Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. Aug 26, 2021; 13(8): 1049-1057
Published online Aug 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i8.1049
Published online Aug 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i8.1049
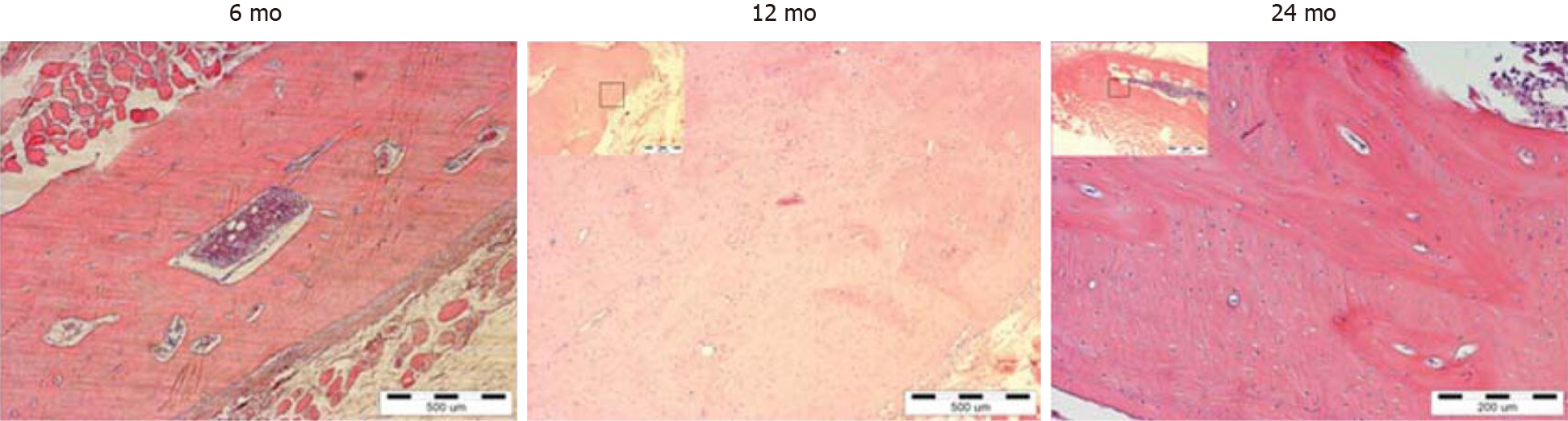
Figure 4 Regeneration of bone lesion after implantation of antler stem cells in mandibular bone lesions in rabbits[43].
Six and twelve months post antler stem cells implantation, restructuring of coarse fibrous bone into lamellar bone tissue occurred. Twenty-four months after implantation, mature lamellar bone developed, with visible osteons and two or three systemic lamellae around blood vessels. H&E staining in all sections. Citation: Cegielski M, Dziewiszek W, Zabel M, Dziegiel P, Kuryszko J, Izykowska I, Zatoński M, Bochnia M. Experimental xenoimplantation of antlerogenic cells into mandibular bone lesions in rabbits: two-year follow-up. In Vivo 2010; 24: 165-172. Copyright © International Institute of Anticancer Research. Published by International Institute of Anticancer Research.
- Citation: Zhang W, Ke CH, Guo HH, Xiao L. Antler stem cells and their potential in wound healing and bone regeneration. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(8): 1049-1057
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i8/1049.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i8.1049