Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Stem Cells. Feb 26, 2022; 14(2): 183-199
Published online Feb 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i2.183
Published online Feb 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i2.183
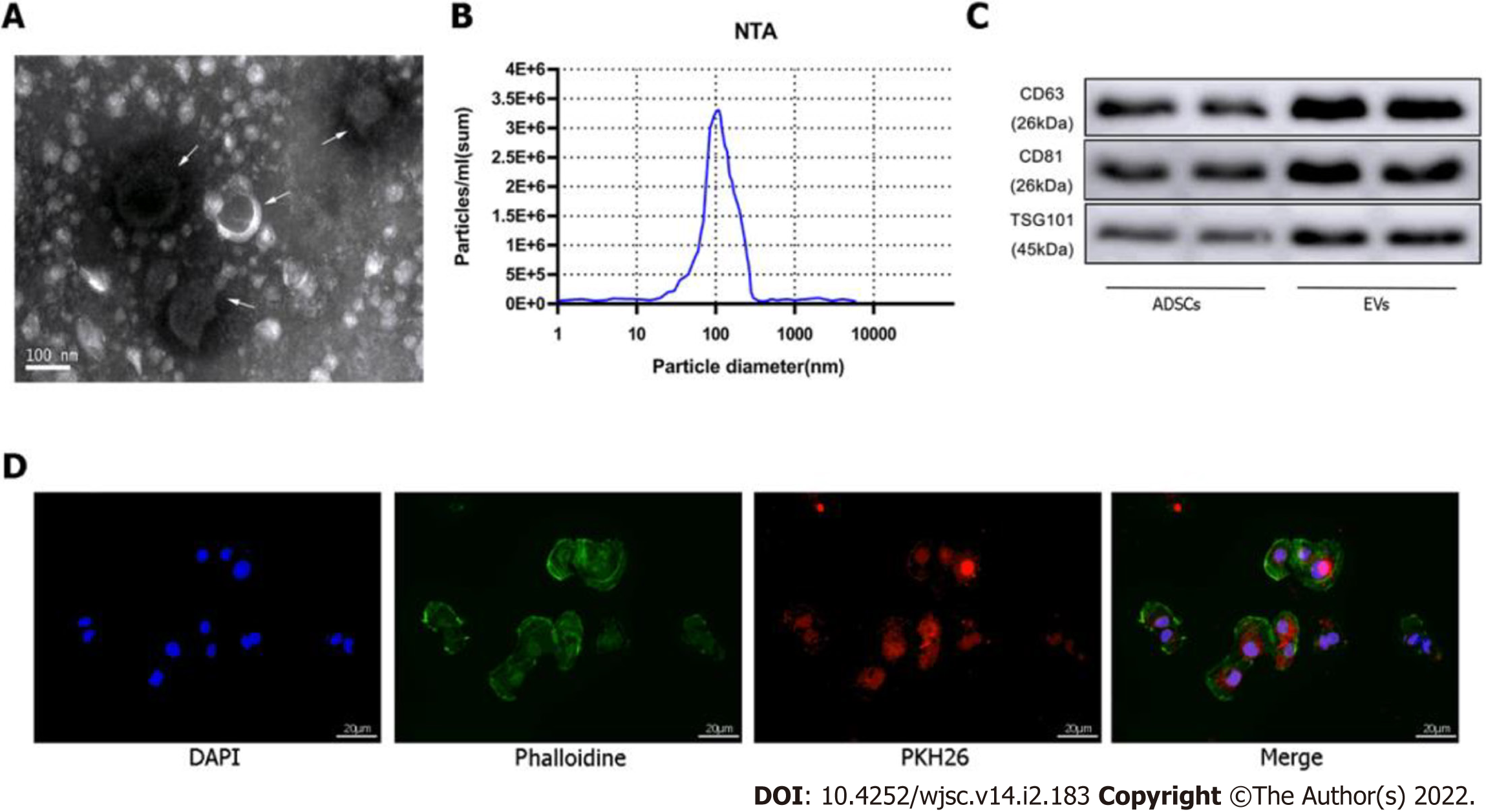
Figure 2 Identification of extracellular vesicles.
A: Transmission electron microscopy characterization of extracellular vesicles (EVs); B: Size distribution by intensity was detected using the NanoSight Instrument; C: EV biomarkers cluster of differentiation 63 (CD63), CD81, and tumor susceptibility gene 101 were identified by western blotting of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell (ADSC)-derived EVs and ADSCs; D: EV tracer assay was used to identify exosomes phagocytosed by cardiomyocytes. ADSC: Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell; EV: Extracellular vesicles.
- Citation: Mao CY, Zhang TT, Li DJ, Zhou E, Fan YQ, He Q, Wang CQ, Zhang JF. Extracellular vesicles from hypoxia-preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells alleviates myocardial injury by targeting thioredoxin-interacting protein-mediated hypoxia-inducible factor-1α pathway. World J Stem Cells 2022; 14(2): 183-199
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v14/i2/183.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v14.i2.183