Copyright
©©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Stem Cells. Jan 26, 2022; 14(1): 104-116
Published online Jan 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i1.104
Published online Jan 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i1.104
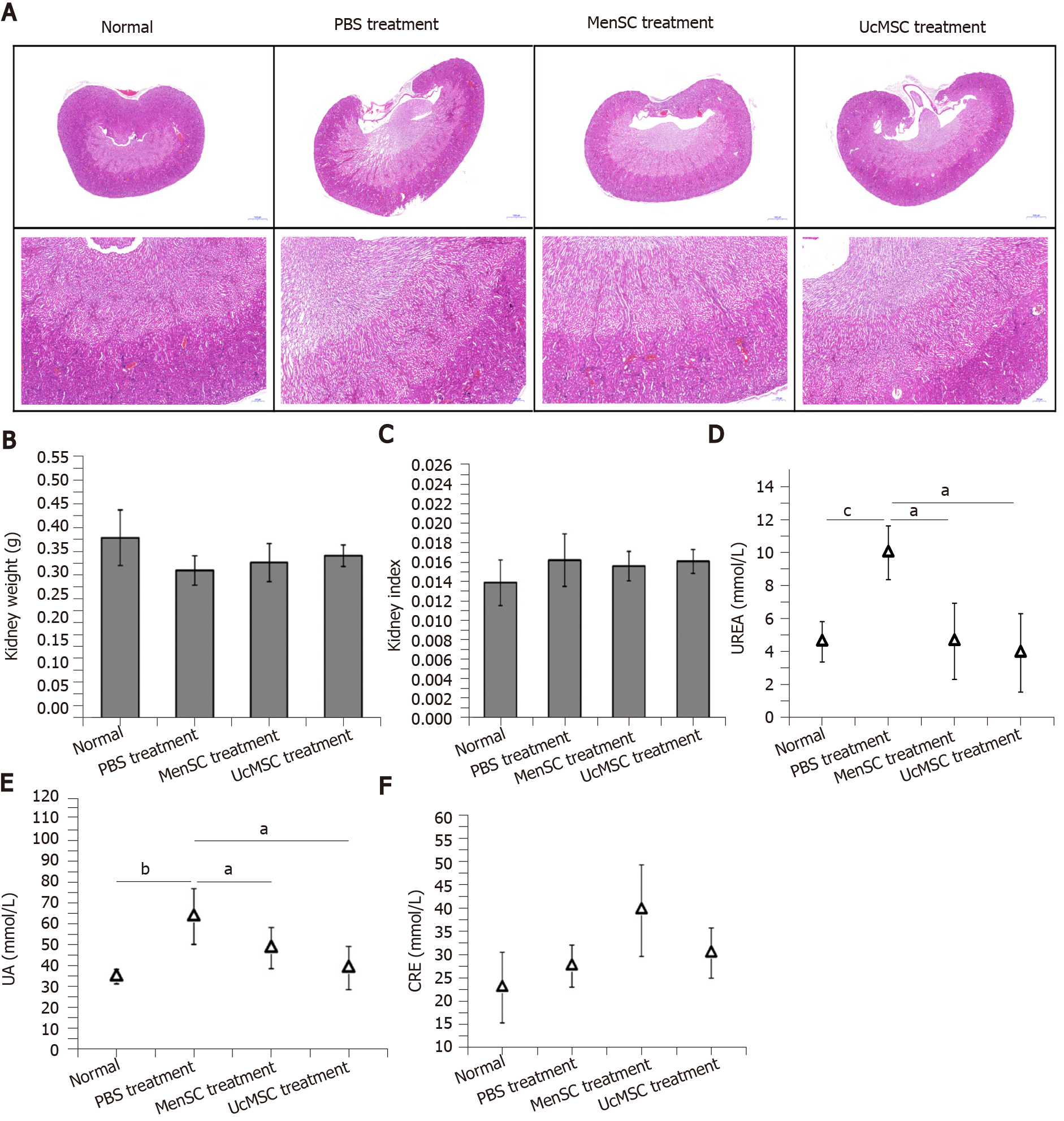
Figure 4 Morphological and functional differences in the kidneys of streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes mice after mesenchymal stem cell transplantation.
A: Morphological changes in the kidneys of mice were examined by hematoxylin and eosin staining. The images in the top row provide a full view of the kidneys, and the images in the bottom row are locally magnified; B and C: Mesenchymal stem cell treatment had no obvious effect on the kidney weights or kidney indexes of streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes mice; D-F: The serum concentrations of UREA, uric acid, and creatinine in the mice were measured. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001. MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell; UcMSC: Umbilical cord-derived MSC; MenSC: Menstrual blood-derived endometrial stem cells; UA: Uric acid; CRE: Creatinine.
- Citation: Sun YL, Shang LR, Liu RH, Li XY, Zhang SH, Ren YK, Fu K, Cheng HB, Yahaya BH, Liu YL, Lin JT. Therapeutic effects of menstrual blood-derived endometrial stem cells on mouse models of streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes. World J Stem Cells 2022; 14(1): 104-116
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v14/i1/104.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v14.i1.104