Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Stem Cells. Nov 26, 2022; 14(11): 798-814
Published online Nov 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i11.798
Published online Nov 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i11.798
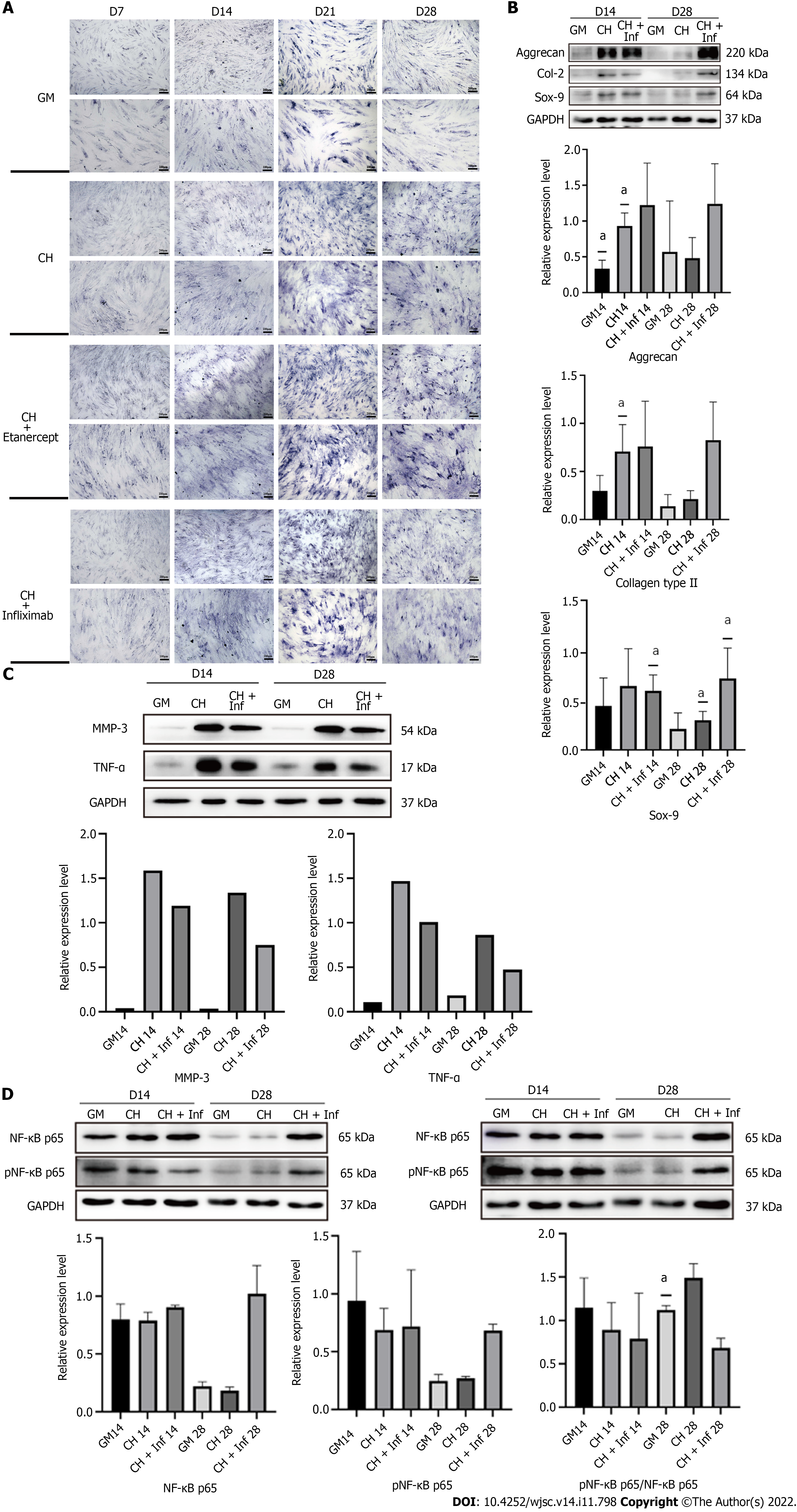
Figure 5 Detection of human adipose-derived stem cells chondrogenic differentiation marker proteins and tumor necrosis factor-alpha and matrix metalloproteinase 3 performed after treatment with chondrogenic differentiation medium containing Infliximab.
A: Toluidine blue staining; B: Western blot detection of Col-2, Aggrecan and Sox-9 of adipose-derived stem cells treated with chondrogenic differentiation medium containing Infliximab; C: Western blot detection of matrix metalloproteinase 3 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha pathway; D: Western blot detection of nuclear factor kappa-B pathway. aP < 0.05. TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; MMP-3: Matrix metalloproteinase 3; IL-1β: Interleukin-1β; GM: Human adipose-derived stem cells (hADSCs) grown in growth medium alone; CH: hADSCs treated with chondrogenic differentiation medium; CHE: hADSCs treated with chondrogenic differentiation medium and 1 μg/mL etanercept; CH+Inf: hADSCs treated with chondrogenic differentiation medium and 10 μg/mL infliximab.
- Citation: Wan JT, Qiu XS, Fu ZH, Huang YC, Min SX. Tumor necrosis factor-α inhibition restores matrix formation by human adipose-derived stem cells in the late stage of chondrogenic differentiation. World J Stem Cells 2022; 14(11): 798-814
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v14/i11/798.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v14.i11.798