Copyright
©©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Stem Cells. Jan 26, 2022; 14(1): 76-91
Published online Jan 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i1.76
Published online Jan 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i1.76
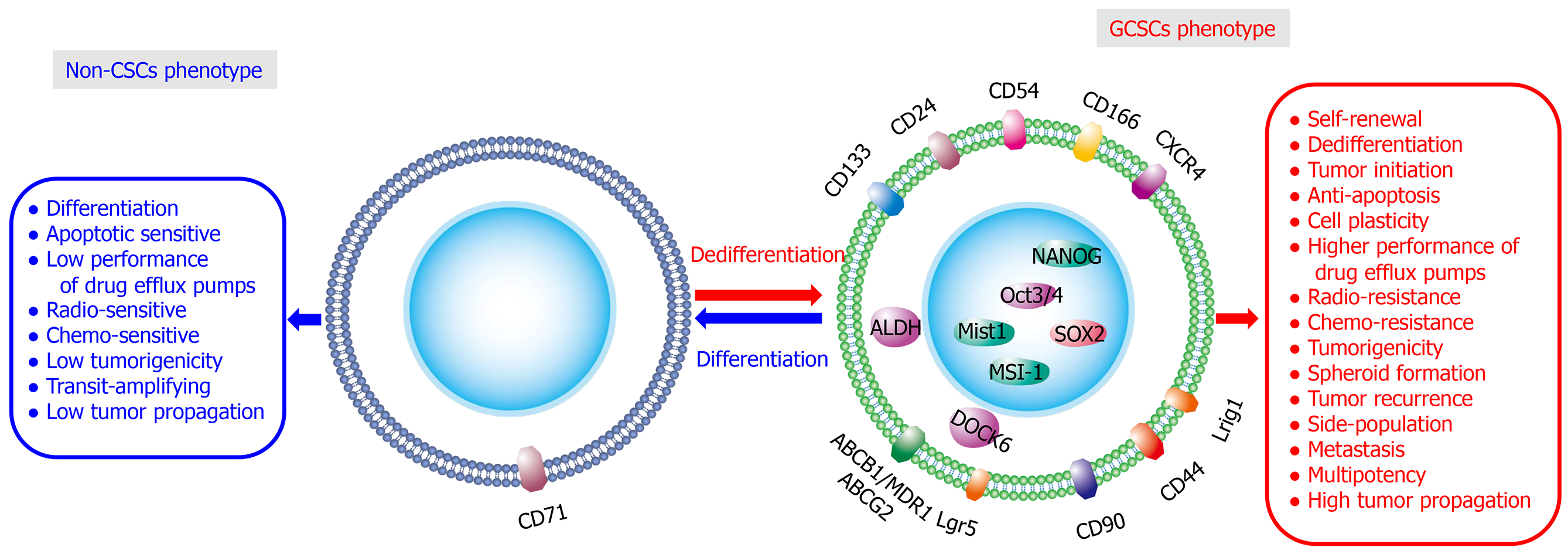
Figure 1 Molecular properties of gastric cancer stem cells.
Main gastric cancer stem cells (GCSCs)-surface markers (such as CD44, CD44v, CD71, CD90, CD133, Lgr5, ALDH1, CXCR4, ABC, and Lrig1) and GCSC-intracellular markers (such as DOCK6, Mist1, MSI-1, NANOG, Oct3/4, and SOX2). GCSCs represent a subpopulation of cancer cells (non-CSCs) existing within heterogeneous tumors implicated in tumor initiation, growth, metastasis, and chemo-/radioresistance, antiapoptosis, cancer recurrence, and metastasis. However, a small number of non-CSCs can dedifferentiate and transform into GCSCs through TME-induced EMT. The newly generated GCSCs from non-CSCs, together with the intrinsic GCSCs, consequently contribute to recurrence and metastasis of cancer. CD44: cluster of differentiation 44; CD44v: CD44v: CD44 splice variant; CD71: cluster of differentiation 71; CD90: cluster of differentiation 90; CD133: cluster of differentiation 133; Lgr5: leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein coupled receptor 5; ALDH1: aldehyde dehydrogenase 1; CXCR4: C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4; ABC: ATP-binding cassette subfamily; Lrig1: leucine rich repeats and immunoglobulin like domains protein 1; DOCK6: dedicator of cytokinesis 6; Mist1: muscle, intestine and stomach expression 1; MSI-1: musashi RNA binding protein 1; NANOG: nanog homeobox; Oct3/4: octamer-binding transcription factor 3/4; SOX2: sex determining region Y-box 2.
- Citation: Hsieh HL, Yu MC, Cheng LC, Yeh TS, Tsai MM. Molecular mechanism of therapeutic approaches for human gastric cancer stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2022; 14(1): 76-91
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v14/i1/76.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v14.i1.76