Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Stem Cells. Oct 26, 2022; 14(10): 756-776
Published online Oct 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i10.756
Published online Oct 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i10.756
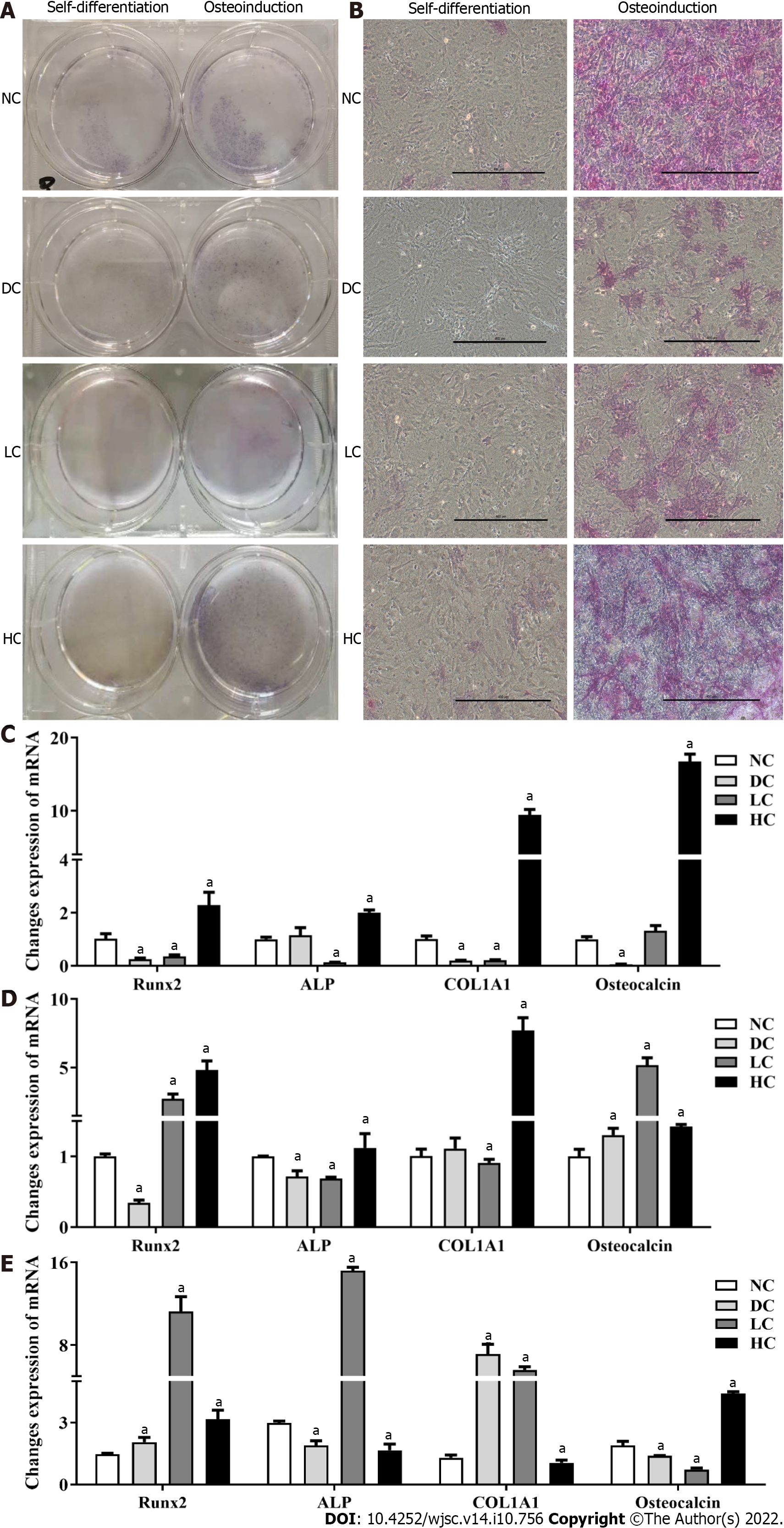
Figure 6 Effects of maternal dietary calcium intake during pregnancy and lactation on osteogenic differentiation potential of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells among male offspring under agent induction.
A and B: Morphology of BMSCs under osteogenic differentiation; C and D: Expression of target genes on osteogenic differentiation under osteogenic induction and self-differentiation status; E: Ratio of gene expressions between osteogenic differentiation and self-differentiation. All data presented as mean ± standard error (n = 9/group). One-way analysis of variance was performed to compare the differences among the above four groups, and then Student–Newman–Keuls test was used to determine the differences between each two groups. Compared to the NC group, aP < 0.05. NC: Normal-calcium reproductive diet; DC: Deficient-calcium reproductive diet; LC: Low-calcium reproductive diet; HC: High-calcium reproductive diet; BMSCs: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.
- Citation: Li P, Wang Y, Li P, Liu YL, Liu WJ, Chen XY, Tang TT, Qi KM, Zhang Y. Maternal inappropriate calcium intake aggravates dietary-induced obesity in male offspring by affecting the differentiation potential of mesenchymal stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2022; 14(10): 756-776
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v14/i10/756.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v14.i10.756