Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2021; 13(7): 685-736
Published online Jul 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i7.685
Published online Jul 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i7.685
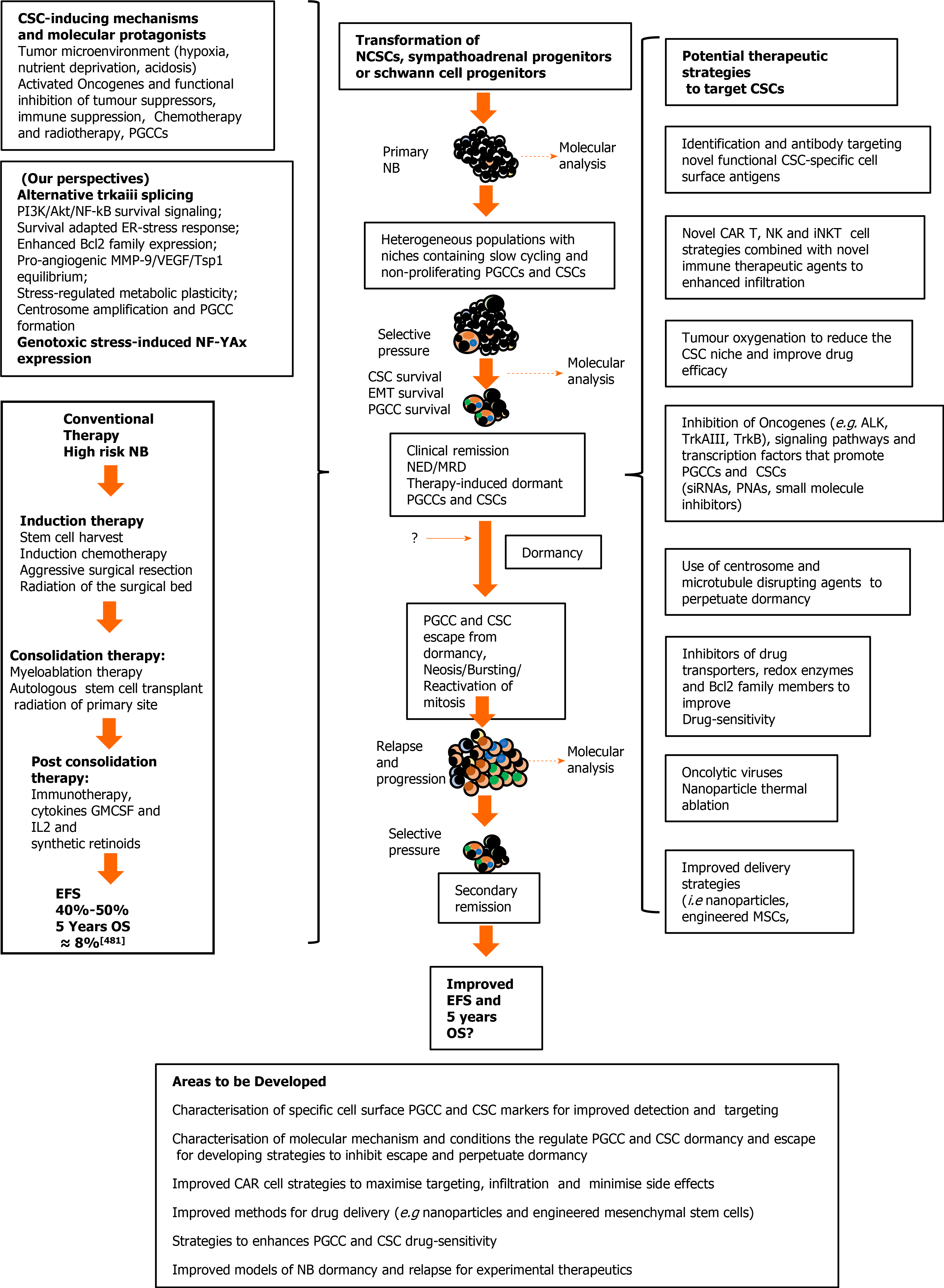
Figure 5 Cancer stem cell involvement in neuroblastoma relapse and progression, and potential therapeutic strategies.
Neuroblastomas (NB) progression (center); mechanisms, molecular protagonists and conventional therapeutic strategies that select and induce the NB polyploid giant cancer cells (PGCC) and cancer stem cells (CSC), responsible for post-therapeutic relapse and low 5-year overall survival rates, in high risk unfavourable NB (right); potential therapeutic strategies to detect, target and eliminate NB PGCC and CSC subpopulations (left), and areas requiring further development (bottom). EFS: Event free survival; OS: Overall survival; CSC: Cancer stem cell; IL-2: Interleukin 2; GMCSF: Granulocyte Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor; NCSC: Neural crest stem cells; NB: Neuroblastomas; NK: Natural killer cells; ALK: Anaplastic lymphoma kinase; siRNA: Small interfering ribonucleic acid; PNA: Peptide nucleic acid; MSC: Mesenchymal stem cells; PGCCs: Polyploid giant cancer cells.
- Citation: Farina AR, Cappabianca LA, Zelli V, Sebastiano M, Mackay AR. Mechanisms involved in selecting and maintaining neuroblastoma cancer stem cell populations, and perspectives for therapeutic targeting. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(7): 685-736
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i7/685.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i7.685