Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Stem Cells. Feb 26, 2022; 14(2): 183-199
Published online Feb 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i2.183
Published online Feb 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i2.183
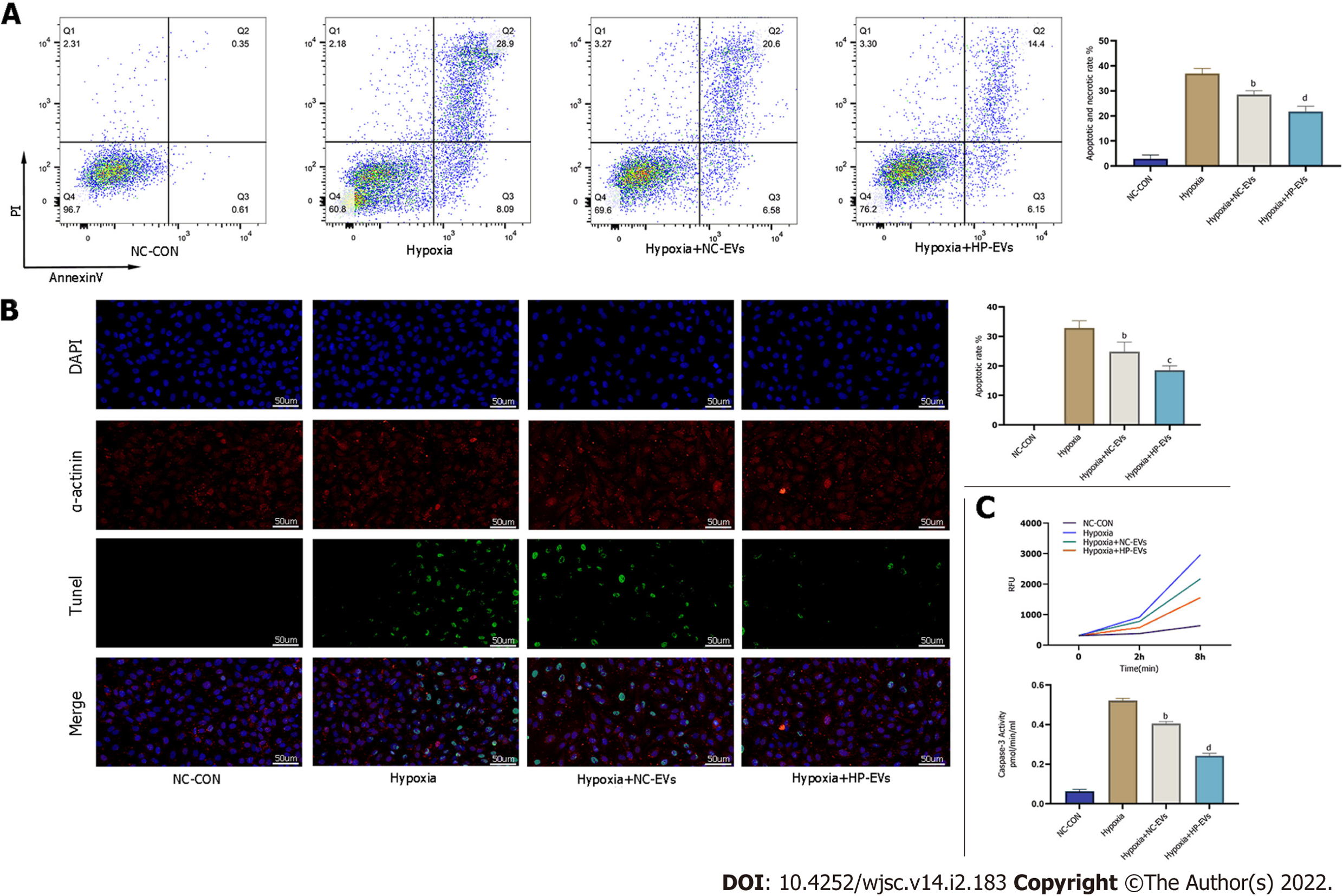
Figure 5 Hypoxia-preconditioned extracellular vesicles alleviated hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis in vitro.
A: Degree of cardiomyocyte (CM) apoptosis in control, hypoxia, normoxic extracellular vesicle (NC-EV), and hypoxia-preconditioned EV (HP-EV) groups after 2 h of hypoxia followed by 12 h of reoxygenation, as determined by the Annexin V/PI assay (n = 5); B: Degree of CM apoptosis in control, hypoxia, NC-EV, and HP-EV groups after 2 h of hypoxia followed by 12 h of reoxygenation, as determined by the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end-labeling assay (n = 5); C: Caspase-3 activity of CMs in the control, hypoxia, NC-EV, and HP-EV groups after 2 h of hypoxia followed by 12 h of reoxygenation (n = 5). All data are expressed as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 compared with Hypoxia group; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 compared with Hypoxia + NC-EVs group. HP-EV: Hypoxia-preconditioned extracellular vesicles; NC-EV: Normoxic extracellular vesicle.
- Citation: Mao CY, Zhang TT, Li DJ, Zhou E, Fan YQ, He Q, Wang CQ, Zhang JF. Extracellular vesicles from hypoxia-preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells alleviates myocardial injury by targeting thioredoxin-interacting protein-mediated hypoxia-inducible factor-1α pathway. World J Stem Cells 2022; 14(2): 183-199
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v14/i2/183.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v14.i2.183