Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Stem Cells. Feb 26, 2022; 14(2): 163-182
Published online Feb 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i2.163
Published online Feb 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i2.163
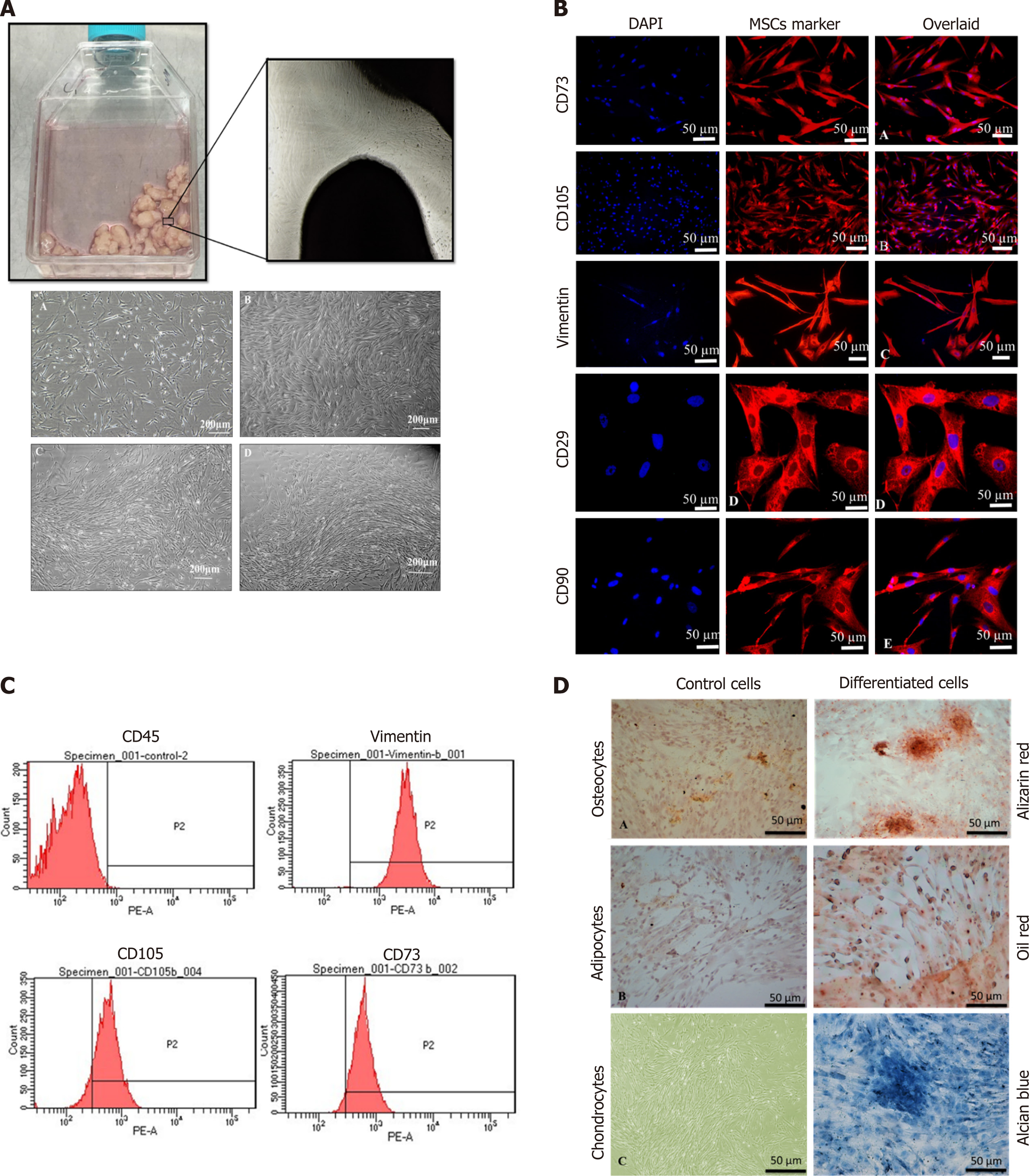
Figure 1 Characterization of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells.
A: Culture of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hUC-MSCs) showed spindle-shaped fibroblast-like morphology at passage P1 to P4; B: MSCs showed positive expression of CD73, CD105, Vimentin, CD29, and CD90. Nuclei were stained with DAPI; C: Histogram of MSCs with specific markers. MSCs showed negative expression of CD45, while positive expression for Vimentin, CD105, and CD73; D: Tri-lineage differentiation of hUC-MSCs. Alizarin Red stained calcium deposits produced by osteocytes, Oil red O-stained lipid vacuoles produced by adipocytes, and Alcian blue stained proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans secreted by chondrocytes.
- Citation: Khalid S, Ekram S, Salim A, Chaudhry GR, Khan I. Transcription regulators differentiate mesenchymal stem cells into chondroprogenitors, and their in vivo implantation regenerated the intervertebral disc degeneration. World J Stem Cells 2022; 14(2): 163-182
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v14/i2/163.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v14.i2.163