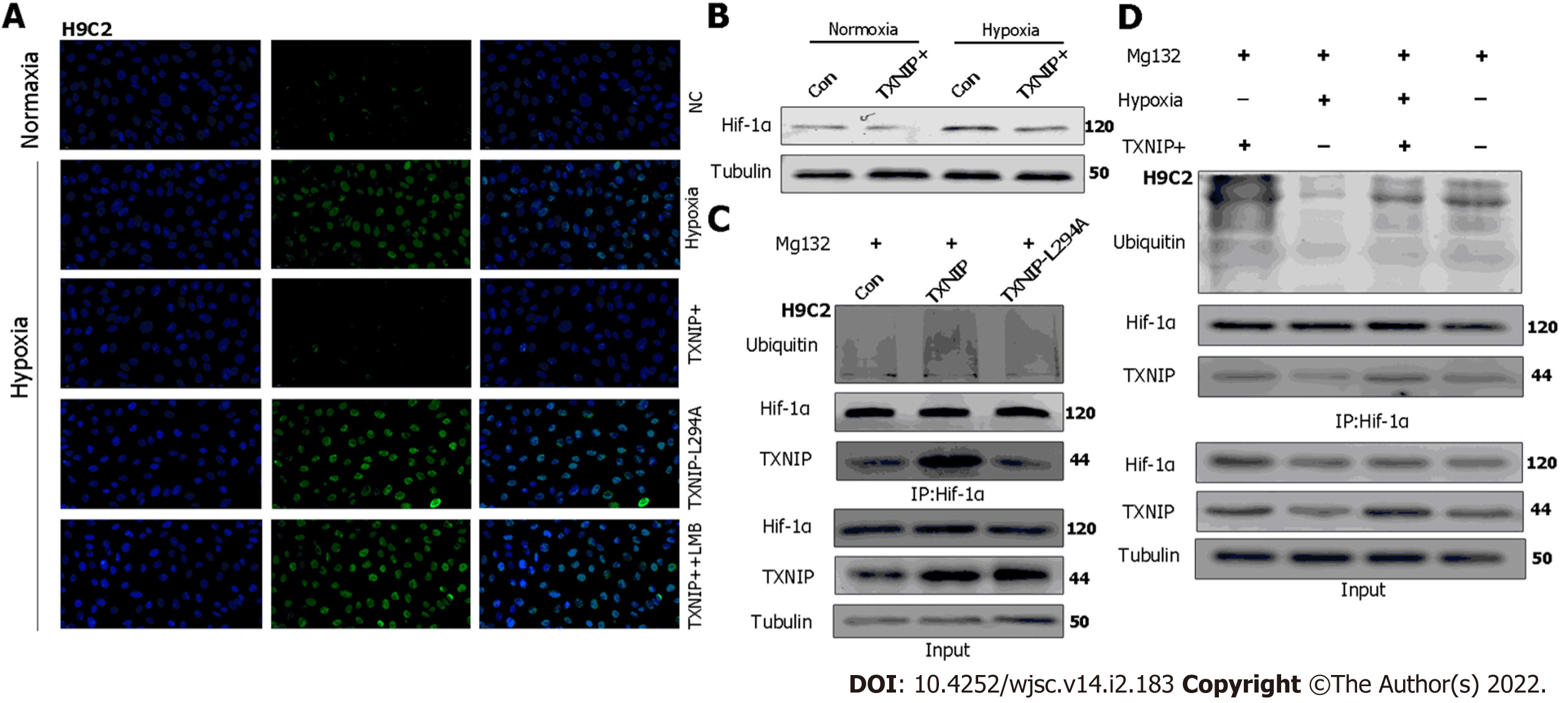
Figure 8 Thioredoxin-interacting protein promotes the ubiquitination of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha through the chromosomal region maintenance-1 nuclear export pathway.
A: H9C2 cardiomyocytes (CMs) overexpressing thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) or TXNIP-L294A mutant as indicated and leptomycin B were used to inhibit the chromosomal region maintenance 1 nuclear export pathway. The expression and cellular localization of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1α) was analyzed by immunofluorescence staining; B: H9C2CMs were treated with hypoxia or normoxia and TXNIP was overexpressed as indicated. The expression of HIF-1α was analyzed by western blotting; C: H9C2 CMs were pretreated with MG132 for 2 h and TXNIP or TXNIP-L294A-mutant were overexpressed as indicated. The interaction of TXNIP and HIF-1α, and HIF-1α ubiquitination were assessed by immunoprecipitation with an anti-HIF-1α antibody; D: H9C2 CMs were pretreated with MG132 for 2 h. TXNIP was overexpressed and hypoxia treatment was applied as indicated. The interaction of TXNIP and HIF-1α, and HIF-1α ubiquitination were assessed by immunoprecipitation with an anti-HIF-1α antibody.
- Citation: Mao CY, Zhang TT, Li DJ, Zhou E, Fan YQ, He Q, Wang CQ, Zhang JF. Extracellular vesicles from hypoxia-preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells alleviates myocardial injury by targeting thioredoxin-interacting protein-mediated hypoxia-inducible factor-1α pathway. World J Stem Cells 2022; 14(2): 183-199
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v14/i2/183.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v14.i2.183