Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2021; 13(7): 877-893
Published online Jul 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i7.877
Published online Jul 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i7.877
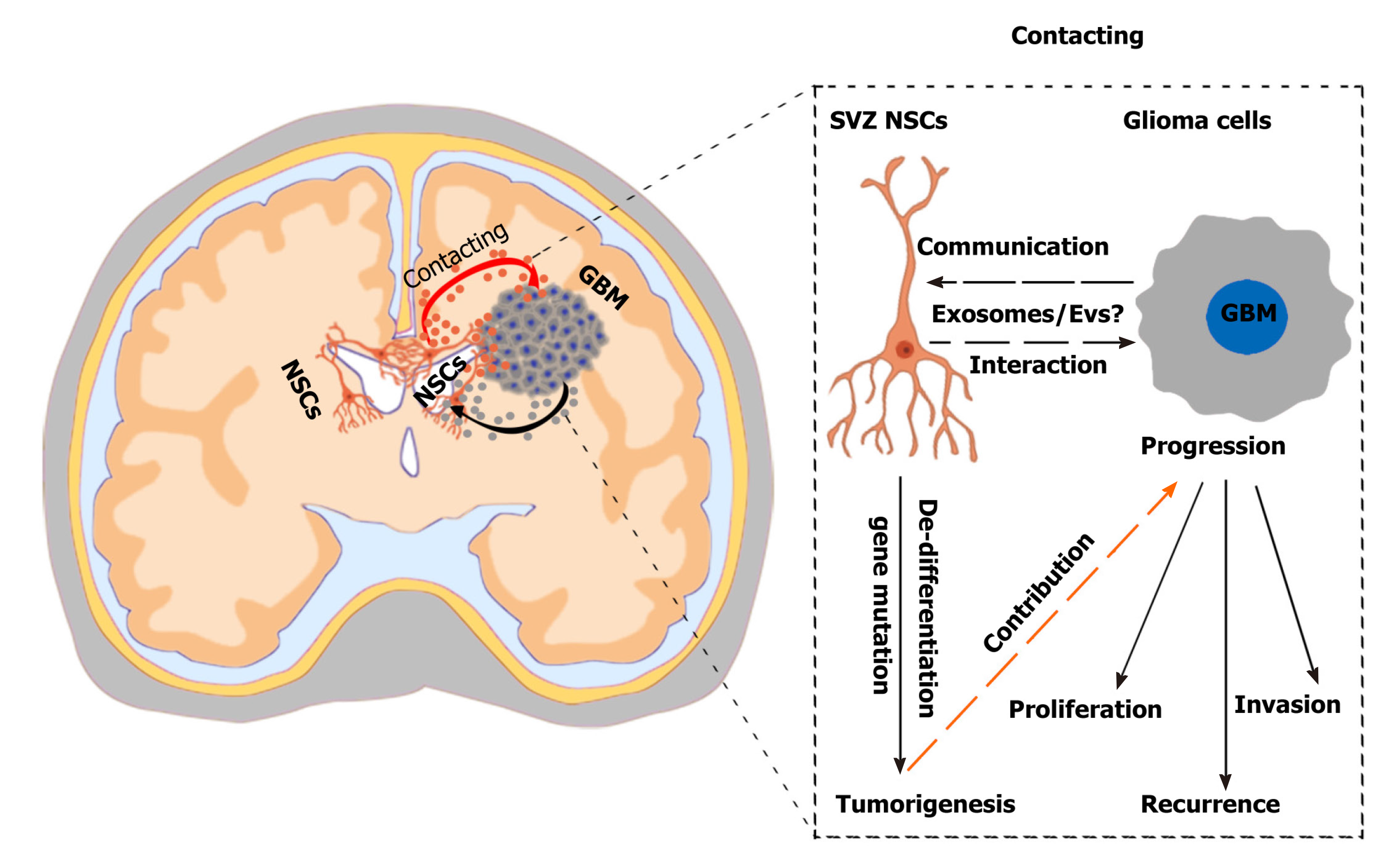
Figure 2 Challenges and effects of neural stem cells in the subventricular zone in glioma progression.
A hypothetical scenario shows the crosstalk between neural stem cells (NSCs) in the subventricular zone (SVZ) and glioblastoma multiformes and the effects of SVZ NSCs in glioma progression. SVZ NSCs can exert chemoattractant effects on glioma cells through secretion of chemoattractant complex factors [such as pleiotrophin, HSP90B, and secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine (SPARC)/SPARC-like protein 1], and glioblastomas can induce SVZ NSCs to de-differentiate into tumor-promoting cells via glioblastoma-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs). The SVZ NSC-glioma interactions are mainly mediated by the secreted factors, especially EVs/exosomes. Understanding the biological mechanisms mediated by cytokines and EVs/exosomes will help to discover new therapeutic strategy. NSCs: Neural stem cells; SVZ: Subventricular zone; GBM: Glioblastoma multiforme.
- Citation: Zhang GL, Wang CF, Qian C, Ji YX, Wang YZ. Role and mechanism of neural stem cells of the subventricular zone in glioblastoma. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(7): 877-893
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i7/877.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i7.877