Copyright
©©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Stem Cells. Jan 26, 2022; 14(1): 41-53
Published online Jan 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i1.41
Published online Jan 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i1.41
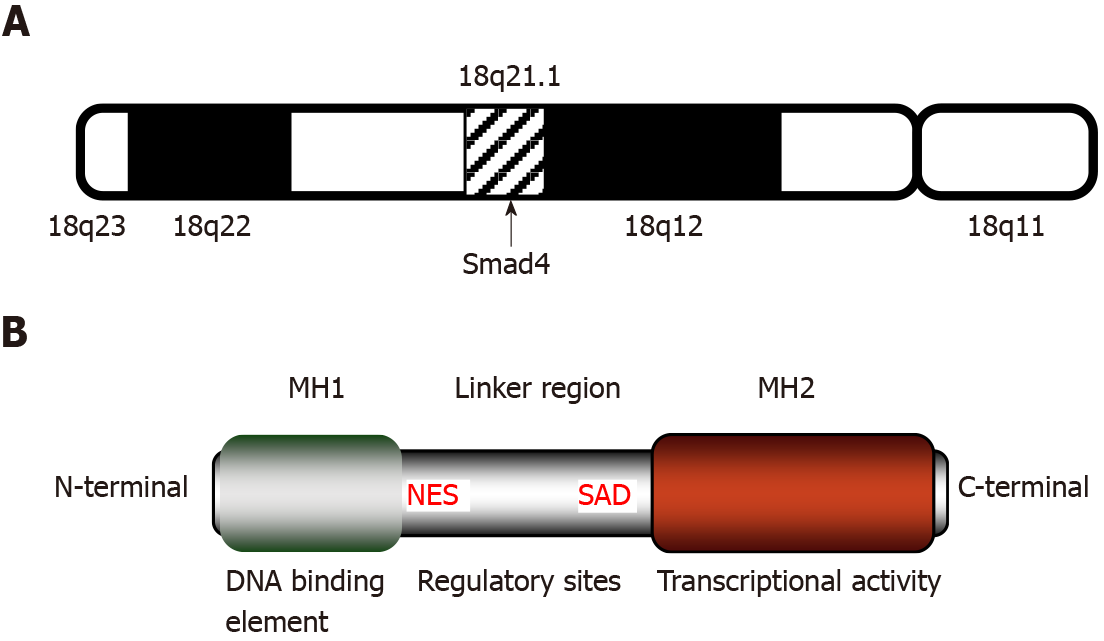
Figure 1 Structure and features of mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 4.
A: Location of the mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 4 (Smad4) gene. Smad4 is located at q21.1 of human chromosome 18; B: Structural diagram of Smad4 protein. Smad4 protein consists of three domains: Mad homology domain 1 (MH1) at the N-terminal, MH2 at the C-terminal, and the linker region connecting MH1 and MH2. Functionally, MH1 is responsible for binding to the Smad-binding site, and MH2 is indispensable for transforming growth factor-β transcriptional activity. The middle linker is rich in regulatory sites controlling various signaling pathways and kinases and is essential for the regulation of transcriptional activity. MH1: Mad homology domain 1; MH2: Mad homology domain 2; NES: Nuclear export signal; SAD: Smad activation domain; Smad4: Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 4.
- Citation: Dai CJ, Cao YT, Huang F, Wang YG. Multiple roles of mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 4 in tumorigenesis, stem cells, drug resistance, and cancer therapy. World J Stem Cells 2022; 14(1): 41-53
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v14/i1/41.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v14.i1.41