Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. May 26, 2021; 13(5): 416-438
Published online May 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i5.416
Published online May 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i5.416
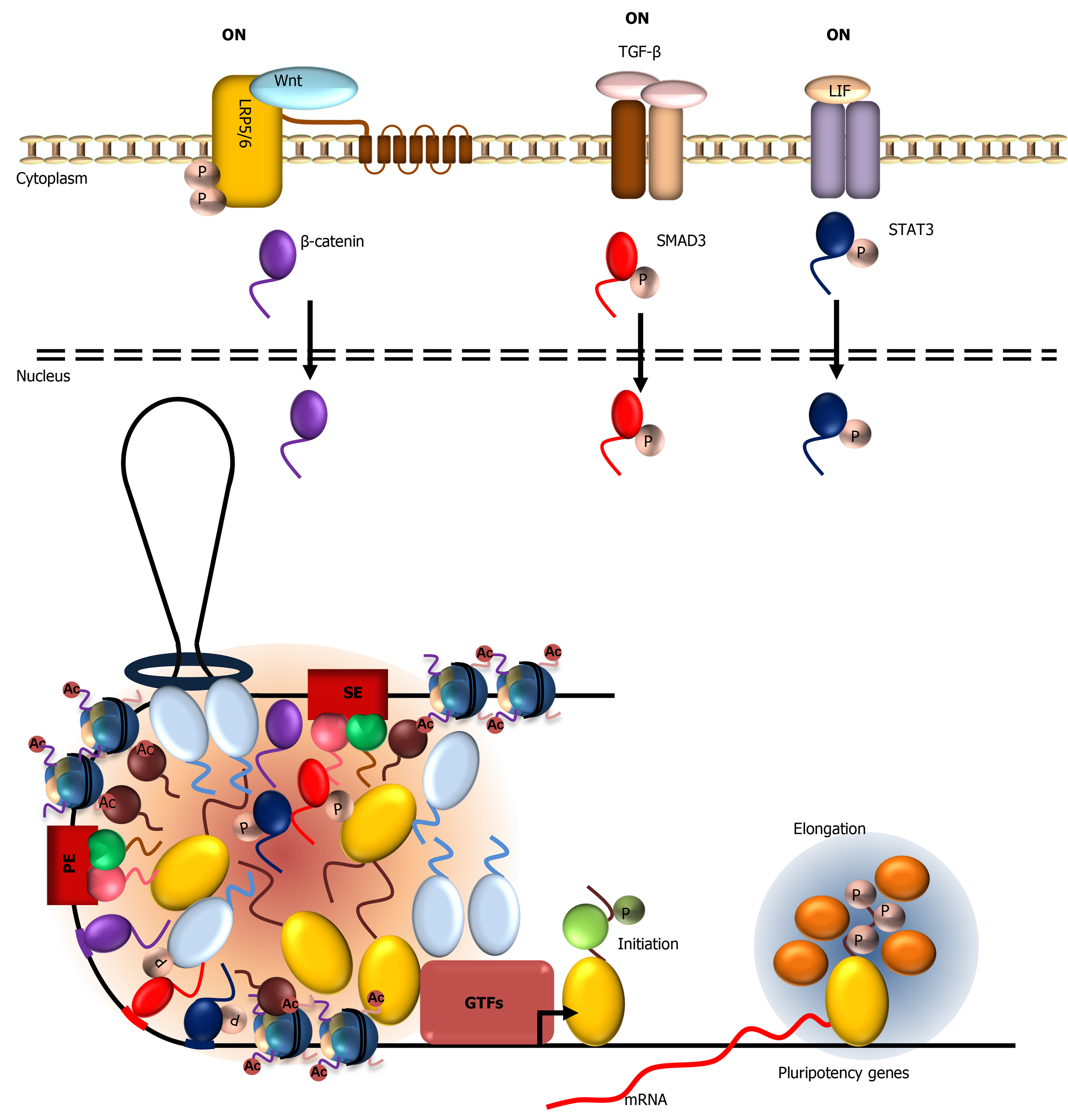
Figure 3 Activation of the wingless-related integration site, transforming growth factor beta, and Janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription signaling pathways leads to nuclear translocation of their respective terminal signaling effectors: β-catenin, SMAD family member 3, and signal transducers and activators of transcription 3.
These low complexity domain (LCD)-containing transcription factors bind their respective signal-responsive elements in pluripotency gene promoters and form LCD-mediated condensates with Mediator to modulate ESC-specific transcriptional activation in a signal-dependent manner. JAK: Janus kinase; STAT: Signal transducers and activators of transcription; SMAD3: SMAD family member 3; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor beta; Wnt: Wingless-related integration site.
- Citation: Vodnala M, Choi EB, Fong YW. Low complexity domains, condensates, and stem cell pluripotency. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(5): 416-438
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i5/416.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i5.416