Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. May 26, 2021; 13(5): 416-438
Published online May 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i5.416
Published online May 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i5.416
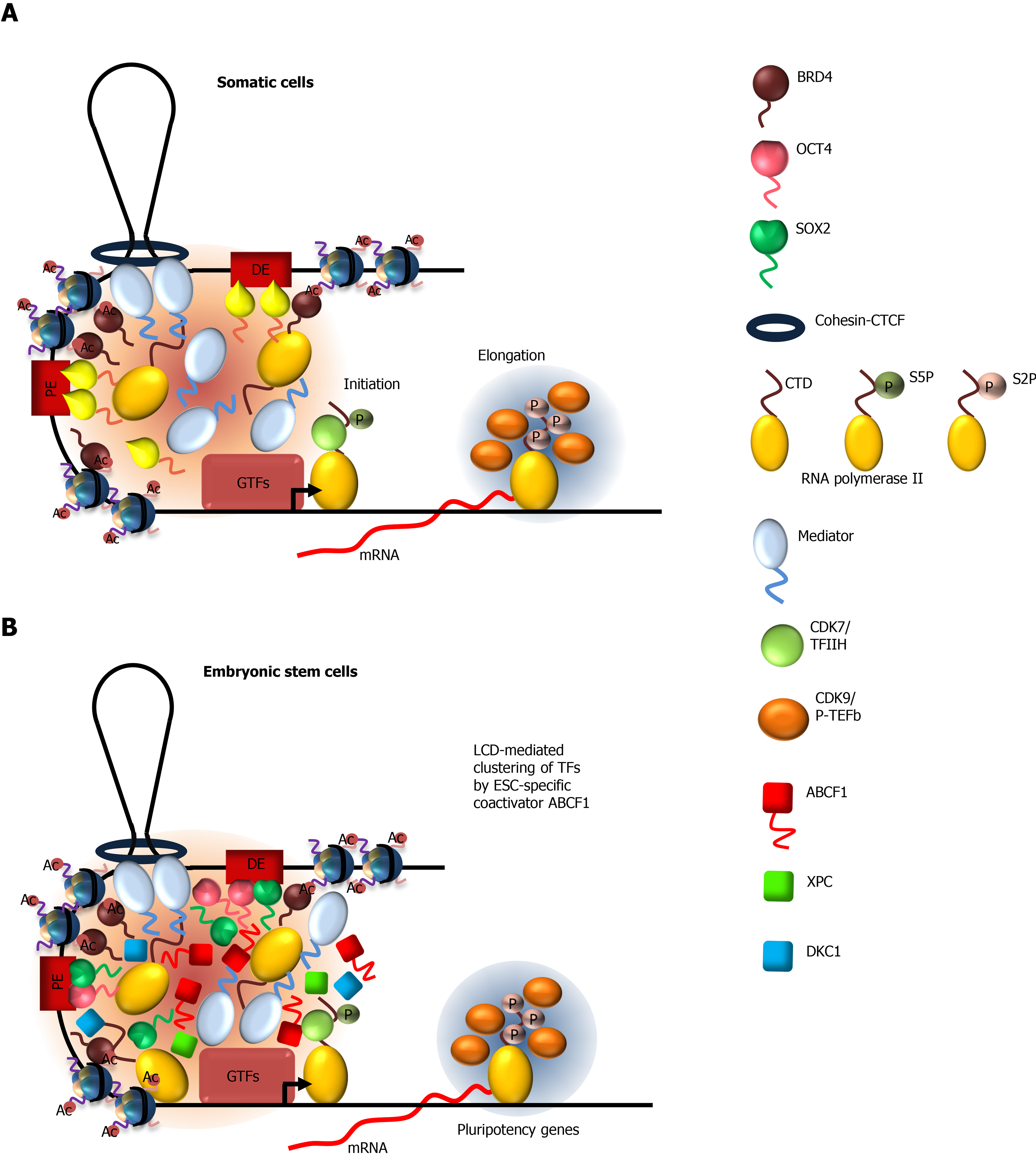
Figure 1 Models depicting the mechanisms by which low-complexity sequence domain-driven interactions between transcription factors and coactivators at gene enhancers contribute to transcriptional activation.
A: Mechanism of transcriptional activation in somatic cells. Low complexity domain (LCD)-mediated interactions between Mediator and TFs, Mediator-bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4), and Mediator-RNA polymerase II (Pol II), as well as binding of BRD4 to acetylated histones, facilitate the formation of a transcription factor-rich compartment at proximal enhancer, and at distal enhancers brought into close proximity through DNA looping by cohesion-CTCF. Increasing local concentration of these factors promotes the formation of the pre-initiation complex composed of general transcription factors and Pol II. Phosphorylation of the C-terminal domain (CTD) at serine 5 (S5P) of Pol II by cyclin-dependent kinase 7/TFIIH disrupts Mediator-Pol II condensates, allowing transcriptional initiation and promoter escape by Pol II. During the early elongation phase of transcription, positive transcription elongation factor b preferentially forms condensates with S5P CTD of Pol II. This results in efficient hyperphosphorylation of the CTD at serine 2 and productive transcription elongation by Pol II; B: Optimal activation of pluripotency genes by stem cell-specific transcription factors octamer-binding transcription factor 4 (OCT4) and SOX2 in ESCs requires cell-specific coactivators ATP-binding cassette subfamily F member 1 (ABCF1), xeroderma pigmentosum, complementation group C (XPC), and dyskerin (DKC1). The LCD of ABCF1 forms selective multivalent interactions with SOX2, XPC, DKC1 and Pol II to promote the assembly of Pol II transcription machinery at pluripotency genes. Activation of OCT4/SOX2-target genes in vivo likely requires both promiscuous LCD-mediated interactions by Mediator and selective LCD-dependent interactions by ABCF1. LCDs are represented by wavy lines. ABCF1: ATP-binding cassette subfamily F member 1; Ac: Acetylated; BRD4: Bromodomain-containing protein 4; CDK: Cyclin-dependent kinase; DE: Distal enhancer; DKC1: Dyskerin; GTFs: General transcription factors; ESC: Embryonic stem cell; General transcription factors; LCD: Low complexity domain; OCT4: Octamer-binding transcription factor 4; P-TEFb: Positive transcription elongation factor b; PE: Proximal enhancer; S2P: Phosphorylated serine 2; S5P: Phosphorylated serine 5; SOX2: SRY-box 2; TF: Transcription factor; XPC: Xeroderma pigmentosum, complementation group C.
- Citation: Vodnala M, Choi EB, Fong YW. Low complexity domains, condensates, and stem cell pluripotency. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(5): 416-438
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i5/416.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i5.416