Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Stem Cells. Feb 26, 2022; 14(2): 146-162
Published online Feb 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i2.146
Published online Feb 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i2.146
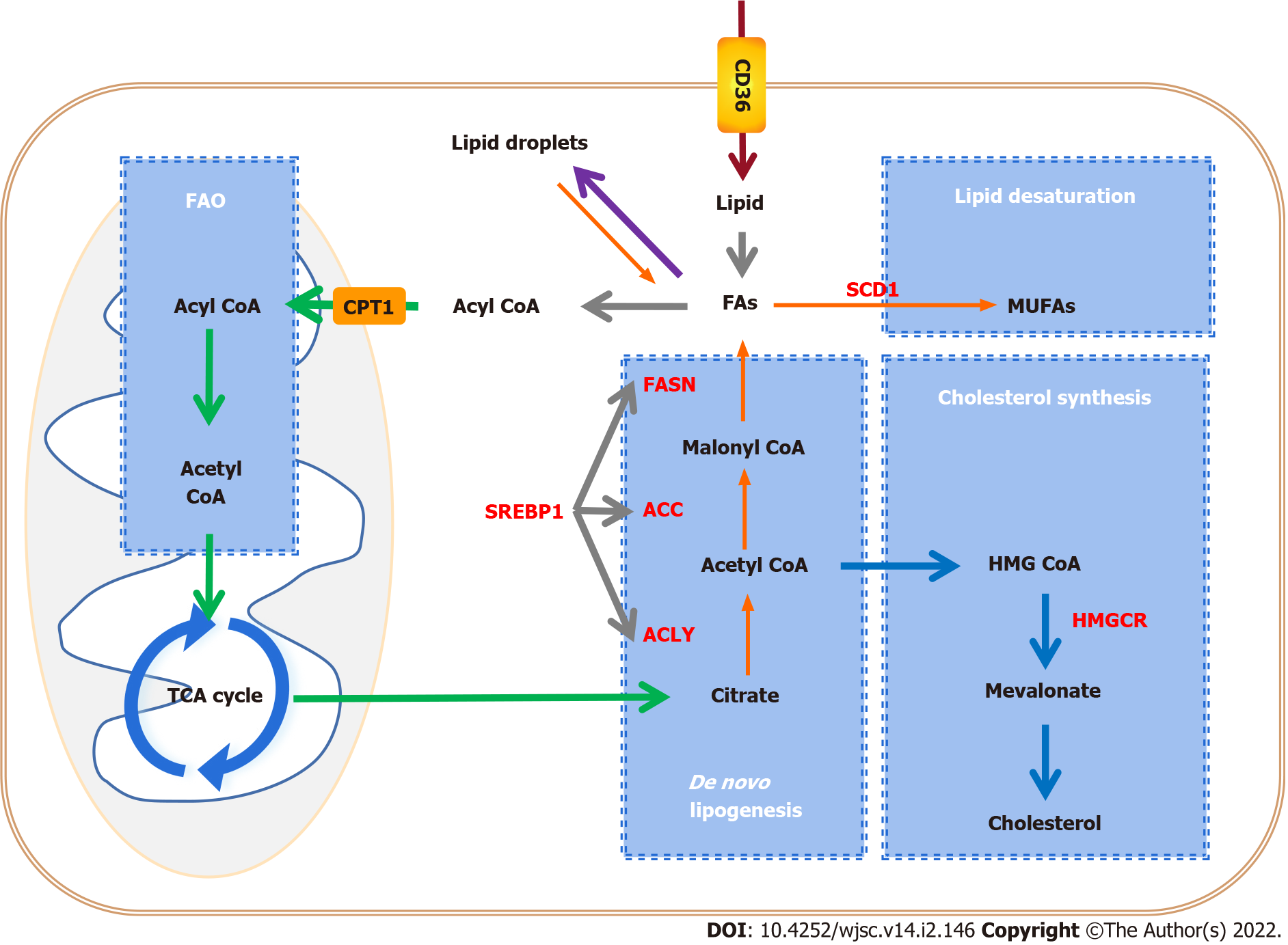
Figure 2 Alteration of lipid metabolic pathways in tumors and cancer stem cells.
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) enhance lipid metabolic activities, such as fatty acid synthesis, fatty acid oxidation, and lipid storage, to promote self-renewal and proliferation. Key enzymes that control lipid metabolism (red letters) are considered to be ideal therapeutic targets for CSCs. CPT1: Carnitine palmitoyl-transferase 1; FAO: Fatty acid oxidation; TCA cycle: Tricarboxylic acid cycle; CD36: Cluster of differentiation 36; FA: Fatty acid; FASN: Fatty acid synthase; ACC: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase; ACLY: ATP citrate lyase; SREBP1: Sterol-regulatory element binding protein 1; SCD1: Stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1; MUFA: Monounsaturated fatty acid; HMGCR: 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase.
- Citation: Wang SY, Hu QC, Wu T, Xia J, Tao XA, Cheng B. Abnormal lipid synthesis as a therapeutic target for cancer stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2022; 14(2): 146-162
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v14/i2/146.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v14.i2.146