Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. May 26, 2021; 13(5): 416-438
Published online May 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i5.416
Published online May 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i5.416
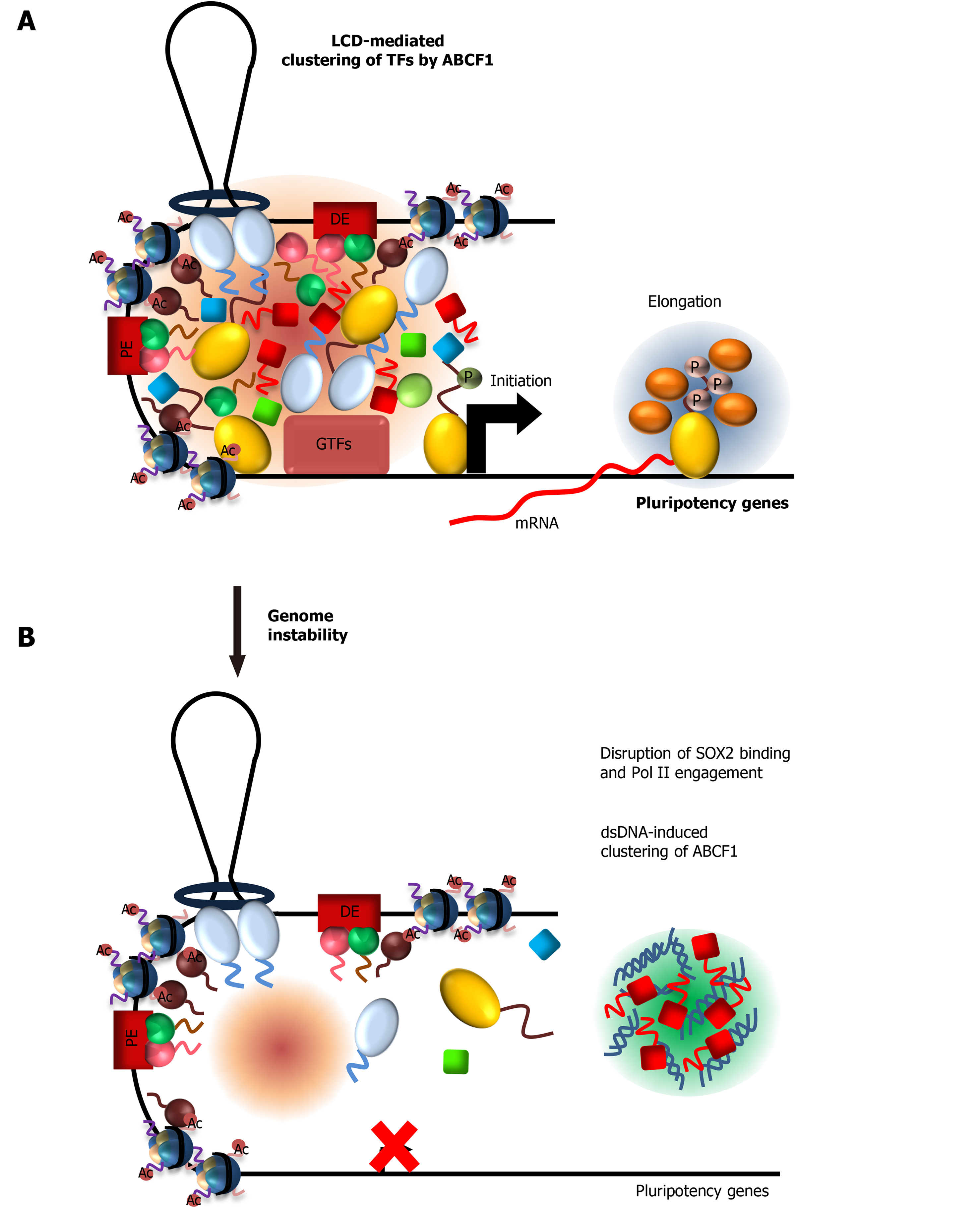
Figure 5 ATP-binding cassette subfamily F member 1 couples stem cell-specific transcription with DNA sensing in Embryonic stem cells.
A: ATP-binding cassette subfamily F member 1 (ABCF1) low complexity domain promotes specific clustering and formation of a hub comprising of sex-determining region Y-box 2 (SOX2), xeroderma pigmentosum, complementation group C (XPC), dyskerin (DKC1), and RNA polymerase II (Pol II) molecules at target gene promoter to stimulate transcription, presumably by increasing local concentration of these factors; B: ABCF1 proteins available for transcription are diverted to bind intracellular double-stranded DNA (dsDNAs) generated from genome instability, due to increased propensity of ABCF1 to form condensates with dsDNAs. Decrease in ABCF1 at gene promoters destabilizes the multivalent interactions between SOX2, XPC, DKC1, and Pol II. This leads to disruption of the protein hub and decrease in gene transcription by Pol II. Downregulation of pluripotency-associated genes promotes differentiation of compromised ESCs and their elimination from the self-renewing population, thereby preserving genome fidelity in ESCs. LCD: Low complexity domain; TF: Transcription factor; dsDNA: Double-stranded DNA; Pol II: RNA Polymerase II; ABCF1: ATP-binding cassette subfamily F member 1; SOX2: Sex-determining region Y-box 2.
- Citation: Vodnala M, Choi EB, Fong YW. Low complexity domains, condensates, and stem cell pluripotency. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(5): 416-438
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i5/416.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i5.416